Dealing with Rows and Columns in Pandas DataFrame (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 11 Nov, 2025
A Pandas DataFrame is a two-dimensional data structure made up of rows and columns, similar to a spreadsheet or SQL table. In Pandas, you can easily select, add, delete or rename rows and columns to manage and analyze your data efficiently.
Below is the Sample DataFrame used in this article:
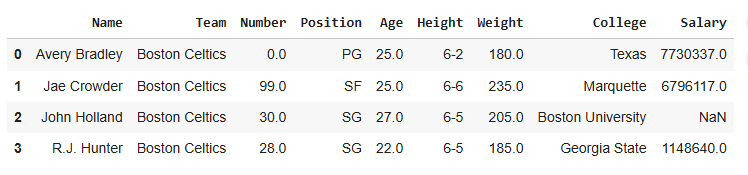
sample_dataframe
To Download the Sample DataFrame used in this article, click here
Dealing with Columns
Below image shows a sample Pandas DataFrame with rows and columns labeled. The rows represent individual records (like players), while the columns represent attributes such as Name, Team, Number, Position and Age.
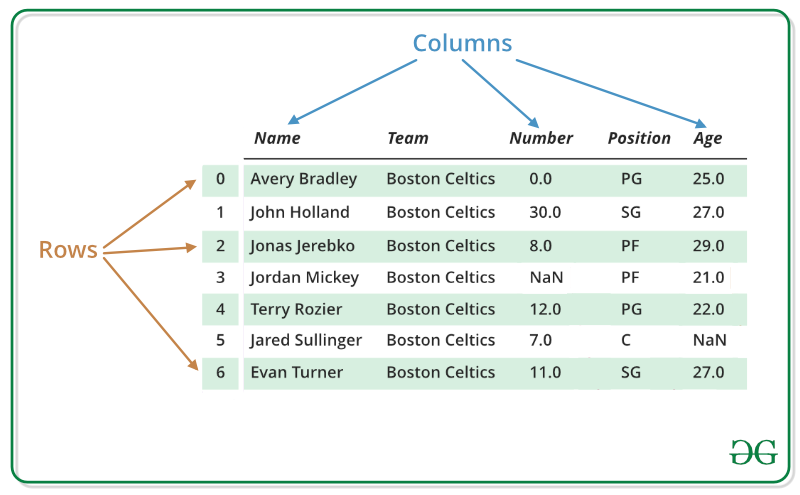
Selecting Columns
You can access one or more columns using their column names.
Python `
import pandas as pd df = pd.read_csv('your_file.csv')
print(df[['Name', 'Age']])
`
**Output
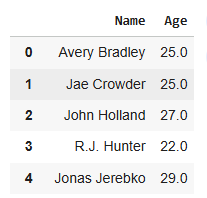
**Explanation: **df[['Name', 'Age']]: selects the specified columns and returns a new DataFrame with only those columns.
Adding Columns
New columns can be added by assigning a list or series to a column name.
Python `
df['Experience'] = 1 print(df.head())
`
**Output
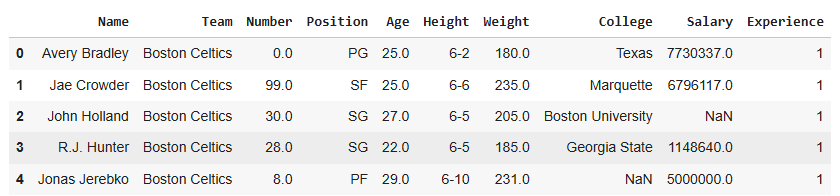
**Explanation: **df['Experience'] = [...]: adds a new column Experience with the given values.
Deleting Columns
You can delete a column from the DataFrame using the drop() method.
Python `
df.drop('Experience', axis=1, inplace=True) print(df.head())
`
**Output

**Explanation: df.drop('Experience', axis=1, inplace=True): removes the 'Experience' column from the DataFrame permanently.
Dealing with Rows
Selecting Rows
Rows can be selected using .loc[] by row label or index.
Python `
data = pd.read_csv("your_file.csv", index_col="Name")
first = data.loc["Avery Bradley"] second = data.loc["R.J. Hunter"]
print(first, "\n\n", second)
`
**Output
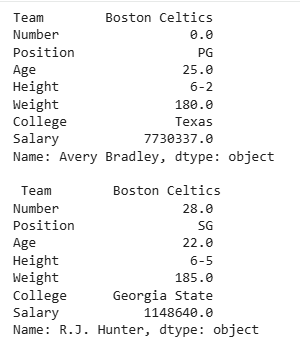
**Explanation: ****.loc[row_label]:** returns a Series corresponding to the row. You can select multiple rows similarly by passing a list.
Adding Rows
New rows can be added using pd.concat().
Python `
import pandas as pd df = pd.read_csv('your_file.csv')
new_row = { 'Name': 'Geeks', 'Team': 'Boston', 'Number': 3, 'Position': 'PG', 'Age': 33, 'Height': '6-2', 'Weight': 189, 'College': 'MIT', 'Salary': 99999 } df = pd.concat([df, pd.DataFrame([new_row])], ignore_index=True) df.tail(2)
`
**Output
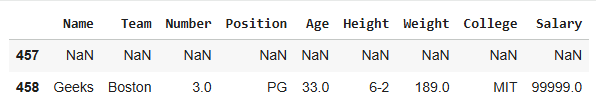
**Explanation:
- **pd.concat([new_row, df]): combines the new row with the existing DataFrame.
- ****.reset_index(drop=True):** resets the index to maintain sequential row numbering.
Deleting Rows
Rows can be removed using drop() with row labels.
Python `
data = pd.read_csv("your_file.csv", index_col="Name") data.drop(["Avery Bradley", "John Holland", "R.J. Hunter"], inplace=True)
`
**Output
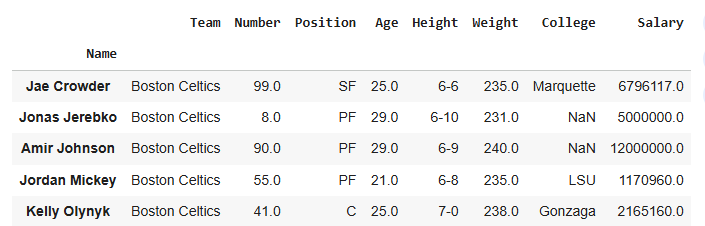
**Explanation: data.drop(["Avery Bradley", "John Holland", "R.J. Hunter"], inplace=True): deletes the specified rows from the DataFrame permanently.
Related Articles
Problem related to Columns
- How to get column names in Pandas dataframe
- How to rename columns in Pandas DataFrame
- How to drop one or multiple columns in Pandas Dataframe
- Get unique values from a column in Pandas DataFrame
- How to lowercase column names in Pandas dataframe
- Apply uppercase to a column in Pandas dataframe
- Capitalize first letter of a column in Pandas dataframe
- Get n-largest values from a particular column in Pandas DataFrame
- Get n-smallest values from a particular column in Pandas DataFrame
- Convert a column to row name/index in Pandas
- Apply function to every row in a Pandas DataFrame
- How to get rows names in Pandas dataframe