Program to find transpose of a matrix (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 08 May, 2025
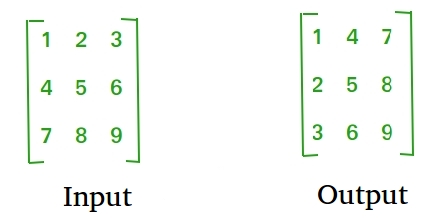
Given a matrix of size n X m, find the transpose of the matrix. Transpose of a matrix is obtained by changing rows to columns and columns to rows. In other words, transpose of mat[n][m] is obtained by changing mat[i][j] to mat[j][i].
**Example:
**Approach using (N^2) space
- Run a nested loop using two integer pointers i and j for 0 <= i < n and 0 <= j < m
- Set mat[i][j] equal to mat[j][i]
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ `
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
// Function to store the transpose of mat in res
void transpose(vector<vector>& mat, vector<vector>& res) {
int rows = mat.size();
int cols = mat[0].size();
// Resize res to have dimensions swapped
res.resize(cols, vector<int>(rows));
// Fill res with transposed values of mat
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
res[j][i] = mat[i][j];
}
}}
// Driver code int main() { vector<vector> mat = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } };
// Create a result matrix for the transpose
vector<vector<int>> res;
// Function call to calculate the transpose
transpose(mat, res);
// Print the result matrix
cout << "Result matrix is:\n";
for (auto& row : res) {
for (auto& elem : row) {
cout << " " << elem;
}
cout << "\n";
}
return 0;}
C
// Import necessary libraries #include <stdio.h>
// Define macros for matrix dimensions #define M 2 // Number of rows in the original matrix #define N 3 // Number of columns in the original matrix
// Function to store the transpose of mat in res void transpose(int mat[M][N], int res[N][M]) {
// Fill res with transposed values of mat
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
res[j][i] = mat[i][j];
}
}}
// Driver code int main() { int mat[M][N] = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } };
// Create a result matrix for the transpose
int res[N][M];
// Function call to calculate the transpose
transpose(mat, res);
// Print the result matrix
printf("Result matrix is:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
printf("%d ", res[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;}
Java
// Import necessary classes import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Scanner;
public class TransposeMatrix {
// Function to store the transpose of mat in res
public static void transpose(int[][] mat, int[][] res) {
int rows = mat.length;
int cols = mat[0].length;
// Fill res with transposed values of mat
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
res[j][i] = mat[i][j];
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] mat = {
{ 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 }
};
// Create a result matrix for the transpose
int[][] res = new int[mat[0].length][mat.length];
// Function call to calculate the transpose
transpose(mat, res);
// Print the result matrix
System.out.println("Result matrix is:");
for (int[] row : res) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(row));
}
}}
Python
Function to store the transpose of mat in res
def transpose(mat):
# Fill res with transposed values of mat
return [[mat[j][i] for j in range(len(mat))] for i in range(len(mat[0]))]Driver code
if name == 'main': mat = [ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6] ]
# Function call to calculate the transpose
res = transpose(mat)
# Print the result matrix
print("Result matrix is:")
for row in res:
print(" ".join(map(str, row)))C#
// Function to store the transpose of mat in res void Transpose(int[][] mat, out int[][] res) { int rows = mat.Length; int cols = mat[0].Length;
// Resize res to have dimensions swapped
res = new int[cols][];
for (int i = 0; i < cols; i++) {
res[i] = new int[rows];
}
// Fill res with transposed values of mat
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
res[j][i] = mat[i][j];
}
}}
// Driver code public static void Main() { int[][] mat = { new int[] { 1, 2, 3 }, new int[] { 4, 5, 6 } };
// Create a result matrix for the transpose
int[][] res;
// Function call to calculate the transpose
Transpose(mat, out res);
// Print the result matrix
Console.WriteLine("Result matrix is:");
foreach (var row in res) {
foreach (var elem in row) {
Console.Write(" " + elem);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}}
JavaScript
// Function to store the transpose of mat in res function transpose(mat) { let rows = mat.length; let cols = mat[0].length;
// Create a result matrix for the transpose
let res = Array.from({ length: cols }, () => new Array(rows));
// Fill res with transposed values of mat
for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
res[j][i] = mat[i][j];
}
}
return res;}
// Driver code let mat = [ [ 1, 2, 3 ], [ 4, 5, 6 ] ];
// Function call to calculate the transpose let res = transpose(mat);
// Print the result matrix console.log("Result matrix is:"); for (let row of res) { console.log(" "+ row.join(' ')); }
