Python Matrix (original) (raw)
A matrix is a way to organize numbers in a rectangular grid made up of rows and columns. We can assume it like a table, where:
- Rows go across (left to right)
- Columns go down (top to bottom)
The size of a matrix is defined by the number of rows (m) and columns (n). If a matrix has 3 rows and 4 columns, it’s called a 3×4 matrix.
Matrices are used in:
- Solving linear equations
- Image transformations (rotations, scaling)
- Machine learning algorithms
- Data representation
In this tutorial, we’ll explore different ways to create and work with matrices in Python, including using the NumPy library for matrix operations.
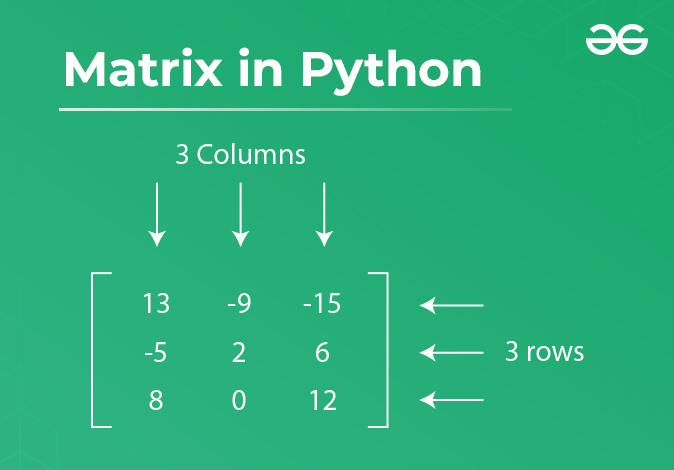
Visual representation of a matrix
Creating a simple matrix using Python
Method 1: Creating a matrix with a List of list
A Matrix is fundamentally a 2D list therefore we can create a Matrix by creating a 2D list (list of lists).
Python `
mat = [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]]
print("Matrix =", mat)
`
Output
Matrix = [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]]
Method 2: Take Matrix input from user in Python
In this example we are going to take user inputs for rows and columns for the matrix and then print the complete matrix.
Python `
rows = int(input("rows: ")) col = int(input("columns: "))
matrix = [] print("entries row-wise:")
for i in range(rows):
row = []
for j in range(col):
row.append(int(input())) # user input for rows
matrix.append(row) # adding rows to the matrix
print("\n2D matrix is:")
for i in range(rows): for j in range(col): print(matrix[i][j], end=" ") print()
`
**Output:
Enter the number of rows: 2
Enter the number of columns: 2
Enter the entries row-wise:
1
2
3
4
The 2D matrix is:
1 2
3 4
Method 3: Create a matrix using list comprehension
List comprehension is an elegant way to define and create a list in Python, we are using the range function for printing 4 rows and 4 columns.
Python `
matrix = [[col for col in range(4)] for row in range(4)] print(matrix)
`
Output
[[0, 1, 2, 3], [0, 1, 2, 3], [0, 1, 2, 3], [0, 1, 2, 3]]
Explanation:
- Outer loop ****(for row in range(4))** runs 4 times to create 4 rows.
- Inner loop ****(for col in range(4))** fills each row with values 0 to 3.
Assigning Value in a matrix
Method 1: Assign value to an individual cell in Matrix
Here we are replacing and assigning value to an individual cell (1 row and 1 column = 11) in the Matrix.
Python `
x = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]] x[1][1] = 11
print(x)
`
Output
[[1, 2, 3], [4, 11, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
Method 2: Using Negative Indexing
We are assigning a value to an individual cell using negative indexing in this example (-2 row and -1 column = 21) in the Matrix.
Python `
x = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
x[-2][-1] = 21 # row = -2 , column = -1 print(x)
`
**Output:
[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, **21], [7, 8, 9]]
Accessing Value in a matrix
Method 1: Direct Indexing
We can access elements of a Matrix by using its row and column index.
