Python If Else Statements Conditional Statements (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 08 Mar, 2025
In Python, If-Else isa fundamental conditional statement used for decision-making in programming. If...Else statement allows to execution of specific blocks of code depending on the condition is True or False.
if Statement
**if statement is the most simple decision-making statement. If the condition evaluates to True, the block of code inside the if statement is executed.

If Statement
**Example of If Statement:
Python `
i = 10
Checking if i is greater than 15
if (i > 15): print("10 is less than 15")
print("I am Not in if")
`
if....else Statement
**if...else statement is a control statement that helps in decision-making based on specific conditions. When the if condition is False. If the condition in the if statement is not true, the else block will be executed.
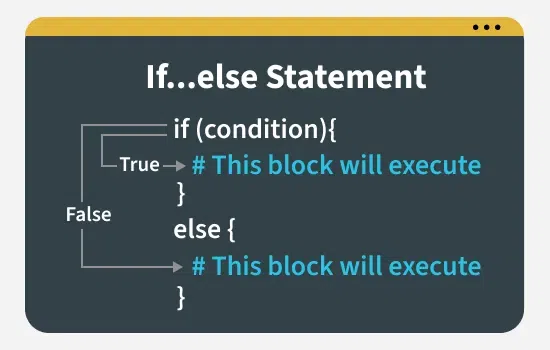
If....else Statement
Let's look at some examples of if-else statements.
Simple if-else
Python `
i = 20
Checking if i is greater than 0
if (i > 0): print("i is positive") else: print("i is 0 or Negative")
`
If Else in One-line
If we need to execute a single statement inside the **if or else block then one-line shorthand can be used.
Python `
a = -2
Ternary conditional to check if number is positive or negative
res = "Positive" if a >= 0 else "Negative" print(res)
`
Logical Operators with If..Else
We can combine multiple conditions using logical operators such as **and, **or, and **not.
Python `
age = 25 exp = 10
Using '>' operator & 'and' with if-else
if age > 23 and exp > 8: print("Eligible.") else: print("Not eligible.")
`
Nested If Else Statement
**Nested if...else statement occurs when if...else structure is placed inside another **if or **else block. Nested If..else allows the execution of specific code blocks based on a series of conditional checks.
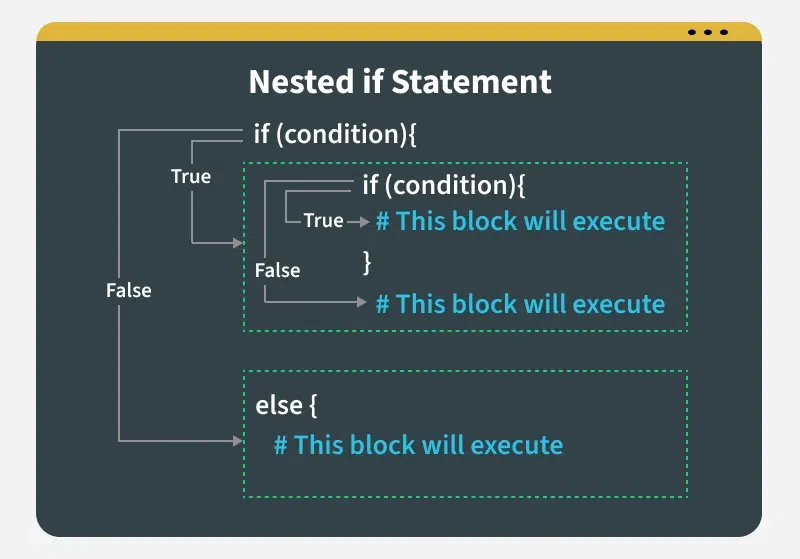
Nested if Statement
**Example of Nested If Else Statement:
Python `
i = 10 if (i == 10):
# First if statement
if (i < 15):
print("i is smaller than 15")
# Nested - if statement
# Will only be executed if statement above
# it is true
if (i < 12):
print("i is smaller than 12 too")
else:
print("i is greater than 15")
else: print("i is not equal to 10")
`
if…elif…else Statement
if-elif-else statement in Python is used for multi-way decision-making. This allows us to check multiple conditions sequentially and execute a specific block of code when a condition is True. If none of the conditions are true, the **else block is executed.
**Example:
Python `
i = 25
Checking if i is equal to 10
if (i == 10): print("i is 10")
Checking if i is equal to 15
elif (i == 15): print("i is 15")
Checking if i is equal to 20
elif (i == 20): print("i is 20")
If none of the above conditions are true
else: print("i is not present")
`
**Similar Reads:
