Pandas DataFrame assign() Method Create new Columns in DataFrame (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 11 Jul, 2025
The **assign() method in Pandas is used to create or modify columns in a **DataFrame while preserving the original DataFrame. It returns a new DataFrame with the specified modifications. This method allows adding single or multiple columns, performing calculations using existing columns and applying functions dynamically. If a column name already exists, assign() updates its values.
**Example:
Python `
import pandas as pd
a = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3]}) print(a)
add a new column
b = a.assign(B=[4,5,6]) print(b)
`
**Output:

add a new column
**Explanation: This code first creates a Pandas DataFrame a with a single column 'A' containing values [1, 2, 3]. It then uses the **assign() method to add a new column 'B' with values [4, 5, 6], resulting in a modified DataFrame **b while keeping the original DataFrame unchanged.
Syntax
DataFrame.assign(**kwargs)
**Parameters:
- **kwargs: Column names as keyword arguments.
- If the values provided are callable (i.e., functions), they will be computed on the DataFrame.
- If the values are not callable (e.g., Series, scalar, or array), they are directly assigned.
**Returns: A new DataFrame with additional or modified columns while keeping the original DataFrame unchanged.
For the link to the CSV file Used in the Code, click **here
Examples of using assign()
Let's explore some practical examples demonstrating how to use the assign() method.
Example 1: Assigning a New Column with Salary Increment
Python `
import pandas as pd
Reading data from CSV file
df = pd.read_csv("nba.csv")
Displaying the first 10 rows
df.head(10)
create a new column
df_new = df.assign(Revised_Salary=lambda x: x['Salary'] + x['Salary'] * 0.10)
df_new.head(10)
`
**Output
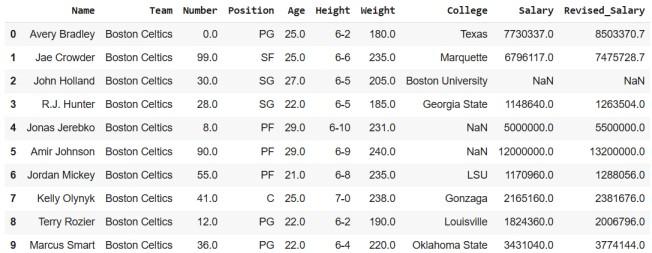
Assigning a new column
**Explanation: This code displays the first 10 rows using head(10). After that, a **new DataFrame (df_new) is created using the assign() method, where a new column "Revised_Salary" is added. This column is calculated by increasing each value in the "Salary" column by 10%. Finally, the first 10 rows of the updated DataFrame are displayed using head(10).
Example 2: Assigning Multiple Columns at Once
We can add multiple new columns simultaneously using the **assign() method. In this example:
- The New_Team column is created by appending '_GO' to each team name.
- The Revised_Salary column is calculated by increasing the original Salary column by 10%. Python `
import pandas as pd
Reading data from CSV file
df = pd.read_csv("nba.csv")
Creating multiple new columns
df_new = df.assign(
New_Team=lambda x: x['Team'] + '_GO',
Revised_Salary=lambda x: x['Salary'] + x['Salary'] * 0.10
)
df_new.head(10)
`
Output
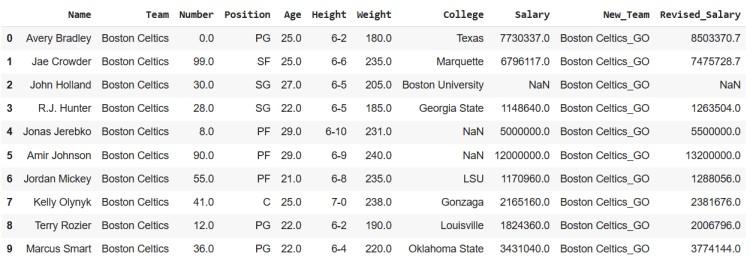
Assigning Multiple Columns at Once
**Explanation: This code creates a new **DataFrame (df_new) by adding two new columns using the **assign() method. The ****"New_Team"** column is generated by appending "_GO" to each value in the "Team" column. The "Revised_Salary" column is computed by increasing each value in the "Salary" column by 10%. Finally, the first 10 rows of the updated DataFrame are displayed using head(10).