Python | Build a REST API using Flask (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 25 Feb, 2022
Prerequisite: Introduction to Rest APIREST stands for REpresentational State Transfer and is an architectural style used in modern web development. It defines a set or rules/constraints for a web application to send and receive data. In this article, we will build a REST API in Python using the Flask framework. Flask is a popular micro framework for building web applications. Since it is a micro-framework, it is very easy to use and lacks most of the advanced functionality which is found in a full-fledged framework. Therefore, building a REST API in Flask is very simple. There are two ways of creating a REST API in Flask:
- Using Flask without any external libraries
- Using flask_restful library
Libraries required:
flask_restful can be installed via the pip command:
sudo pip3 install flask-restful Method 1: using only Flask
Here, there are two functions: One function to just return or print the data sent through GET or POST and another function to calculate the square of a number sent through GET request and print it.
python3 1== `
Using flask to make an api
import necessary libraries and functions
from flask import Flask, jsonify, request
creating a Flask app
app = Flask(name)
on the terminal type: curl http://127.0.0.1:5000/
returns hello world when we use GET.
returns the data that we send when we use POST.
@app.route('/', methods = ['GET', 'POST']) def home(): if(request.method == 'GET'):
data = "hello world"
return jsonify({'data': data})A simple function to calculate the square of a number
the number to be squared is sent in the URL when we use GET
on the terminal type: curl http://127.0.0.1:5000 / home / 10
this returns 100 (square of 10)
@app.route('/home/int:num', methods = ['GET']) def disp(num):
return jsonify({'data': num**2})driver function
if name == 'main':
app.run(debug = True)`
Output: 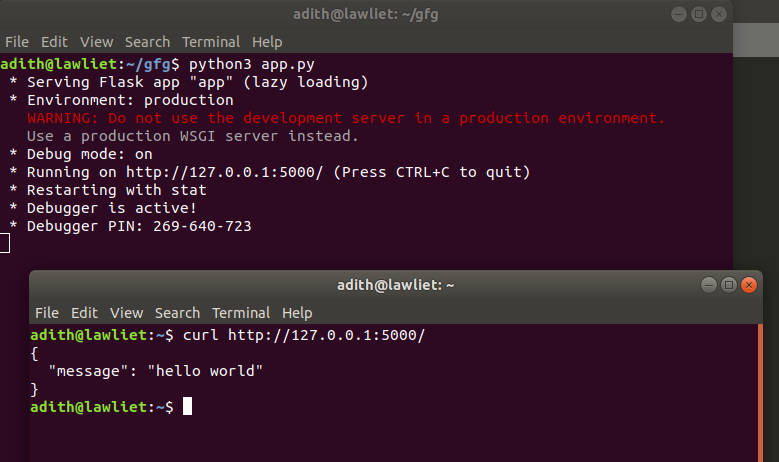 Executing the square function:
Executing the square function: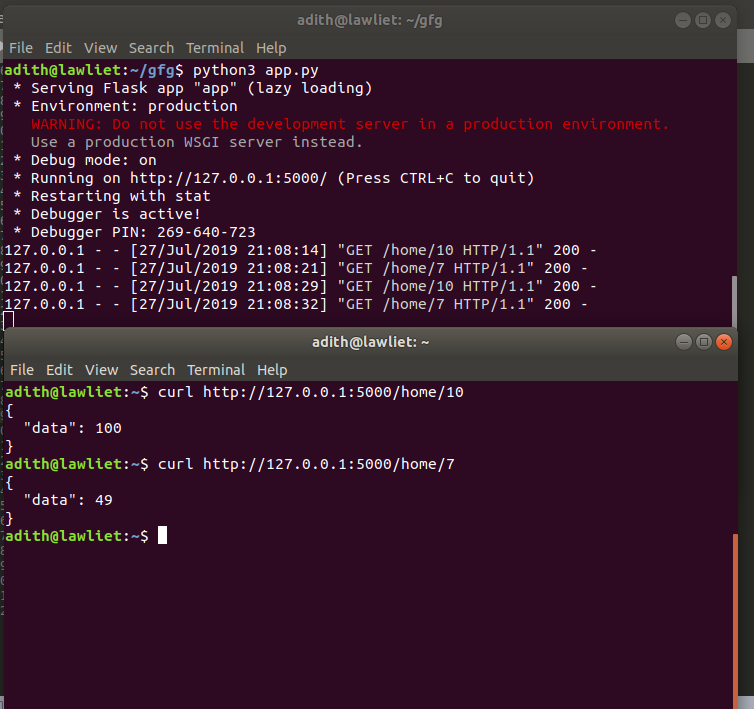
Method 2: Using flask-restful
Flask Restful is an extension for Flask that adds support for building REST APIs in Python using Flask as the back-end. It encourages best practices and is very easy to set up. Flask restful is very easy to pick up if you're already familiar with flask. In flask_restful, the main building block is a resource. Each resource can have several methods associated with it such as GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc. for example, there could be a resource that calculates the square of a number whenever a get request is sent to it. Each resource is a class that inherits from the Resource class of flask_restful. Once the resource is created and defined, we can add our custom resource to the api and specify a URL path for that corresponding resource.
python3 1== `
using flask_restful
from flask import Flask, jsonify, request from flask_restful import Resource, Api
creating the flask app
app = Flask(name)
creating an API object
api = Api(app)
making a class for a particular resource
the get, post methods correspond to get and post requests
they are automatically mapped by flask_restful.
other methods include put, delete, etc.
class Hello(Resource):
# corresponds to the GET request.
# this function is called whenever there
# is a GET request for this resource
def get(self):
return jsonify({'message': 'hello world'})
# Corresponds to POST request
def post(self):
data = request.get_json() # status code
return jsonify({'data': data}), 201another resource to calculate the square of a number
class Square(Resource):
def get(self, num):
return jsonify({'square': num**2})adding the defined resources along with their corresponding urls
api.add_resource(Hello, '/') api.add_resource(Square, '/square/int:num')
driver function
if name == 'main':
app.run(debug = True)`
Output: 