Print Right View of a Binary Tree (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 26 Sep, 2024
Given a Binary Tree, the task is to print the Right view of it. The right view of a Binary Tree is a set of **rightmost nodes for every level.
**Examples:
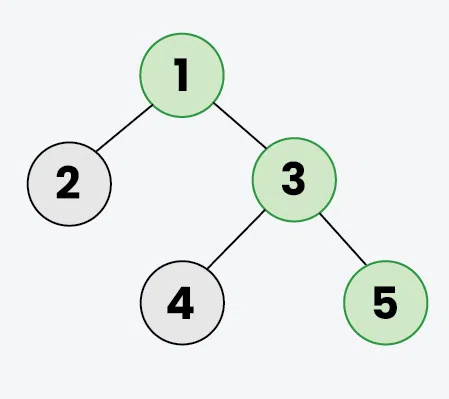
_Example 1: The **Green _colored nodes (1, 3, 5) represents the Right view in the below Binary tree.
_Example 2: The **Green _colored nodes (1, 3, 4, 5) represents the Right view in the below Binary tree.
Table of Content
- [Expected Approach - 1] Using Recursion – O(n) Time and O(n) Space
- [Expected Approach – 2] Using Level Order Traversal – O(n) Time and O(n) Space
- [Expected Approach - 3] Using Morris Traversal – O(n) Time and O(1) Space
[Expected Approach - 1] Using Recursion – O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The idea is to use recursion and keep track of the maximum level also. And traverse the tree in a manner that the right subtree is visited **before the left subtree.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Perform **Postorder traversal to get the rightmost node first.
- Maintain a variable name **maxLevel which will store till which it prints the right view.
- While traversing the tree in a postorder manner if the **current level is greater than maxLevel then print the current node and update **maxLevel by the current level.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ `
// C++ program to print right view of Binary Tree // using recursion #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
class Node { public: int data; Node *left, *right;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = right = nullptr;
}};
// Helper function for the right view using Recursion void RecursiveRightView(Node* root, int level, int& maxLevel, vector& result) { if (!root) return;
// If current level is more than max level,
// this is the first node of that level
if (level > maxLevel) {
result.push_back(root->data);
maxLevel = level;
}
// Traverse right subtree first, then left subtree
RecursiveRightView(root->right, level + 1,
maxLevel, result);
RecursiveRightView(root->left, level + 1,
maxLevel, result);}
// Function to return the right view of the binary tree vector rightView(Node *root) { vector result; int maxLevel = -1;
// Start recursion with root at level 0
RecursiveRightView(root, 0, maxLevel, result);
return result;}
void printArray(vector& arr) { for (int val : arr) { cout << val << " "; } cout << endl; }
int main() {
// Representation of the input tree:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \
// 4 5
Node *root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->right->left = new Node(4);
root->right->right = new Node(5);
vector<int> result = rightView(root);
printArray(result);
return 0;}
C
// C program to print right view of Binary Tree // using recursion #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
struct Node { int data; struct Node *left, *right; };
// Helper function for the right view using Recursion void RecursiveRightView(struct Node* root, int level, int* maxLevel, int* result, int* index) { if (!root) return;
// If current level is more than max level,
// this is the first node of that level
if (level > *maxLevel) {
result[(*index)++] = root->data;
*maxLevel = level;
}
// Traverse right subtree first, then
// left subtree
RecursiveRightView(root->right, level + 1,
maxLevel, result, index);
RecursiveRightView(root->left, level + 1,
maxLevel, result, index);}
// Function to return the right view of the binary tree void rightView(struct Node* root, int* result, int* size) { int maxLevel = -1; int index = 0;
// Start recursion with root at level 0
RecursiveRightView(root, 0, &maxLevel,
result, &index);
*size = index;}
void printArray(int* arr, int size) { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { printf("%d ", arr[i]); } printf("\n"); }
struct Node* createNode(int x) { struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); newNode->data = x; newNode->left = newNode->right = NULL; return newNode; }
int main() {
// Representation of the input tree:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \
// 4 5
struct Node *root = createNode(1);
root->left = createNode(2);
root->right = createNode(3);
root->right->left = createNode(4);
root->right->right = createNode(5);
int result[100];
int size = 0;
rightView(root, result, &size);
printArray(result, size);
return 0;}
Java
// Java program to print right view of binary tree // using Recursion import java.util.ArrayList;
class Node { int data; Node left, right;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = right = null;
}}
// Helper function for the right view using Recursion class GfG { static void RecursiveRightView(Node root, int level, int[] maxLevel, ArrayList result) { if (root == null) return;
// If current level is more than max level,
// this is the first node of that level
if (level > maxLevel[0]) {