`
Output
Result matrix is: 1 4 2 5 3 6
**Time complexity: O(m x n).
**Auxiliary Space: O(m x n)
**Approach using constant space for Square Matrix
_This approach works only for square matrices (i.e., - where no. of rows are equal to the number of columns). This algorithm is also known as an "in-place" algorithm as it uses no extra space to solve the problem.
Follow the given steps to solve the problem:
- Run a nested loop using two integer pointers i and j for 0 <= i < N and i+1 <= j < N
- Swap mat[i][j] with mat[j][i]
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ `
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
// Function to convert mat to its transpose void transpose(vector<vector>& mat) { int n = mat.size(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { swap(mat[i][j], mat[j][i]); } } }
// Driver code int main() { vector<vector> mat = { { 1, 1, 1, 1 }, { 2, 2, 2, 2 }, { 3, 3, 3, 3 }, { 4, 4, 4, 4 } };
transpose(mat);
cout << "Modified matrix is:" << endl;
for (const auto& row : mat) {
for (int elem : row) {
cout << elem << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;}
C
#include <stdio.h> #define N 4
// Function to convert mat to its transpose void transpose(int mat[N][N]) { for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j < N; j++) { int temp = mat[i][j]; mat[i][j] = mat[j][i]; mat[j][i] = temp; } } }
// Driver code int main() { int mat[N][N] = { { 1, 1, 1, 1 }, { 2, 2, 2, 2 }, { 3, 3, 3, 3 }, { 4, 4, 4, 4 } };
transpose(mat);
printf("Modified matrix is:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
printf("%d ", mat[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;}
Java
import java.util.Arrays;
public class GfG { static void transpose(int[][] mat) { int n = mat.length; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { int temp = mat[i][j]; mat[i][j] = mat[j][i]; mat[j][i] = temp; } } }
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] mat = {
{ 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 2, 2, 2, 2 },
{ 3, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 4, 4, 4, 4 }
};
transpose(mat);
System.out.println("Modified matrix is:");
for (int[] row : mat) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(row));
}
}}
Python
Function to convert mat to its transpose
def transpose(mat): n = len(mat) for i in range(n): for j in range(i + 1, n): mat[i][j], mat[j][i] = mat[j][i], mat[i][j]
Driver code
if name == 'main': mat = [ [1, 1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2, 2], [3, 3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4, 4] ]
transpose(mat)
print("Modified matrix is:")
for row in mat:
print(' '.join(map(str, row)))C#
using System;
class Program {
// Function to convert mat to its transpose
static void Transpose(int[,] mat) {
int n = mat.GetLength(0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
int temp = mat[i, j];
mat[i, j] = mat[j, i];
mat[j, i] = temp;
}
}
}
// Driver code
static void Main() {
int[,] mat = {
{ 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 2, 2, 2, 2 },
{ 3, 3, 3, 3 },
{ 4, 4, 4, 4 }
};
Transpose(mat);
Console.WriteLine("Modified matrix is:");
for (int i = 0; i < mat.GetLength(0); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < mat.GetLength(1); j++) {
Console.Write(mat[i, j] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}}
JavaScript
// Function to convert mat to its transpose function transpose(mat) { let n = mat.length; for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (let j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { [mat[i][j], mat[j][i]] = [mat[j][i], mat[i][j]]; } } }
// Driver code const mat = [ [1, 1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2, 2], [3, 3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4, 4] ];
transpose(mat);
console.log("Modified matrix is:"); mat.forEach(row => { console.log(row.join(' ')); });
`
Output
Modified matrix is: 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
**Time complexity: O(n2).
**Auxiliary Space: O(1)