Vertical Traversal using Brute Force (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 23 Jul, 2025
Given a Binary Tree, the task is to find its vertical traversal starting from the **leftmost level to the **rightmost level.
**Note that if multiple nodes at same **level pass through a vertical line, they should be printed as they appear in the **level order traversal of the tree.
**Examples:
**Input:
**Output: [[4], [2], [1, 5, 6], [3, 8], [7], [9]]
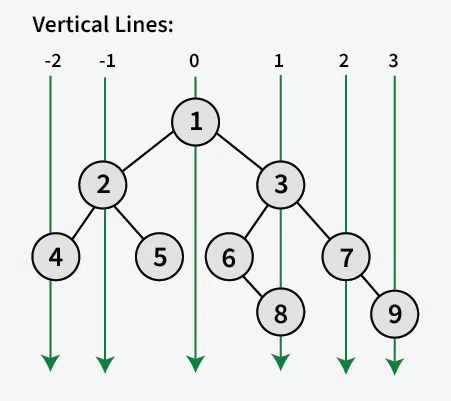
**Explanation: The below image shows the horizontal distances used to print vertical traversal starting from the leftmost level to the rightmost level.
**Approach:
The idea is to traverse the tree once and get the **minimum and **maximum horizontal distance with respect to **root. For the tree shown above, minimum distance is **-2 (for node with value 4) and **maximum distance is **3 (For node with value 9).
Once we have **maximum and **minimum distances from root, we iterate for each vertical line at distance **minimum to **maximum from root, and for each vertical line traverse the tree and print the nodes which lie on that vertical line.
C++ `
//Driver Code Starts // C++ code of Vertical Traversal using Brute Force #include #include using namespace std;
class Node { public: int data; Node* left; Node* right;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = nullptr;
right = nullptr;
}}; //Driver Code Ends
// A utility function to find min and max // distances with respect to root. void findMinMax(Node* node, int& min, int& max, int hd) {
// Base case
if (node == nullptr) return;
// Update min and max
if (hd < min) min = hd;
else if (hd > max) max = hd;
// Recur for left and right subtrees
findMinMax(node->left, min, max, hd - 1);
findMinMax(node->right, min, max, hd + 1);}
// A utility function to collect all // nodes on a given vertical line_no. // hd is horizontal distance of current node with respect to root. void collectVerticalLine(Node* node, int line, int hd, vector& res) { // Base case if (node == nullptr) return;
// If this node is on the given vertical line
if (hd == line)
res.push_back(node->data);
// Recur for left and right subtrees
collectVerticalLine(node->left, line, hd - 1, res);
collectVerticalLine(node->right, line, hd + 1, res);}
// The main function that returns a // vector of nodes in vertical order vector<vector> verticalOrder(Node* root) { vector<vector> res;
// Find min and max distances with
// respect to root
int min = 0, max = 0;
findMinMax(root, min, max, 0);
// Iterate through all possible vertical
// lines from leftmost to rightmost
for (int line = min; line <= max; line++) {
vector<int> verticalNodes;
collectVerticalLine(root, line, 0, verticalNodes);
res.push_back(verticalNodes);
}
return res;}
//Driver Code Starts int main() {
// Create binary tree
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \ / \
// 4 5 6 7
// \ \
// 8 9
Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
root->right->left = new Node(6);
root->right->right = new Node(7);
root->right->left->right = new Node(8);
root->right->right->right = new Node(9);
vector<vector<int>> res = verticalOrder(root);
// Print grouped vertical nodes
for (vector<int> group : res) {
cout << "[ ";
for (int val : group)
cout << val << " ";
cout << "] ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;}
//Driver Code Ends
Java
//Driver Code Starts // Java code of Vertical Traversal using Brute Force import java.util.ArrayList;
class Node { int data; Node left, right;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}}
class GfG { //Driver Code Ends
// A utility function to find min and max
// distances with respect to root.