result.add(root.data);
maxLevel[0] = level;
}
// Traverse right subtree first, then left subtree
RecursiveRightView(root.right, level + 1,
maxLevel, result);
RecursiveRightView(root.left, level + 1,
maxLevel, result);
}
// Function to return the right view of the binary tree
static ArrayList<Integer> rightView(Node root) {
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
int[] maxLevel = new int[] {-1};
// Start recursion with root at level 0
RecursiveRightView(root, 0, maxLevel, result);
return result;
}
static void printArray(ArrayList<Integer> arr) {
for (int val : arr) {
System.out.print(val + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Representation of the input tree:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \
// 4 5
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.right.left = new Node(4);
root.right.right = new Node(5);
ArrayList<Integer> result = rightView(root);
printArray(result);
}}
Python
Python program to print right view of Binary Tree
using Recursion
class Node: def init(self, data): self.data = data self.left = None self.right = None
Helper function for the right view using Recursion
def RecursiveRightView(root, level, maxLevel, result): if root is None: return
# If current level is more than max level,
# this is the first node of that level
if level > maxLevel[0]:
result.append(root.data)
maxLevel[0] = level
# Traverse right subtree first, then left subtree
RecursiveRightView(root.right, level + 1,
maxLevel, result)
RecursiveRightView(root.left, level + 1,
maxLevel, result)Function to return the right view of the binary tree
def rightView(root): result = [] maxLevel = [-1]
# Start recursion with root at level 0
RecursiveRightView(root, 0, maxLevel, result)
return resultdef printArray(arr): for val in arr: print(val, end=" ") print()
if name == "main":
# Representation of the input tree:
# 1
# / \
# 2 3
# / \
# 4 5
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.right.left = Node(4)
root.right.right = Node(5)
result = rightView(root)
printArray(result)C#
// C# program to print right view of binary tree // using Recursion using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
class Node { public int data; public Node left, right;
public Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = right = null;
}}
class GfG {
// Helper function for the right view using Recursion
static void RecursiveRightView(Node root, int level,
ref int maxLevel, List<int> result) {
if (root == null) return;
// If current level is more than max level,
// this is the first node of that level
if (level > maxLevel) {
result.Add(root.data);
maxLevel = level;
}
// Traverse right subtree first, then left subtree
RecursiveRightView(root.right, level + 1,
ref maxLevel, result);
RecursiveRightView(root.left, level + 1,
ref maxLevel, result);
}
// Function to return the right view of the binary tree
static List<int> rightView(Node root) {
List<int> result = new List<int>();
int maxLevel = -1;
// Start recursion with root at level 0
RecursiveRightView(root, 0, ref maxLevel, result);
return result;
}
static void PrintList(List<int> arr) {
foreach (int val in arr) {
Console.Write(val + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void Main(string[] args) {
// Representation of the input tree:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \
// 4 5
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.right.left = new Node(4);
root.right.right = new Node(5);
List<int> result = rightView(root);
PrintList(result);
}}
JavaScript
// JavaScript program to print right view // of binary tree using Recursion class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } }
// Helper function for the right view using Recursion function recursiveRightView(root, level, maxLevel, result) { if (root === null) return;
// If current level is more than max level,
// this is the first node of that level
if (level > maxLevel[0]) {
result.push(root.data);
maxLevel[0] = level;
}
// Traverse right subtree first, then left subtree
recursiveRightView(root.right, level + 1,
maxLevel, result);
recursiveRightView(root.left, level + 1,
maxLevel, result);}
// Function to return the right view of the binary tree function rightView(root) { let result = []; let maxLevel = [-1];
// Start recursion with root at level 0
recursiveRightView(root, 0, maxLevel, result);
return result;}
// Function to print the array function printArray(arr) { console.log(arr.join(' ')); }
// Representation of the input tree:
// 1
// /
// 2 3
// / \
// 4 5
let root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.right.left = new Node(4);
root.right.right = new Node(5);
let result = rightView(root);
printArray(result);
`
**Time Complexity: O(n), We traverse all nodes of the binary tree exactly once, where n is the number of nodes.
**Auxiliary Space: O(h), The space required for the recursion stack will be proportional to the **height(h) of the tree, which could be as large as n for a skewed tree.
