Python def Keyword (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 27 Dec, 2024
Python def keyword is used to define a function, it is placed before a function name that is provided by the user to create a user-defined function. In Python, a function is a logical unit of code containing a sequence of statements indented under a name given using the “def” keyword. In Python def keyword is the most used keyword.
**Example:
Python `
defining function
def func(): print("Hello")
calling function
func()
`
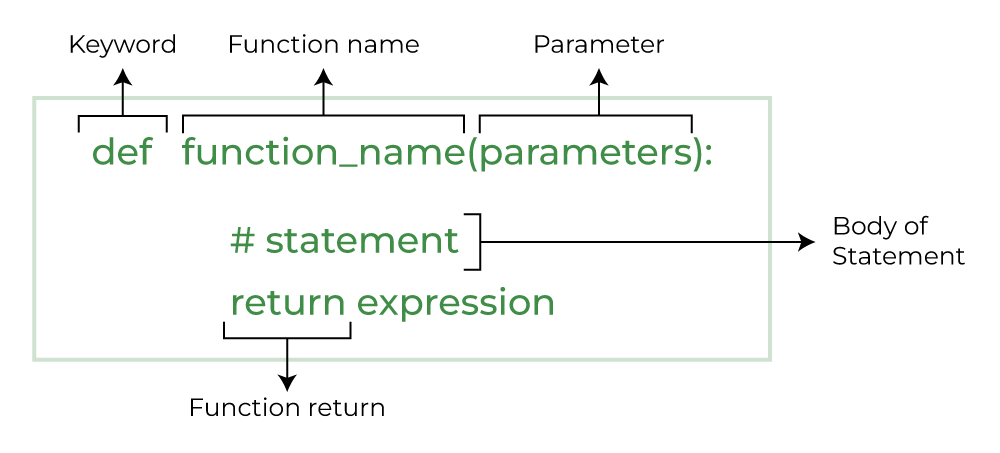
Let’s explore python def keyword in detail:
Table of Content
- Python def Syntax
- Passing Function as an Argument
- Python def keyword example with *args
- Python def keyword example with **kwargs
- Python def keyword example with the class
**Python def Syntax
**def function_name:
function definition statements…
**Use of def keyword
- In the case of classes, the def keyword is used for defining the methods of a class.
- def keyword is also required to define the special member function of a class like __init__().
The possible practical application is that it provides the feature of code reusability rather than writing the piece of code again and again we can define a function and write the code inside the function with the help of the **def keyword. It will be more clear in the illustrated example given below. There can possibly be many applications of def depending upon the use cases.
Example 1: Create function to find the subtraction of two Numbers
In this example, we have created a user-defined function using the def keyword. Function name is **subNumbers() which calculates the differences betweentwo numbers.
Python `
Python3 code to demonstrate
def keyword
function for subtraction of 2 numbers.
def subNumbers(x, y): return (x-y)
main code
a = 90 b = 50
finding subtraction
res = subNumbers(a, b)
print statement
print("subtraction of ", a, " and ", b, " is ", res)
`
Output
subtraction of 90 and 50 is 40
Example 2: Create function with the first 10 prime numbers
In this example, we have created a user-defined function using the def keyword. The program defines a function called **fun() using the def keyword. The function takes a single parameter n, which specifies the number of prime numbers to be printed.
Python `
Python program to print first 10 prime numbers
A function name prime is defined
using def
def fun(n): x = 2 count = 0 while count < n: for d in range(2, int(x ** 0.5) + 1): # check divisibility only up to sqrt(x) if x % d == 0: break # if divisible, it's not prime, so break the loop else: print(x) # prime number count += 1 x += 1
Driver Code
n = 10
fun(n)
`
Output
2 3 5 7 11 13 17 19 23 29
Passing Function as an Argument
In Python, we can pass functions as arguments to other functions. We can pass a function by simply referencing its name without parentheses. The passed function can then be called inside the receiving function.
**Example:
Python `
A function that takes another function as an argument
def fun(func, arg): return func(arg)
def square(x): return x ** 2
Calling fun and passing square function as an argument
res = fun(square, 5) print(res)
`
**Explanation:
- This function takes two parameters: func (a function) and x (a value). It applies the function func to the value x and returns the result.
- We call fun and pass the square function (without parentheses) and the number 5. The square function is applied to 5, and the result is printed.
Python def keyword example with *args
In Python, *args is used to pass a variable number of arguments to a function. The * allows a function to accept any number of positional arguments. This is useful when we are not sure how many arguments will be passed to the function.
**Example:
Python `
def fun(*args): for arg in args: print(arg)
Calling the function with multiple arguments
fun(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
`
Python def keyword example with **kwargs
In Python, **kwargs is used to pass a variable number of keyword arguments to a function. The ** syntax collects the keyword arguments into a dictionary, where the keys are the argument names and the values are the corresponding argument values. This allows the function to accept any number of named (keyword) arguments.
Python `
def fun(**kwargs): for k, val in kwargs.items(): print(f"{k}: {val}")
Calling the function with keyword arguments
fun(name="Alice", age=30, city="New York")
`
Output
name: Alice age: 30 city: New York
**Explanation:
- **kwargs collects the keyword arguments passed to example_function into a dictionary kwargs.
- Inside the function, you can iterate over the dictionary and print the key-value pairs.
Python def keyword example with the class
In Python, the def keyword is used to define functions and it can also be used to define methods inside a class. A method is a function that is associated with an object and is called using the instance of the class.
When using def inside a class, we can define methods that can access and modify the attributes of the class and its instances.
Python `
class Person: # Constructor to initialize the person's name and age def init(self, name, age): self.name = name # Set the name attribute self.age = age # Set the age attribute
# Method to print a greeting message
def greet(self):
print(f"Name - {self.name} and Age - {self.age}.")Create an instance of the Person class
p1 = Person("Alice", 30)
Call the greet method to display the greeting message
p1.greet()
`
Output
Name - Alice and Age - 30.