Find First n Fibonacci Numbers (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 03 Jan, 2025
Given an integer **n. The task is tofind the first **n Fibonacci Numbers.
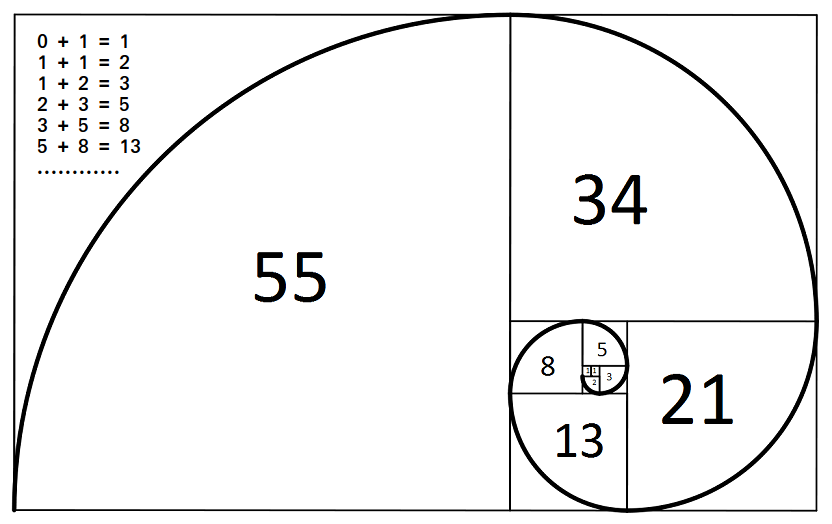
**Examples :
**Input: n = 3
**Output: 0 1 1**Input: n = 7
**Output: 0 1 1 2 3 5 8
Recursive Approach - O(n*2n) Time and O(n) Space
Find nth fibonacci number by calling for n-1 and **n-2 and adding their return value. The base case will be if n=0 or n=1 then the fibonacci number will be **0 and 1 respectively.
C++ `
#include #include using namespace std;
int findFibonacci(int n) {
// base case n = 0 n = 1 if (n == 0) { return 0; } else if (n == 1) { return 1; } else { return findFibonacci(n - 2) + findFibonacci(n - 1); } }
vector fibonacciNumbers(int n) { vector ans; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { ans.push_back(findFibonacci(i)); } return ans; }
int main() { int n = 7; vector res = fibonacciNumbers(n); for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++) { cout << res[i] << " "; } return 0; }
C
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
int findFibonacci(int n) { // base case n = 0 , n = 1 if (n == 0) { return 0; } else if (n == 1) { return 1; } else { return findFibonacci(n - 2) + findFibonacci(n - 1); } }
int* fibonacciNumbers(int n) { int* ans = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int)); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { ans[i] = findFibonacci(i); } return ans; }
int main() { int n = 7; int* res = fibonacciNumbers(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { printf("%d ", res[i]); } free(res); return 0; }
Java
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List;
class GfG { static int findFibonacci(int n) {
// base case n = 0 , n = 1
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
} else if (n == 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return findFibonacci(n - 2) + findFibonacci(n - 1);
}}
static List fibonacciNumbers(int n) { List ans = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { ans.add(findFibonacci(i)); } return ans; }
public static void main(String[] args) { int n = 7; List res = fibonacciNumbers(n); for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++) { System.out.print(res.get(i) + " "); } } }
Python
def findFibonacci(n):
#base case n = 0 , n = 1
if n == 0:
return 0
elif n == 1:
return 1
else:
return findFibonacci(n-2) + findFibonacci(n-1)def fibonacciNumbers(n): ans = [] for i in range(n): ans.append(findFibonacci(i)) return ans
if name == 'main': n = 7 res = fibonacciNumbers(n) for num in res: print(num, end=' ')
C#
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
class GfG { static int FindFibonacci(int n) {
// base case n = 0 , n = 1
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
} else if (n == 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return FindFibonacci(n - 2) + FindFibonacci(n - 1);
}}
static List FibonacciNumbers(int n) { List ans = new List(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { ans.Add(FindFibonacci(i)); } return ans; }
static void Main() { int n = 7; List res = FibonacciNumbers(n); foreach (int num in res) { Console.Write(num + " "); } } }
JavaScript
function findFibonacci(n) {
//base case n = 0 , n = 1
if (n === 0) {
return 0;
} else if (n === 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return findFibonacci(n - 2) + findFibonacci(n - 1);
}}
function fibonacciNumbers(n) { let ans = []; for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { ans.push(findFibonacci(i)); } return ans; }
// Driver Code let n = 7; let res = fibonacciNumbers(n); console.log(res.join(' '));
`
**Time Complexity: O(n*2n)
**Auxiliary Space: O(n), For recursion call stack.
Iterative Approach - O(n) Time and O(1) Space
To find Fibonacci numbers by maintaining two variables (
f1andf2) to represent consecutive Fibonacci numbers. Starting with 0 and 1, it iteratively computes the next Fibonacci number, appends it to the result list, and updates the variables accordingly.
C++ `
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
vector fibonacciNumbers(int n) { vector ans; int f1 = 0, f2 = 1, i; ans.push_back(f1);
for (i = 1; i < n; i++) { ans.push_back(f2); int next = f1 + f2; f1 = f2; f2 = next; } return ans; }
int main() { int n = 7; vector res = fibonacciNumbers(n); for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++) { cout << res[i] << " "; } return 0; }
Java
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List;
class GfG { static List fibonacciNumbers(int n) { List ans = new ArrayList<>(); int f1 = 0, f2 = 1; ans.add(f1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
ans.add(f2);
int next = f1 + f2;
f1 = f2;
f2 = next;
}
return ans;}
public static void main(String[] args) { int n = 7; List res = fibonacciNumbers(n); for (int num : res) { System.out.print(num + " "); } } }
Python
def fibonacci_numbers(n): ans = [] f1, f2 = 0, 1 ans.append(f1)
for i in range(1, n):
ans.append(f2)
next = f1 + f2
f1 = f2
f2 = next
return ansif name == "main": n = 7 res = fibonacci_numbers(n) print(' '.join(map(str, res)))
C#
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
class GfG { static List FibonacciNumbers(int n) { List ans = new List(); int f1 = 0, f2 = 1; ans.Add(f1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
ans.Add(f2);
int next = f1 + f2;
f1 = f2;
f2 = next;
}
return ans;}
static void Main() { int n = 7; List res = FibonacciNumbers(n); foreach (int num in res) { Console.Write(num + " "); } } }
JavaScript
function fibonacciNumbers(n) { let ans = []; let f1 = 0, f2 = 1; ans.push(f1);
for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
ans.push(f2);
let next = f1 + f2;
f1 = f2;
f2 = next;
}
return ans;}
// Driver Code let n = 7; let res = fibonacciNumbers(n); console.log(res.join(' '));
`
**Time Complexity: O(n)
**Auxiliary Space: O(1)