[Expected Approach – 2] Using Level Order Traversal – O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The idea is to traverse the tree level by level and print the last node at each level (**the rightmost node). A simple solution is to do level order traversal and print the last node in every level. Please refer to Right view of Binary Tree using Queue for implementation.
**[Expected Approach - 3] Using Morris Traversal – O(n) Time and O(1) Space
The idea is to use **Morris Traversalto print the right view of the binary tree by dynamically adjusting the tree's structure during traversal. An empty list is maintained to store the rightmost nodes encountered at each level.
Follow the steps below to implement the idea:
- Create an empty list view to store the **right view nodes and set a variable level to 0 to track the **current level of traversal.
- Use a pointer root to traverse the binary tree. While root is not **null, proceed with the traversal.
- If the current node has a right child, find its inorder predecessor by traversing the leftmost nodes of the right subtree.
- If the left child of the predecessor is null, add the current node's value to view if it’s the first visit to that level. Then establish a thread from the predecessor to the current node and move to the **right child.
- If the left child of the predecessor is already pointing to the current node (indicating a second visit), remove the thread and move to the left child of the **current node.
- If the current node does not have a right child, add its value to **res if it’s the first visit at that level, then move to its **left child for further traversal.
Below is the implementation of the above approach.
C++ `
// C++ program to print right view of Binary // tree using modified Morris Traversal #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
class Node { public: int data; Node* left; Node* right;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = right = nullptr;
}};
// Function to return the right view of the binary tree vector rightView(Node* root) {
// To store the right view nodes
vector<int> res;
// Current level of traversal
int level = 0;
// Traverse the tree using modified Morris Traversal
while (root) {
// If the node has a right child,
// find the inorder predecessor
if (root->right) {
Node *pred = root->right;
int backDepth = 1;
// Find the leftmost node in the right subtree
while (pred->left != nullptr &&
pred->left != root) {
pred = pred->left;
backDepth++;
}
// If threading is not yet established
if (pred->left == nullptr) {
// Add the current node to the view if
// visiting the level for the first time
if (res.size() == level) {
res.push_back(root->data);
}
// Establish the thread and move
// to the right subtree
pred->left = root;
root = root->right;
level++;
}
else {
// Threading was already done
//(second visit) remove the thread and
// go to the left subtree
pred->left = nullptr;
root = root->left;
level -= backDepth;
}
}
else {
// If no right child, process the current
// node and move to the left child
if (res.size() == level) {
res.push_back(root->data);
}
root = root->left;
level++;
}
}
// Return the right view nodes
return res;}
void printArray(vector& arr) {
for (int val : arr) {
cout << val << " ";
}
cout << endl;}
int main() {
// Representation of the input tree:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \
// 4 5
Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->right->left = new Node(4);
root->right->right = new Node(5);
vector<int> result = rightView(root);
printArray(result);
return 0;}
Java
// Java program to print right view of Binary // tree using modified Morris Traversal import java.util.ArrayList;
class Node { int data; Node left, right;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = right = null;
}}
// Function to return the right view of the binary tree class GfG {
public static ArrayList<Integer> rightView(Node root) {
// To store the right view nodes
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
// Current level of traversal
int level = 0;
// Traverse the tree using modified
// Morris Traversal
while (root != null) {
// If the node has a right child,
// find the inorder predecessor
if (root.right != null) {
Node pred = root.right;
int backDepth = 1;
// Find the leftmost node in the
// right subtree
while (pred.left != null
&& pred.left != root) {
pred = pred.left;
backDepth++;
}
// If threading is not yet established
if (pred.left == null) {
// Add the current node to the view if
// visiting the level for the first time
if (res.size() == level) {
res.add(root.data);
}
// Establish the thread and move
// to the right subtree
pred.left = root;
root = root.right;
level++;
}
else {
// Threading was already done
// (second visit) remove the thread
// and go to the left subtree
pred.left = null;
root = root.left;
level -= backDepth;
}
}
else {
// If no right child, process the current
// node and move to the left child
if (res.size() == level) {
res.add(root.data);
}
root = root.left;
level++;
}
}
return res;
}
static void printArray(ArrayList<Integer> arr) {
for (int val : arr) {
System.out.print(val + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Representation of the input tree:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \
// 4 5
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.right.left = new Node(4);
root.right.right = new Node(5);
ArrayList<Integer> result = rightView(root);
printArray(result);
}}
Python
Python program to print right view of Binary Tree
