Adding New Column to Existing DataFrame in Pandas (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 11 Jul, 2025
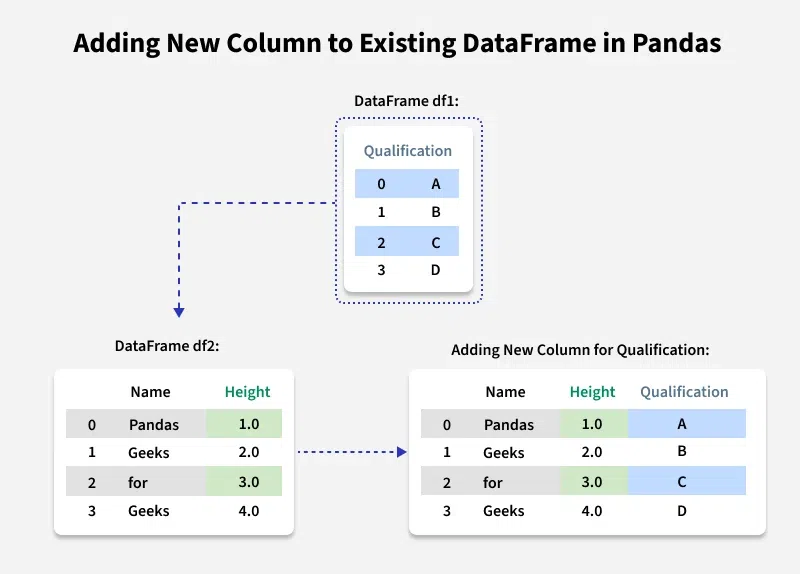
Adding a new column to a DataFrame in Pandas is a simple and common operation when working with data in Python. You can quickly create new columns by directly assigning values to them. Let's discuss how to add new columns to the existing DataFrame in Pandas. There can be multiple methods, based on different requirement.
Adding New Column to Existing DataFrame in Pandas
By Declaring a New List as column
Let's first create a dataframe. We will keep using this dataframe for all examples in this article.
Python `
import pandas as pd
Define a dictionary containing Students data
data = {'Name': ['Pandas', 'Geeks', 'for', 'Geeks'], 'Height': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'Qualification': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']}
Convert the dictionary into DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
`
We can simply add new column to the DataFrame with the specified list values. Note that the length of your list should match the length of index column, else it will show an error.
Python `
Declare a list that is to be converted into a column
address = ['NewYork', 'Chicago', 'Boston', 'Miami']
Using 'Address' as the column name
and equating it to the list
df['Address'] = address
display(df)
`
**Output:
Adding New Column to Existing DataFrame in Pandas
**Note: Using list for adding column will modify the existing dataframe.
Table of Content
- By using DataFrame.assign() method
- By using Dictionary
- By using DataFrame.insert()
- By using Dataframe.loc()
By using DataFrame.assign() method
Adding New Column with assign() method creates a new DataFrame with the specified column(s) added. The original DataFrame remains unchanged unless we explicitly reassign the result back to it.
Python `
import pandas as pd
Define a dictionary containing Students data
data = {'Name': ['Pandas', 'Geeks', 'for', 'Geeks'], 'Height': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'Qualification': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']}
Convert the dictionary into DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
using assign() and passing address list as parameter
df = df.assign(address = ['NewYork', 'Chicago', 'Boston', 'Miami'])
print(df)
`
**Output:
Name Height Qualification Address ****address** 0 Pandas 1 A New York NewYork
1 Geeks 2 B Chicago Chicago
2 for 3 C Boston Boston
3 Geeks 4 D Miami Miami
By using Dictionary
We can use a Python dictionary to add a new column in pandas DataFrame. This method is recommended when you want to **add multiple columns at once or if you have columns in a dictionary format.
Python `
import pandas as pd
Define a dictionary containing Students data
data = {'Name': ['Pandas', 'Geeks', 'for', 'Geeks'], 'Height': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'Qualification': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']}
Convert the dictionary into DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
address dictionary with names as keys & addresses as values
address = {'Pandas': 'NewYork', 'Geeks': 'Chicago', 'for': 'Boston', 'Geeks_2': 'Miami'}
Add the 'Address' column by mapping the 'Name' column
to the address dictionary
df['Address'] = df['Name'].map(address)
print(df)
`
**Output:
Name Height Qualification ****Address** 0 Pandas 1 A NewYork
1 Geeks 2 B Chicago
2 for 3 C Boston
3 Geeks 4 D Chicago
**We can also use assign() method for adding Multiple columns at the same time by passing multiple key-value pairs (where the key is the column name and the value is the column data). It returns a new DataFrame, leaving the original one unchanged. We can achieve that using dictionary unpacking.
Python `
#example - add both "Age" and "City" columns new_columns = {'Age': [21, 22, 23, 24], 'City': ['NY', 'LA', 'SF', 'DC']}
unpacks new_columns dictionary and adds both "Age" and "City"
df = df.assign(**new_columns) print(df)
`
**Output:
Name Height Qualification Address **Age City** 0 Pandas 1 A NewYork 21 NY
1 Geeks 2 B Chicago 22 LA
2 for 3 C Boston 23 SF
3 Geeks 4 D Chicago 24 DC
Check out more ways to add multiple columns in Pandas Dataframe.
By using DataFrame.insert()
insert() method modifies the original dataframe, so there’s no need to reassign the DataFrame after using it. **It gives the freedom to add a column at any position and not just at the end. It also provides different options for inserting the column values.
Python `
import pandas as pd
Define a dictionary containing Students data
data = {'Name': ['Pandas', 'Geeks', 'for', 'Geeks'], 'Height': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'Qualification': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']}
Convert the dictionary into DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
Using insert() to add a column at position 2 (3rd column)
df.insert(2, "Age", [21, 23, 24, 21], True) print(df)
`
**Output:
Name Height Age Qualification 0 Pandas 1 21 A
1 Geeks 2 23 B
2 for 3 24 C
3 Geeks 4 21 D
By using Dataframe.loc()
Using .loc[], you can add a new column directly or modify values based on conditions, or when adding new columns based on specific row selections.
Python `
import pandas as pd
dictionary containing Students data
data = {'Name': ['Pandas', 'Geeks', 'for', 'Geeks'], 'Height': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'Qualification': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']}
Convert the dictionary into DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
Using .loc[] to add a "Category" column
based on height condition
df.loc[df['Height'] >= 3, 'Category'] = 'Tall' df.loc[df['Height'] < 3, 'Category'] = 'Short'
Observe the result
print(df)
`
**Output:
Name Height Grades Qualification Address Category 0 Pandas 1 A A NewYork Short
1 Geeks 2 B B Chicago Short
2 for 3 C C Boston Tall
3 Geeks 4 D D Chicago Tall