static void findMinMax(Node node, int[] minMax, int hd) {
// Base case
if (node == null) return;
// Update min and max
if (hd < minMax[0]) minMax[0] = hd;
else if (hd > minMax[1]) minMax[1] = hd;
// Recur for left and right subtrees
findMinMax(node.left, minMax, hd - 1);
findMinMax(node.right, minMax, hd + 1);
}
// A utility function to collect all
// nodes on a given vertical line_no.
static void collectVerticalLine(Node node, int lineNo,
int hd, ArrayList<Integer> res) {
// Base case
if (node == null) return;
// If this node is on the given vertical line
if (hd == lineNo) res.add(node.data);
// Recur for left and right subtrees
collectVerticalLine(node.left, lineNo, hd - 1, res);
collectVerticalLine(node.right, lineNo, hd + 1, res);
}
// The main function that returns an ArrayList of ArrayLists
// representing vertical order traversal
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> verticalOrder(Node root) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
// Find min and max distances with respect to root
int[] minMax = new int[]{0, 0};
findMinMax(root, minMax, 0);
// Iterate through all possible vertical
// lines from leftmost to rightmost
for (int lineNo = minMax[0]; lineNo <= minMax[1]; lineNo++) {
ArrayList<Integer> verticalNodes = new ArrayList<>();
collectVerticalLine(root, lineNo, 0, verticalNodes);
res.add(verticalNodes);
}
return res;
}//Driver Code Starts public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create binary tree
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \ / \
// 4 5 6 7
// \ \
// 8 9
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left.right = new Node(8);
root.right.right.right = new Node(9);
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = verticalOrder(root);
// Print grouped vertical nodes
for (ArrayList<Integer> group : res) {
System.out.print("[ ");
for (int val : group) {
System.out.print(val + " ");
}
System.out.print("] ");
}
System.out.println();
}}
//Driver Code Ends
Python
#Driver Code Starts
Python code of Vertical Traversal
using Brute Force
class Node: def init(self, x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None #Driver Code Ends
A utility function to find min and max
distances with respect to root.
def findMinMax(node, minMax, hd): if node is None: return
# Update min and max
if hd < minMax[0]:
minMax[0] = hd
elif hd > minMax[1]:
minMax[1] = hd
# Recur for left and right subtrees
findMinMax(node.left, minMax, hd - 1)
findMinMax(node.right, minMax, hd + 1)A utility function to collect all
nodes on a given vertical line_no.
def collectVerticalLine(node, lineNo, hd, res): if node is None: return
# If this node is on the given vertical line
if hd == lineNo:
res.append(node.data)
# Recur for left and right subtrees
collectVerticalLine(node.left, lineNo, hd - 1, res)
collectVerticalLine(node.right, lineNo, hd + 1, res)The main function that returns a list of lists
of nodes in vertical order
def verticalOrder(root): res = []
# Find min and max distances with respect to root
minMax = [0, 0]
findMinMax(root, minMax, 0)
# Iterate through all possible vertical lines
for lineNo in range(minMax[0], minMax[1] + 1):
verticalNodes = []
collectVerticalLine(root, lineNo, 0, verticalNodes)
res.append(verticalNodes)
return res#Driver Code Starts if name == "main":
# Create binary tree
# 1
# / \
# 2 3
# / \ / \
# 4 5 6 7
# \ \
# 8 9
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(7)
root.right.left.right = Node(8)
root.right.right.right = Node(9)
res = verticalOrder(root)
# Print grouped vertical nodes
for temp in res:
print("[", " ".join(map(str, temp)), "]", end=" ")
print()#Driver Code Ends
C#
//Driver Code Starts // C# code of Vertical Traversal using Brute Force using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
class Node { public int data; public Node left, right;
public Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}}
class GfG { //Driver Code Ends
// A utility function to find min and
// max distances with respect to root.