using modified Morris Traversal
class Node: def init(self, x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None
Function to return the right view of the binary tree
def rightView(root):
# To store the right view nodes
res = []
# Current level of traversal
level = 0
# Traverse the tree using modified Morris Traversal
while root:
# If the node has a right child,
# find the inorder predecessor
if root.right:
pred = root.right
backDepth = 1
# Find the leftmost node in the right subtree
while pred.left and pred.left != root:
pred = pred.left
backDepth += 1
# If threading is not yet established
if pred.left is None:
# Add the current node to the view if
# visiting the level for the first time
if len(res) == level:
res.append(root.data)
# Establish the thread and move
# to the right subtree
pred.left = root
root = root.right
level += 1
else:
# Threading was already done
# (second visit) remove the thread
# and go to the left subtree
pred.left = None
root = root.left
level -= backDepth
else:
# If no right child, process the current
# node and move to the left child
if len(res) == level:
res.append(root.data)
root = root.left
level += 1
# Return the right view nodes
return resdef printArray(arr): for val in arr: print(val, end=" ") print()
if name == "main":
# Representation of the input tree:
# 1
# / \
# 2 3
# / \
# 4 5
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.right.left = Node(4)
root.right.right = Node(5)
result = rightView(root)
printArray(result)C#
// C# program to print right view of Binary Tree // using modified Morris Traversal using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
class Node { public int data; public Node left, right;
public Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = right = null;
}}
// Function to return the right view of the binary tree class GfG {
static List<int> rightView(Node root) {
// To store the right view nodes
List<int> res = new List<int>();
// Current level of traversal
int level = 0;
// Traverse the tree using modified
// Morris Traversal
while (root != null) {
// If the node has a right child,
// find the inorder predecessor
if (root.right != null) {
Node pred = root.right;
int backDepth = 1;
// Find the leftmost node in the
// right subtree
while (pred.left != null
&& pred.left != root) {
pred = pred.left;
backDepth++;
}
// If threading is not yet established
if (pred.left == null) {
// Add the current node to the view if
// visiting the level for the first time
if (res.Count == level) {
res.Add(root.data);
}
// Establish the thread and move
// to the right subtree
pred.left = root;
root = root.right;
level++;
}
else {
// Threading was already done
// (second visit) remove the thread
// and go to the left subtree
pred.left = null;
root = root.left;
level -= backDepth;
}
}
else {
// If no right child, process the current
// node and move to the left child
if (res.Count == level) {
res.Add(root.data);
}
root = root.left;
level++;
}
}
// Return the right view nodes
return res;
}
static void printArray(List<int> arr) {
foreach (int val in arr) {
Console.Write(val + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}static void Main(string[] args) {
// Representation of the input tree:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \
// 4 5
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.right.left = new Node(4);
root.right.right = new Node(5);
List<int> result = rightView(root);
printArray(result);
}}
JavaScript
// JavaScript program to print right view of Binary // tree using modified Morris Traversal
class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } }
// Function to return the right view of the binary tree function rightView(root) {
// To store the right view nodes
const res = [];
// Current level of traversal
let level = 0;
// Traverse the tree using modified Morris Traversal
while (root) {
// If the node has a right child,
// find the inorder predecessor
if (root.right) {
let pred = root.right;
let backDepth = 1;
// Find the leftmost node in the right subtree
while (pred.left && pred.left !== root) {
pred = pred.left;
backDepth++;
}
// If threading is not yet established
if (pred.left === null) {
// Add the current node to the view if
// visiting the level for the first time
if (res.length === level) {
res.push(root.data);
}
// Establish the thread and move
// to the right subtree
pred.left = root;
root = root.right;
level++;
}
else {
// Threading was already done (second visit)
// remove the thread and go to the left subtree
pred.left = null;
root = root.left;
level -= backDepth;
}
}
else {
// If no right child, process the current
// node and move to the left child
if (res.length === level) {
res.push(root.data);
}
root = root.left;
level++;
}
}
// Return the right view nodes
return res;}
function printArray(arr) { console.log(arr.join(' ')); }
// Representation of the input tree:
// 1
// /
// 2 3
// /
// 4 5
const root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.right.left = new Node(4);
root.right.right = new Node(5);
const result = rightView(root); printArray(result);
`
****Time Complexity:**O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the binary tree. This is because we visit each node exactly twice (once when we find its inorder predecessor, and once when we visit it from its inorder predecessor).
**Auxiliary Space: O(1), because we only use a constant amount of extra space for the pointers. We do not use any additional data structures or recursive function calls that would increase the space complexity.