Pandas DataFrame.reset_index() (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 28 Jul, 2025
The reset_index() method in Pandas is used to manage and reset the index of a DataFrame. It is useful after performing operations that modify the index such as filtering, grouping or setting a custom index. By default reset_index() reverts to a clean, default integer-based index (0, 1, 2, ...) which makes the DataFrame easier to work with.
**Now lets see a basic example:
Python `
import pandas as pd
data = {'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Max'], 'Age': [25, 30, 35]} df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['a', 'b', 'c'])
print("Original DataFrame:") print(df)
df_reset = df.reset_index()
print("\nDataFrame after reset_index():") print(df_reset)
`
**Output:
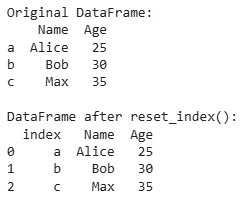
Basic example
This code creates a DataFrame with 'Name' and 'Age' columns and a custom index ('a', 'b', 'c'). The reset_index() function moves these index labels into a new 'index' column and replaces them with default row numbers (0, 1, 2).
Syntax
DataFrame.reset_index(level=None, drop=False, inplace=False, col_level=0, col_fill='')
**Parameters:
- **level (optional): Specifies the index level to reset (useful for multi-level indices). It can be an integer, string or a list of levels.
- **drop (default: False): If True, removes the old index instead of adding it as a column.
- **inplace (default: False): If True, modifies the original DataFrame in place. If False, returns a new DataFrame.
- **col_level (default: 0): Used to select the level of the column to insert the index labels.
- **col_fill (default: ''): If the DataFrame has multiple column levels, this determines how missing levels are filled in the column headers.
**Returns: The reset_index() method returns a new DataFrame with the index reset, unless inplace=True is specified. In that case, the original DataFrame is modified directly without creating a new one.
Lets see some other examples for **DataFrame.reset_index() to understand it in a better way.
**Example 1: Resetting Index of a Pandas DataFrame
In this example, we will set the "First Name" column as the index of the DataFrame and then reset the index using the reset_index() method. This process will move the custom index back to a regular column and restore the default integer-based index.
Python `
import pandas as pd
data = pd.DataFrame({ 'First Name': ['John', 'Jane', 'Emily', 'Michael', 'Sara'], 'Last Name': ['Doe', 'Smith', 'Jones', 'Brown', 'Davis'], 'Age': [28, 34, 22, 45, 29], 'Department': ['HR', 'Finance', 'IT', 'Marketing', 'Sales'], 'Salary': [55000, 68000, 48000, 75000, 60000] })
print("Original Employee Dataset:") display(data.head())
data.set_index("First Name", inplace=True) print("\nAfter Setting 'First Name' as Index:") display(data.head())
data.reset_index(inplace=True) print("\nAfter Resetting Index:") display(data.head())
`
**Output:
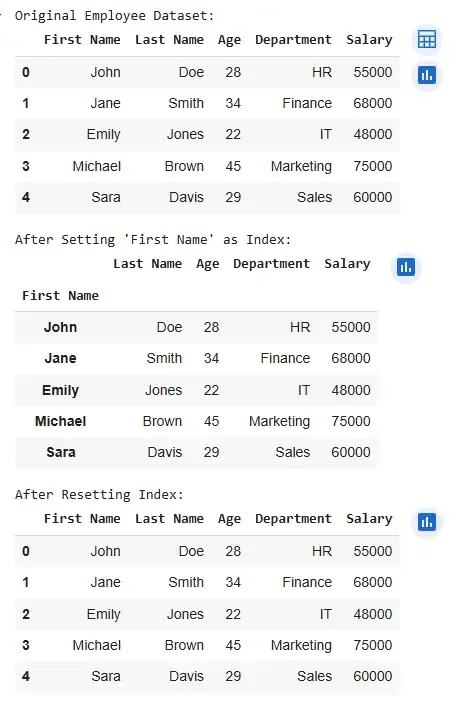
Resetting Index of a Pandas DataFrame
**Example 2: Resetting the Index After Filtering Data
When filtering a DataFrame, the original row indices are retained which can lead to inconsistencies during further operations. Using reset_index() ensures that the index is clean and sequential.
Python `
import pandas as pd
data = {'ID': [101, 102, 103, 104, 105], 'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'David', 'Emma'], 'Dept': ['HR', 'IT', 'IT', 'Finance', 'HR'], 'Salary': [50000, 60000, 65000, 70000, 55000]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data) print("Original DataFrame:") print(df)
df_it = df[df['Dept'] == 'IT'] print("\nFiltered DataFrame:") print(df_it)
df_it = df_it.reset_index(drop=True) print("\nFiltered DataFrame after reset_index():") print(df_it)
`
**Output:
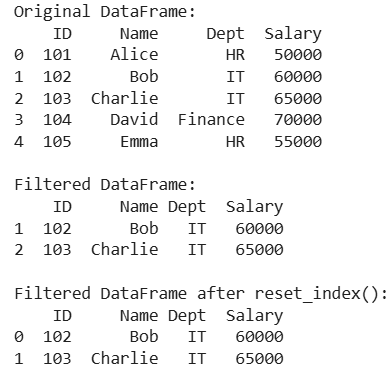
Resetting Index After Filtering Data
The filtered DataFrame (df_filtered) contains only employees from the IT department but retains the original row indices (1 and 2). By applying reset_index(drop=True), we remove the old indices and replace them with a clean, default integer index (0, 1) which results in a more structured and easier-to-analyze DataFrame.
Example 3: Resetting Index for Multi-Level DataFrames
If our DataFrame has a multi-level index, reset_index() can reset one or more of the index levels, turning them back into regular columns.
Python `
import pandas as pd
data = {'Region': ['North', 'North', 'South', 'South'], 'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'Miami', 'Houston'], 'Population': [8.4, 3.9, 0.4, 2.3]} df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.set_index(['Region', 'City'], inplace=True)
print("DataFrame with Multi-Level Index:") print(df)
df_reset = df.reset_index(level='City')
print("\nDataFrame after resetting the 'City' level of the index:") print(df_reset)
`
**Output:
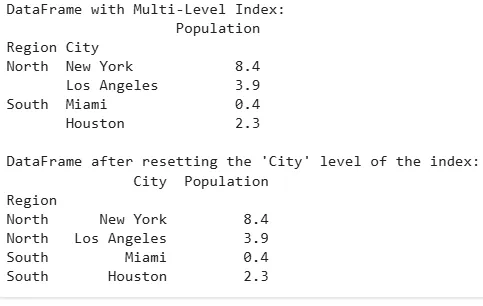
Resetting Index for Multi-Level DataFrames
Key Use Cases of reset_index()
- **Simplifying Data Manipulation: After performing operations like filtering or sorting, we may want to reset the index to have a clean, sequential index.
- **Handling Multi-Level Indexes: When working with multi-level indexes, it can be used to remove specific index levels without affecting the rest of the structure.
- **Restoring Default Index: If you've set a custom index using the set_index() method, reset_index() restores the default integer-based index.
By understanding and using reset_index(), we can efficiently manage and reorganize our DataFrame's index which makes our data easier to manipulate and analyze in various situations.