numpy.polyval() in Python (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 29 Nov, 2018
numpy.polyval(p, x) method evaluates a polynomial at specific values. If 'N' is the length of polynomial 'p', then this function returns the value 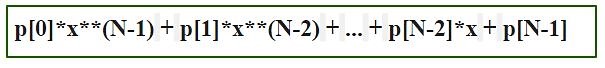
**Parameters :**p : [array_like or poly1D] polynomial coefficients are given in decreasing order of powers. If the second parameter (root) is set to True then array values are the roots of the polynomial equation.For example : poly1d(3, 2, 6) = 3x2 + 2x + 6x : [array_like or poly1D] A number, an array of numbers, for evaluating 'p'.**Return:**Evaluated value of polynomial.
Code : Python code explaining polyval()
Python3 1== `
Python code explaining
numpy.polyval()
importing libraries
import numpy as np import pandas as pd
Constructing polynomial
p1 = np.poly1d([1, 2]) p2 = np.poly1d([4, 9, 5, 4])
print ("P1 : ", p1) print ("\n p2 : \n", p2)
`
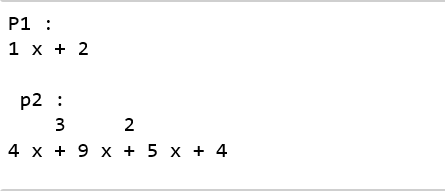
Python3 1== `
Solve for x = 2
print ("\n\np1 at x = 2 : ", p1(2)) print ("p2 at x = 2 : ", p2(2))
`

Python3 1== `
a = np.polyval([1, 2], 2) b = np.polyval([4, 9, 5, 4], 2)
print ("\n\nUsing polyval") print ("p1 at x = 2 : ", a) print ("p2 at x = 2 : ", b)
c = np.polyval(np.poly1d([4, 9, 5, 4]), np.poly1d(2)) print ("\nc : ", c)
`
