numpy.polyder() in Python (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 04 Dec, 2020
The numpy.polyder() method evaluates the derivative of a polynomial with specified order.
**Syntax :**numpy.polyder(p, m)
Parameters :
p : [array_like or poly1D]the polynomial coefficients are given in decreasing order of powers. If the second parameter (root) is set to True then array values are the roots of the polynomial equation.
For example : poly1d(3, 2, 6) = 3x2 + 2x + 6m : [int, optional] Order of differentiation.
Return: Derivative of polynomial.
Code : Python code explaining polyder()
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
p1 = np.poly1d([ 1 , 2 ])
p2 = np.poly1d([ 4 , 9 , 5 , 4 ])
print ( "P1 : " , p1)
print ( "\n p2 : \n" , p2)
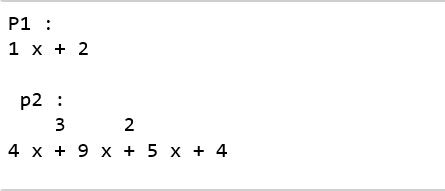
print ( "\n\np1 at x = 2 : " , p1( 2 ))
print ( "p2 at x = 2 : " , p2( 2 ))

a = np.polyder(p1, 1 )
b = np.polyder(p2, 1 )
print ( "\n\nUsing polyder" )
print ( "p1 derivative of order = 1 : \n" , a)
print ( "p2 derivative of order = 1 : \n" , b)

a = np.polyder(p1, 2 )
b = np.polyder(p2, 2 )
print ( "\n\nUsing polyder" )
print ( "p1 derivative of order = 2 : " , a)
print ( "p2 derivative of order = 2 : " , b)

Similar Reads
- numpy.poly1d() in Python The numpy.poly1d() function helps to define a polynomial function. It makes it easy to apply "natural operations" on polynomials. Syntax: numpy.poly1d(arr, root, var) Parameters : arr : [array_like] The polynomial coefficients are given in decreasing order of powers. If the second parameter (root) i 3 min read
- numpy.poly() in Python The numpy.poly() function in the Sequence of roots of the polynomial returns the coefficient of the polynomial. Syntax :numpy.poly(seq) Parameters : Seq : sequence of roots of the polynomial roots, or a matrix of roots. Return: 1D array having coefficients of the polynomial from the highest degree t 2 min read
- numpy.polydiv() in Python The numpy.polydiv() method evaluates the division of two polynomials and returns the quotient and remainder of the polynomial division. Syntax : numpy.polydiv(p1, p2) Parameters : p1 : [array_like or poly1D]Coefficients of dividend polynomial. p2 : [array_like or poly1D]Coefficients of divisor polyn 1 min read
- numpy.polyadd() in Python numpy.polyadd() : This function helps to find the sum of two polynomials and then returning the result as a polynomial. Each input polynomial must be a sequence of polynomial coefficients, from highest to lowest degree. Parameters : p1 : Input polynomial 1 p2 : Input polynomial 2 Return : Sum of pol 1 min read
- Numpy.prod() in Python numpy.prod() returns the product of array elements over a given axis. Syntax: numpy.prod(a, axis=None, dtype=None, out=None, keepdims=) Parameters a : array_like Its the input data. axis : None or int or tuple of ints, its optional It is theAxis or axes along which a product is performed. The defaul 3 min read
- numpy.polymul() in Python The numpy.polymul() method evaluates the product of two polynomials and returns the polynomial resulting from the multiplication of two input polynomials 'p1' and 'p2'. Syntax : numpy.polymul(p1, p2) Parameters : p1 : [array_like or poly1D]Input polynomial 1. p2 : [array_like or poly1D]Input polynom 1 min read
- numpy.polyval() in Python numpy.polyval(p, x) method evaluates a polynomial at specific values. If 'N' is the length of polynomial 'p', then this function returns the value Parameters : p : [array_like or poly1D] polynomial coefficients are given in decreasing order of powers. If the second parameter (root) is set to True th 2 min read
- numpy.polyint() in Python numpy.polyint(p, m) : Evaluates the anti - derivative of a polynomial with the specified order. m antiderivative 'P' of polynomial 'p' satisfies Parameters : p : [array_like or poly1D] polynomial coefficients are given in decreasing order of powers. If the second parameter (root) is set to True then 2 min read
- numpy.polysub() in Python numpy.polysub() :This function helps to find the difference of two polynomials and then returning the result as a polynomial. Each input polynomial must be a sequence of polynomial coefficients, from highest to lowest degree. Parameters : p1 : Input polynomial 1 : 1x + 2. p2 : Input polynomial 2 : 9 1 min read
- numpy.ones() in Python The numpy.ones() function returns a new array of given shape and type, with ones. Syntax: numpy.ones(shape, dtype = None, order = 'C') Parameters : shape : integer or sequence of integers order : C_contiguous or F_contiguous C-contiguous order in memory(last index varies the fastest) C order means t 2 min read