Text classification using CNN (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 01 Aug, 2025
Text classification involves assigning predefined categories or labels to unstructured text documents. This supervised learning task requires training models on labeled datasets where each document has a known category.
It transforms human-readable text into numerical representations that machine learning algorithms can process. There are several preprocessing steps that significantly impact model performance.

Text classification using CNN
Why use of CNN-based text classification?
- Automatic feature extraction from raw text
- Ability to capture local text patterns and n-gram features
- Robust performance across various text classification tasks
- Less preprocessing required compared to traditional methods
CNN Architecture for Text Processing
Convolutional Neural Networks adapt to text by treating documents as sequences of words rather than spatial images. This adaptation requires modifications to traditional CNN architectures while preserving the core convolution and pooling operations.
- **Embedding Layer: Converts words to dense vector representations
- **Convolutional Layers: Apply filters to detect local text patterns
- **Pooling Layers: Reduce dimensionality while preserving important features
- **Fully Connected Layers: Combine features for final classification
- **Output Layer: Produces probability distributions over target classes
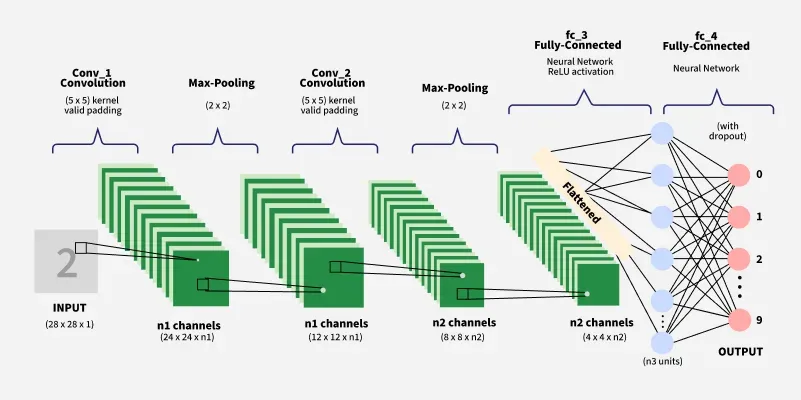
Architecture for Text Processing
The embedding layer serves as the foundation, transforming discrete word tokens into continuous vector space where semantic relationships can be captured. These embeddings can be randomly initialized or pre-trained using methods like Word2Vec or GloVe.
Convolutional layers then apply multiple filters of varying sizes (typically 3, 4 and 5 words) to capture different n-gram patterns. Each filter learns to detect specific linguistic patterns that are relevant for the classification task.
Filter size considerations:
- **Size 3: Captures trigrams and short phrases
- **Size 4: Detects longer phrase patterns
- **Size 5: Identifies extended expressions and longer dependencies
- **Multiple sizes: Provides comprehensive pattern coverage
Basic Implementation Example
1. Importing Libraries
We will import the required libraries such as tensorflow, numpy required for building CNN model, creating layers, handling numerical operations and padding text sequences.
- **tensorflow.keras: Used for importing layers like
Embedding,Conv1DandSequentialfor model building. - **imdb: Loads the IMDB dataset.
- **pad_sequences: Pads text sequences to a fixed length. Python `
import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential from tensorflow.keras.layers import Embedding, Conv1D, GlobalMaxPooling1D, Dense, Dropout from tensorflow.keras.datasets import imdb from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import sequence
`
2. Loading Data
We will load and preprocess the IMDB dataset.
- **imdb.load_data(num_words=10000): Loads the IMDB dataset, keeping only the 10,000 most frequent words.
- **pad_sequences(sequences, maxlen=500): Pads or cuts reviews so each is exactly 500 words long. Python `
vocab_size = 10000 max_length = 500 (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = imdb.load_data(num_words=vocab_size) x_train = sequence.pad_sequences(x_train, maxlen=max_length) x_test = sequence.pad_sequences(x_test, maxlen=max_length)
`
3. Building CNN model
We build a CNN model that converts words into vectors, selects important features using pooling and combines them in fully connected layers. Dropout prevents overfitting and the final layer outputs a probability for classification.
- **models.Sequential(): Creates a linear stack of layers where each layer passes output to the next.
- **layers.Embedding(input_dim=10000, output_dim=100, input_length=500): Converts word indices into 100‑dimensional vectors, helping the model learn word meanings. Handles a vocabulary of 10,000 words and sequences of 500 words.
- **layers.Conv1D(filters=128, kernel_size=5, activation='relu'): Applies 128 sliding filters that look at 5 words at a time to detect patterns.
