numpy.mirr() in Python (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 05 Aug, 2022
numpy.mirr(values, finance_rate, reinvest_rate) : This financial function helps user to compute modified IRR Value i.e. Modified Internal Rate of Return ie. “average” periodically compounded rate of return
IRR equals to -
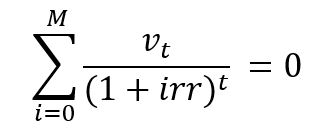
Parameters :
values : [array-like] Input cash flows per time period. net “deposits” are negative and net “withdrawals” are positive
finance_rate : Interest paid on cash amounts.
reinvest_rate : Interest received on cash amounts.
Return : Modified Internal Rate of Return for periodic input values ie. considering interest values.
Code:
Python3 `
Python program explaining
mirr() function
import numpy as np ''' Question :
Investment = 500
Withdrawals at regular interval : 50, 31, 3, 11'''
Solution = np.mirr([-500, 50, 31, 3, 11], .34, .21)
print("Solution - Modified Internal Rate of Return : ", Solution)
`
Output:
Solution - Modified Internal Rate of Return : -0.26165615714437973