static void findMinMax(Node node, int[] minMax, int hd) {
// Base case
if (node == null) return;
// Update min and max
if (hd < minMax[0]) minMax[0] = hd;
else if (hd > minMax[1]) minMax[1] = hd;
// Recur for left and right subtrees
findMinMax(node.left, minMax, hd - 1);
findMinMax(node.right, minMax, hd + 1);
}
// A utility function to collect all
// nodes on a given vertical lineNo.
static void collectVerticalLine(Node node,
int lineNo, int hd, List<int> res) {
// Base case
if (node == null) return;
// If this node is on the
// given vertical line
if (hd == lineNo) res.Add(node.data);
// Recur for left and right subtrees
collectVerticalLine(node.left, lineNo, hd - 1, res);
collectVerticalLine(node.right, lineNo, hd + 1, res);
}
// The main function that returns a list
// of lists of nodes in vertical order
static List<List<int>> verticalOrder(Node root) {
List<List<int>> res = new List<List<int>>();
// Find min and max distances with respect to root
int[] minMax = new int[]{0, 0};
findMinMax(root, minMax, 0);
// Iterate through all possible vertical lines
for (int lineNo = minMax[0];
lineNo <= minMax[1]; lineNo++) {
List<int> verticalNodes = new List<int>();
collectVerticalLine(root, lineNo, 0, verticalNodes);
res.Add(verticalNodes);
}
return res;
}//Driver Code Starts public static void Main() {
// Create binary tree
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \ / \
// 4 5 6 7
// \ \
// 8 9
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left.right = new Node(8);
root.right.right.right = new Node(9);
List<List<int>> res = verticalOrder(root);
// Print grouped vertical nodes
foreach (var temp in res) {
Console.Write("[ ");
foreach (int val in temp) {
Console.Write(val + " ");
}
Console.Write("] ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}}
//Driver Code Ends
` JavaScript ``
//Driver Code Starts // JavaScript code of Vertical Traversal using Brute Force
class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Driver Code Ends
// A utility function to find min // and max distances with respect to root. function findMinMax(node, minMax, hd) {
// Base case
if (node === null) return;
// Update min and max
if (hd < minMax[0]) minMax[0] = hd;
else if (hd > minMax[1]) minMax[1] = hd;
// Recur for left and right subtrees
findMinMax(node.left, minMax, hd - 1);
findMinMax(node.right, minMax, hd + 1);}
// A utility function to collect all // nodes on a given vertical lineNo. function collectVerticalLine(node, lineNo, hd, res) {
// Base case
if (node === null) return;
// If this node is on the given vertical line
if (hd === lineNo) res.push(node.data);
// Recur for left and right subtrees
collectVerticalLine(node.left, lineNo, hd - 1, res);
collectVerticalLine(node.right, lineNo, hd + 1, res);}
// The main function that returns an // array of arrays of nodes in vertical order function verticalOrder(root) { let res = [];
// Find min and max distances with respect to root
let minMax = [0, 0];
findMinMax(root, minMax, 0);
// Iterate through all possible vertical lines
for (let lineNo = minMax[0]; lineNo <= minMax[1]; lineNo++) {
let verticalNodes = [];
collectVerticalLine(root, lineNo, 0, verticalNodes);
res.push(verticalNodes);
}
return res;}
//Driver Code Starts // Driver code if (require.main === module) {
// Create binary tree
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \ / \
// 4 5 6 7
// \ \
// 8 9
let root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left.right = new Node(8);
root.right.right.right = new Node(9);
let res = verticalOrder(root);
console.log(res.map(arr => `[ ${arr.join(" ")} ]`).join(" "));}
//Driver Code Ends
``
Output
[ 4 ] [ 2 ] [ 1 5 6 ] [ 3 8 ] [ 7 ] [ 9 ]
**Time Complexity: O(n2), Time complexity of above algorithm is O(w*n) where w is width of Binary Tree and n is number of nodes in Binary Tree. In worst case, the value of w can be O(n).
**Auxiliary Space: O(h), space use by memory stack, where h is height of the tree.
Please refer the below posts for optimised solutions.
Print a Binary Tree in Vertical Order