- **layers.GlobalMaxPooling1D(): Reduces data by taking the maximum value from each filter’s output, keeping only the most important features.
- **layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'): A fully connected layer with 64 neurons that learns complex patterns.
- **layers.Dropout(0.5): Randomly disables 50% of neurons during training to prevent overfitting.
- **layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'): Final output layer that predicts a probability (0–1) for binary classification. Python `
model = Sequential([ Embedding(vocab_size, 100, input_length=max_length), Conv1D(filters=128, kernel_size=5, activation='relu'), GlobalMaxPooling1D(), Dense(64, activation='relu'), Dropout(0.5), Dense(1, activation='sigmoid') ])
`
4. Compiling and Training the Model
We will compile the model and train it using the IMDB dataset. Here we will use Adam optimizer with binary cross-entropy as loss function.
- **model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']): Defines the optimizer (Adam), loss function (binary cross-entropy) and accuracy metric for evaluating performance.
- **model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=5, batch_size=128, validation_split=0.2): Trains the model for 5 epochs using batches of 128 samples, with 20% of the training data reserved for validation. Python `
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32, epochs=5, validation_split=0.2)
`
5. Evaluating the Model
We will evaluate the trained model on the test dataset.
- **model.evaluate(x_test, y_test): Evaluates model performance by returning loss and accuracy.
- **print(f"Test Accuracy: {test_accuracy:.4f}"): Prints the accuracy percentage on the test data. Python `
test_loss, test_accuracy = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test) print(f"Test Accuracy: {test_accuracy:.4f}")
`
**Output:
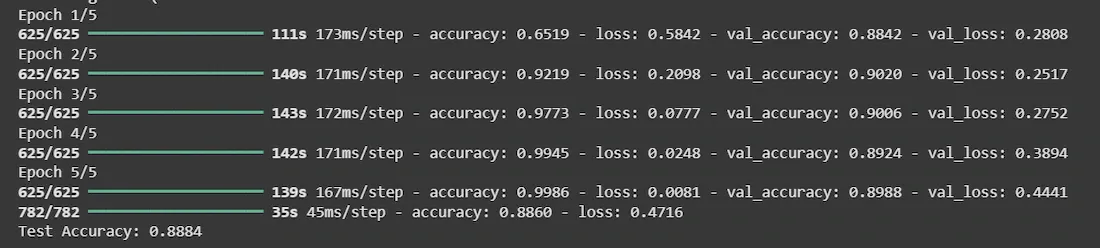
Accuracy using CNN
Performance Analysis
Understanding CNN performance requires monitoring key metrics:
- **Accuracy: Overall correctness across all classes
- **Precision: Proportion of positive predictions that are actually positive
- **Recall: Proportion of actual positive cases correctly identified
- **F1-Score: Harmonic mean of precision and recall
Typical CNN performance on text classification tasks achieves 85-95% accuracy on well-defined problems like sentiment analysis, depending on dataset quality and model architecture complexity.
Real-World Applications
CNN-based text classification has found success across numerous industries:
- **E-commerce: Product categorization, review sentiment analysis
- **Healthcare: Medical document classification, symptom analysis
- **Finance: Fraud detection, risk assessment, compliance monitoring
- **Media: Content moderation, news categorization
- **Customer Service: Ticket classification, automated routing
Challenges and Best Practices
There are many challenges associated with training a CNN model. Some of which are:
**Common Challenges
- **Data quality issues: Mislabeled data or inconsistent category definitions can confuse the model during training and reduce overall accuracy.
- **Class imbalance: When some categories dominate the dataset, models tend to favor those classes, this leads to poor recall and precision for less frequent categories.
- **Domain adaptation: A model trained on one type of text or dataset (e.g., movie reviews) may fail to perform well on a different domain (e.g., medical or legal texts) without fine-tuning.
- **Overfitting: Deep or complex models with too many parameters can memorize training data, causing poor generalization to new, unseen inputs.
**Best Practices:
- **Use dropout layers (0.2–0.5): Randomly dropping connections during training reduces overfitting and helps the network to learn more robust features.
- **Apply L2 regularization: Adds a penalty to the loss function for large weights in dense layers, promoting simpler models that generalize better.
- **Implement early stopping: Stops training when validation loss stops improving, preventing unnecessary epochs and reducing overfitting risk.
- **Employ multiple filter sizes: Using different kernel sizes in convolutional layers captures patterns of varying lengths (e.g., bi-grams, tri-grams), improving feature extraction.