Python `
print("Element at (1,3):", x[0][2]) print("Element at (3,3):", x[2][2])
`
**Output:
Element at (1,3): 3
Element at (3,3): 9
Method 2: Negative Indexing
Here, we are accessing elements of a Matrix by passing its row and column on negative indexing.
Python `
print(x[-1][-2])
`
**Output:
8
Mathematical Operations with Matrix in Python
Example 1: Addition Using Loops
Let’s see how we can add two matrices using for-loop in Python.
Python `
x = [[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6],[7, 8, 9]] y = [[9, 8, 7],[6, 5, 4],[3, 2, 1]] res = [[0]*3 for _ in range(3)]
for i in range(len(x)): for j in range(len(x[0])): res[i][j] = x[i][j] + y[i][j]
for r in res: print(r)
`
**Output:
[10, 10, 10]
[10, 10, 10]
[10, 10, 10]
Example 2: Addition & Subtraction with List Comprehension
Performing the Basic addition and subtraction using list comprehension.
Python `
x = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
y = [[9, 8, 7], [6, 5, 4], [3, 2, 1]]
Matrix addition
add_res = [[x[i][j] + y[i][j] for j in range(len(x[0]))] for i in range(len(x))]
Matrix subtraction
sub_res = [[x[i][j] - y[i][j] for j in range(len(x[0]))] for i in range(len(x))]
print("Matrix Addition:") for row in add_res: print(row)
print("\nMatrix Subtraction:") for row in sub_res: print(row)
`
**Output:
Matrix Addition
[10, 10, 10]
[10, 10, 10]
[10, 10, 10]
Matrix Subtraction
[-8, -6, -4]
[-2, 0, 2]
[4, 6, 8]
Example 3: Python program to multiply and divide two matrices
Performing the basic multiplication and division of two matrices using Python loop.
Python `
x = [[2, 4, 6], [8, 10, 12], [14, 16, 18]]
y = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
Element-wise multiplication
mult_res = [[x[i][j] * y[i][j] for j in range(3)] for i in range(3)]
Element-wise integer division
div_res = [[x[i][j] // y[i][j] for j in range(3)] for i in range(3)]
print("Matrix Multiplication:") for row in mult_res: print(row)
print("\nMatrix Division:") for row in div_res: print(row)
`
**Output:
Matrix Multiplication:
[2, 8, 18]
[32, 50, 72]
[98, 128, 162]
Matrix Division:
[2, 2, 2]
[2, 2, 2]
[2, 2, 2]
Transpose of a Matrix
Example 1: Using loop
Transpose of a matrix is obtained by changing rows to columns and columns to rows. In other words, transpose of A[][] is obtained by changing A[i][j] to A[j][i].
Python `
x = [[9, 8, 7], [6, 5, 4], [3, 2, 1]] transpose = [[0]*3 for _ in range(3)]
for i in range(len(x)): for j in range(len(x[0])): transpose[j][i] = x[i][j]
for r in transpose: print(r)
`
Output
[9, 6, 3] [8, 5, 2] [7, 4, 1]
Example 2: Using List Comprehension
Here’s how to Transpose a matrix using list comprehension.
Python `
transpose = [[x[j][i] for j in range(len(x))] for i in range(len(x[0]))] for row in transpose: print(row)
`
**Output:
[9, 6, 3]
[8, 5, 2]
[7, 4, 1]
NumPy Matrix Operations
Creating a Matrix with Random Values
Here we are creating a Numpy array using numpy.random and a random module.
Python `
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.randint(10, size=(3, 3)) print(arr)
`
**Output:
[[2 7 5]
[8 5 1]
[8 4 6]]
**Explanation:
- The **numpy.random module is used to generate **random numbers.
- **np.random.randint(10, size=(3, 3)) creates a 3×3 matrix with random integers from 0 to 9.
Basic Math Operations with NumPy
Here we are covering different mathematical operations such as **addition, subtraction, **multiplication, and **division using **Numpy.
