numpy.absolute() in Python (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 29 Nov, 2018
numpy.absolute(arr, out = None, ufunc ‘absolute’) : This mathematical function helps user to calculate absolute value of each element. For complex input, a + ib, the absolute value is 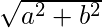 .Parameters :
.Parameters :
arr : [arraylike] Input array or object whose elements, we need to test.
Return :
An array with absolute value of each array.
Code #1 : Working
import numpy as np
arr1 = [ 1 , - 3 , 15 , - 466 ]
print ( "Absolute Value of arr1 : \n" ,
`` np.absolute(arr1))
arr2 = [ 23 , - 56 ]
print ( "\nAbsolute Value of arr2 : \n" ,
`` np.absolute(arr2))
Output :
Absolute Value of arr1 : [ 1 3 15 466]
Absolute Value of arr2 : [23 56]
Code #2 : Working with complex numbers
import numpy as np
a = 4 + 3j
print ( "Absolute(4 + 3j) : " ,
`` np.absolute(a))
b = 16 + 13j
print ( "\nAbsolute value(16 + 13j) : " ,
`` np.absolute(b))
Output :
Absolute(4 + 3j) : 5.0
Absolute value(16 + 13j) : 20.6155281281
Code #3: Graphical Representation of numpy.absolute()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
a = np.linspace(start = - 5 , stop = 5 ,
`` num = 6 , endpoint = True )
print ( "Graphical Representation : \n" ,
`` np.absolute(a))
plt.title( "blue : with absolute\nred : without absolute" )
plt.plot(a, np.absolute(a))
plt.plot(a, a, color = 'red' )
plt.show()
Output :
Graphical Representation : [ 5. 3. 1. 1. 3. 5.]
 References : https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.13.0/reference/generated/numpy.absolute.html.
References : https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.13.0/reference/generated/numpy.absolute.html.
Similar Reads
- numpy.fabs() in Python numpy.fabs() function is used to compute the absolute values element-wise. This function returns the absolute values (positive magnitude) of the data in arr. It always return absolute values in floats. Syntax : numpy.fabs(arr, /, out=None, *, where=True, casting='same_kind', order='K', dtype=None, u 2 min read
- numpy.all() in Python The numpy.all() function tests whether all array elements along the mentioned axis evaluate to True. Syntax: numpy.all(array, axis = None, out = None, keepdims = class numpy._globals._NoValue at 0x40ba726c) Parameters : array :[array_like]Input array or object whose elements, we need to test. axis : 3 min read
- numpy.angle() in Python numpy.angle() function is used when we want to compute the angle of the complex argument. A complex number is represented by “ x + yi " where x and y are real number and i= (-1)^1/2. The angle is calculated by the formula tan-1(x/y). Syntax : numpy.angle(z, deg=0) Parameters : z : [array_like] A com 2 min read
- numpy.around() in Python numpy.around(arr, decimals = 0, out = None) : This mathematical function helps user to evenly round array elements to the given number of decimals. Parameters : array : [array_like] Input array. decimal : [int, optional] Decimal places we want to round off. Default = 0. In case of -ve decimal, it sp 2 min read
- numpy.greater() in Python The numpy.greater() checks whether x1 is greater than x2 or not. Syntax : numpy.greater(x1, x2[, out]) Parameters : x1, x2 : [array_like]Input arrays. If x1.shape != x2.shape, they must be broadcastable to a common shape out : [ndarray, boolean]Array of bools, or a single bool if x1 and x2 are scala 2 min read
- numpy.allclose() in Python numpy.allclose() function is used to find if two arrays are element-wise equal within a tolerance. The tolerance values are positive, typically very small numbers. The relative difference (rtol * abs(arr2)) and the absolute difference atol are added together to compare against the absolute differenc 3 min read
- numpy.any() in Python The numpy.any() function tests whether any array elements along the mentioned axis evaluate to True. Syntax : numpy.any(a, axis = None, out = None, keepdims = class numpy._globals._NoValue at 0x40ba726c) Parameters : array :[array_like]Input array or object whose elements, we need to test. axis : [i 3 min read
- Boolean Array in NumPy - Python The goal here is to work with Boolean arrays in NumPy, which contain only True or False values. Boolean arrays are commonly used for conditional operations, masking and filtering elements based on specific criteria. For example, given a NumPy array [1, 0, 1, 0, 1], we can create a Boolean array wher 3 min read
- numpy.arange() in Python numpy.arange() function creates an array of evenly spaced values within a given interval. It is similar to Python's built-in range() function but returns a NumPy array instead of a list. Let's understand with a simple example: [GFGTABS] Python import numpy as np #create an array arr= np.arange(5 , 1 2 min read
- numpy.floor() in Python The numpy.floor() function returns the largest integer less than or equal to each element in the input array. It effectively rounds numbers down to the nearest whole number. Let's understand with an example: [GFGTABS] Python import numpy as np a = [0.5, 1.5, 2.5, 3, 4.5, 10.1] res = np.floor(a) prin 1 min read