Postorder Traversal of Binary Tree (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 28 Mar, 2025
**Postorder traversal is a tree traversal method that follows the Left-Right-Root order:
- The **left subtree is visited first.
- The **right subtree is visited next.
- The **root node is processed last.
How does Postorder Traversal work?
**Key Properties:
- It is used for tree deletion because subtrees are deleted before the current node.
- It is also useful for generating the postfix expression from an expression tree.
Examples:
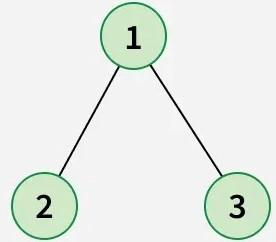
**Input:
**Output: 2 3 1
**Explanation: Postorder Traversal visits the nodes in the following order: **Left, **Right, **Root. Therefore, we visit the left node 2, then the right node 3and lastly the root node 1.**Input:
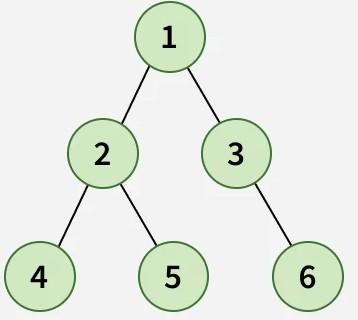
Output: 4 5 2 6 3 1
Explanation: Postorder Traversal (Left → Right → Root).** Visit 4 → 5 → 2 → 6 → 3 → 1, resulting in 4 5 2 6 3 1.
Algorithm:
- If root is NULL then return
- Recursively traverse the left subtree.
- Recursively traverse the right subtree.
- Process the root node (e.g., print its value).
C++ `
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
// Structure of a Binary Tree Node struct Node { int data; struct Node *left, *right; Node(int v) { data = v; left = right = nullptr; } };
// Function to print postorder traversal void printPostorder(struct Node* node) { if (node == nullptr) return;
// First recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node->left);
// Then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node->right);
// Now deal with the node
cout << node->data << " ";}
int main() { struct Node* root = new Node(1); root->left = new Node(2); root->right = new Node(3); root->left->left = new Node(4); root->left->right = new Node(5); root->right->right = new Node(6);
printPostorder(root);
return 0;}
C
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
// Structure of a Binary Tree Node struct Node { int data; struct Node *left, *right; };
// Function to print postorder traversal void printPostorder(struct Node* node) { if (node == NULL) return;
// First recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node->left);
// Then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node->right);
// Now deal with the node
printf("%d ", node->data);}
int main() { struct Node* root = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); root->data = 1; root->left = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); root->left->data = 2; root->right = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); root->right->data = 3; root->left->left = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); root->left->left->data = 4; root->left->right = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); root->left->right->data = 5; root->right->right = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); root->right->right->data = 6;
printPostorder(root);
return 0;}
Java
class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int v) { data = v; left = right = null; } }
public class GfG{ // Function to print postorder traversal void printPostorder(Node node) { if (node == null) return;
// First recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node.left);
// Then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node.right);
// Now deal with the node
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.right = new Node(6);
GfG tree = new GfG();
tree.printPostorder(root);
}}
Python
class Node: def init(self, v): self.data = v self.left = None self.right = None
Function to print postorder traversal
def print_postorder(node): if node is None: return
# First recur on left subtree
print_postorder(node.left)
# Then recur on right subtree
print_postorder(node.right)
# Now deal with the node
print(node.data, end=' ')if name == 'main': root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) root.right.right = Node(6)
print_postorder(root)C#
using System;
// Structure of a Binary Tree Node public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int v) { data = v; left = right = null; } }
public class GfG {
// Function to print postorder traversal
static void printPostorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
// First recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node.left);
// Then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node.right);
// Now deal with the node
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
}
static public void Main()
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.right = new Node(6);
printPostorder(root);
}}
JavaScript
