numpy.swapaxes() function Python (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 22 Apr, 2025
numpy.swapaxes() function allow us to interchange two axes of a multi-dimensional NumPy array. It focuses on swapping only two specified axes while leaving the rest unchanged. It is used to rearrange the structure of an array without altering its actual data. The syntax of numpy.swapaxes() is:
numpy.swapaxes(array, axis1, axis2)
where:
array: is the input array whose axes are to be swapped.axis1: The first axis to be swapped.axis2: The second axis to be swapped withaxis1.
1. Swapping Axes in a 2D Array
For a 2D array, swapping axes is basically transposing the array.
Python `
import numpy as np arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
result = np.swapaxes(arr, axis1=0, axis2=1)
print("Original array:\n", arr) print("Array after swapping axes:\n", result)
`
**Output:

Swapping Axis in 2D Array
2. Swapping Axes in a 3D Array
Suppose you have a 3D array with shape (2, 3, 4) and you want to swap the first axis (axis 0) with the last axis (axis 2).
Python `
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.rand(2, 3, 4)
result = np.swapaxes(arr, axis1=0, axis2=2)
print("Original shape:", arr.shape) print("New shape:", result.shape)
`
**Output :
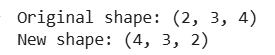
Swapping Axis in 3D Array
In this example the axis at position 0 (size 2) has been swapped with the axis at position 2 (size 4) resulting in a new shape of (4, 3, 2).
Comparison with Other Functions
While numpy.swapaxes() is ideal for swapping two axes there are other functions in NumPy that perform similar tasks:
1. numpy.transpose():
- Reorders all axes based on a given sequence using matrix transpose.
- Useful for complete transpose but less flexible than
swapaxes()for specified axis swapping.
2. numpy.moveaxis():
- Moves one or more axes to new positions.
- More versatile than
swapaxes()but requires specifying source and destination axes.
For scenarios requiring simple interchange of two axes numpy.swapaxes() is the most efficient method.