Python `
import numpy as np
x = np.array([[1, 2], [4, 5]]) y = np.array([[7, 8], [9, 10]])
print("Addition:\n", np.add(x, y)) print("Subtraction:\n", np.subtract(x, y)) print("Multiplication:\n", np.multiply(x, y)) print("Division:\n", np.divide(x, y))
`
Output
Addition: [[ 8 10] [13 15]] Subtraction: [[-6 -6] [-5 -5]] Multiplication: [[ 7 16] [36 50]] Division: [[0.14285714 0.25 ] [0.44444444 0.5 ]]
Dot and cross product with Matrix
In this example, we are going to discuss how we can calculate the dot and the cross products of two matrices using NumPy, it provides built in functions to calculate them. First, let’s discsuss what are dot and cross products in short:
- **Dot Product: Calculates the sum of the products of corresponding elements, often used to find projections or perform matrix multiplication.
- **Cross Product: Produces a vector perpendicular to two 3D vectors, useful in physics for torque, angular momentum, etc. Python `
import numpy as np
x = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]] y = [[9, 8, 7], [6, 5, 4], [3, 2, 1]]
print("Dot Product:\n", np.dot(x, y)) print("Cross Product:\n", np.cross(x, y))
`
Output
Dot Product: [[ 30 24 18] [ 84 69 54] [138 114 90]] Cross Product: [[-10 20 -10] [-10 20 -10] [-10 20 -10]]
Transpose Using NumPy
To perform transpose operation in matrix we can use the numpy.transpose() method.
Python `
import numpy as np
matrix = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]] print(np.transpose(matrix))
`
Output
[[1 4] [2 5] [3 6]]
Creating Empty Matrices
Initializing an empty array, using the np.zeros().
Python `
import numpy as np
a = np.zeros((2, 2), dtype=int) print("2x2 Matrix:\n", a)
b = np.zeros((3, 3)) print("3x3 Matrix:\n", b)
`
Output
2x2 Matrix: [[0 0] [0 0]] 3x3 Matrix: [[0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0.]]
Slicing in Matrix using Numpy
Slicing is the process of choosing specific rows and columns from a matrix and then creating a new matrix by removing all of the non-selected elements.
Python `
import numpy as np
x = np.array([[6, 8, 10], [9, -12, 15], [12, 16, 20], [15, -20, 25]])
print("Full Matrix:\n", x) print("Third Row, Second Column:", x[2:3, 1]) print("Third Row, Third Column:", x[2:3, 2])
`
Output
Full Matrix: [[ 6 8 10] [ 9 -12 15] [ 12 16 20] [ 15 -20 25]] Third Row, Second Column: [16] Third Row, Third Column: [20]
Deleting Rows with NumPy
Here, we are trying to delete rows using the np.delete() function. In the code, we first tried to delete the 0th row, then we tried to delete the 2nd row, and then the 3rd row.
Python `
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[6, 8, 10], [9, -12, 15], [12, 16, 20], [15, -20, 25]])
print("Delete 0th Row:\n", np.delete(a, 0, axis=0)) print("Delete 1st Row:\n", np.delete(a, 1, axis=0))
`
Output
Delete 0th Row: [[ 9 -12 15] [ 12 16 20] [ 15 -20 25]] Delete 1st Row: [[ 6 8 10] [ 12 16 20] [ 15 -20 25]]
Add Rows or Columns to a NumPy Array
We can easily add a new row or column to an existing NumPy array using stacking functions like np.hstack() (horizontal stack) and np.vstack() (vertical stack).
Here’s how to add a column to an existing 2D array:
Python `
import numpy as np
x = np.array([[6, 8, 10], [9, -12, 15], [15, -20, 25]])
new column to be added
col = np.array([1, 2, 3])
add the column (after reshaping it into a column vector)
res = np.hstack((x, np.atleast_2d(col).T))
print("Resultant Array:\n", res)
`
Output
Resultant Array: [[ 6 8 10 1] [ 9 -12 15 2] [ 15 -20 25 3]]