// Structure of a Binary Tree Node class Node { constructor(v) { this.data = v; this.left = null; this.right = null; } }
// Function to print postorder traversal function printPostorder(node) { if (node == null) { return; }
// First recur on left subtree printPostorder(node.left);
// Then recur on right subtree printPostorder(node.right);
// Now deal with the node console.log(node.data + " "); }
// Driver code function main() { let root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.right = new Node(6);
printPostorder(root); }
main();
`
**Time Complexity: O(n)
**Auxiliary Space: O(h), h is the height of the tree
- In the worst case, **h can be the same as **n (when the tree is a skewed tree)
- In the best case, **h can be the same as **log n (when the tree is a complete tree)
**Related articles:
- Types of Tree traversals
- Iterative Postorder traversal (using two stacks)
- Iterative Postorder traversal (using one stack)
- Postorder of Binary Tree without recursion and without stack
- Find Postorder traversal of BST from preorder traversal
- Morris traversal for Postorder
- Print postorder traversal from preoreder and inorder traversal
Similar Reads
- Preorder Traversal of Binary Tree Preorder traversal is a tree traversal method that follows the Root-Left-Right order:The root node of the subtree is visited first.Next, the left subtree is recursively traversed.Finally, the right subtree is recursively traversed.How does Preorder Traversal work?Key Properties: Used in expression t 5 min read
- Mix Order Traversal of a Binary Tree Given a Binary Tree consisting of N nodes, the task is to print its Mix Order Traversal. Mix Order Traversal is a tree traversal technique, which involves any two of the existing traversal techniques like Inorder, Preorder and Postorder Traversal. Any two of them can be performed or alternate levels 13 min read
- Double Order Traversal of a Binary Tree Given a Binary Tree, the task is to find its Double Order Traversal. Double Order Traversal is a tree traversal technique in which every node is traversed twice in the following order: Visit the Node.Traverse the Left Subtree.Visit the Node.Traverse the Right Subtree.Examples:Input: Output: 1 7 4 4 6 min read
- Inorder Traversal of Binary Tree Inorder traversal is a depth-first traversal method that follows this sequence:Left subtree is visited first.Root node is processed next.Right subtree is visited last.How does Inorder Traversal work?Key Properties:If applied to a Binary Search Tree (BST), it returns elements in sorted order.Ensures 5 min read
- Triple Order Traversal of a Binary Tree Given a Binary Tree, the task is to find its Triple Order Traversal. Triple Order Traversal is a tree traversal technique in which every node is traversed thrice in the following order: Visit the root nodeTraverse the left subtreeVisit the root nodeTraverse the right subtreeVisit the root node.Examp 7 min read
- Binary Tree Traversal Binary trees are fundamental data structures in computer science and understanding their traversal is crucial for various applications. Traversing a binary tree means visiting all the nodes in a specific order. There are several traversal methods, each with its unique applications and benefits. This 15+ min read
- Binary Tree Iterator for Inorder Traversal Given a Binary Tree and an input array. The task is to create an Iterator that utilizes next() and hasNext() functions to perform Inorder traversal on the binary tree. Examples: Input: 8 Input Array = [next(), hasNext(), next(), next(), next(), hasNext(), next(), next(), hasNext()] / \ 3 9 / \ 2 4 \ 13 min read
- Specific Level Order Traversal of Binary Tree Given a Binary Tree, the task is to perform a Specific Level Order Traversal of the tree such that at each level print 1st element then the last element, then 2nd element and 2nd last element, until all elements of that level are printed and so on.Examples:Input: Output: 5 3 7 2 8 4 6 9 0 5 1 Explan 8 min read
- Diagonal Traversal of Binary Tree Given a Binary Tree, the task is to print the diagonal traversal of the binary tree.Note: If the diagonal element are present in two different subtrees, then left subtree diagonal element should be taken first and then right subtree. Example:Input: Output: 8 10 14 3 6 7 13 1 4Explanation: The above 7 min read
- Boundary Traversal of binary tree Given a binary tree, the task is to find the boundary nodes of the binary tree Anti-Clockwise starting from the root.The boundary includes:left boundary (nodes on left excluding leaf nodes)leaves (consist of only the leaf nodes)right boundary (nodes on right excluding leaf nodes)The left boundary is 15+ min read