Python Operators (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 07 Mar, 2025
In Python programming, Operators in general are used to perform operations on values and variables. These are standard symbols used for logical and arithmetic operations. In this article, we will look into different types of **Python operators.
- **OPERATORS: These are the special symbols. Eg- + , * , /, etc.
- **OPERAND: It is the value on which the operator is applied.
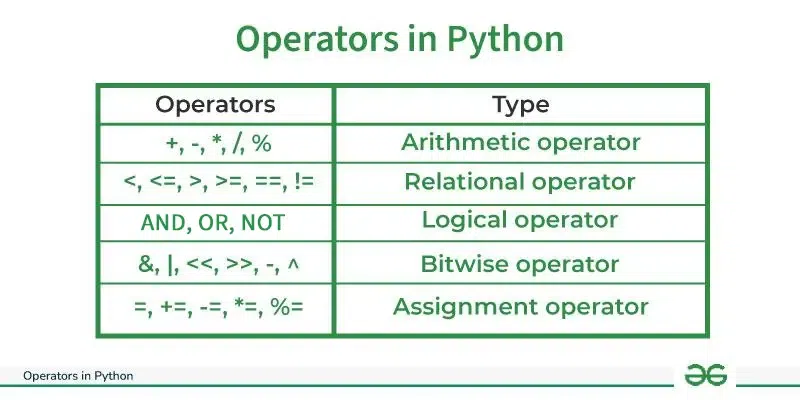
Types of Operators in Python
- Arithmetic Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Identity Operators and Membership Operators
**Arithmetic Operators in Python
Python Arithmetic operators are used to perform basic mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication and **division.
In Python 3.x the result of division is a floating-point while in Python 2.x division of 2 integers was an integer. To obtain an integer result in Python 3.x floored (// integer) is used.
Example of Arithmetic Operators in Python:
Python `
Variables
a = 15 b = 4
Addition
print("Addition:", a + b)
Subtraction
print("Subtraction:", a - b)
Multiplication
print("Multiplication:", a * b)
Division
print("Division:", a / b)
Floor Division
print("Floor Division:", a // b)
Modulus
print("Modulus:", a % b)
Exponentiation
print("Exponentiation:", a ** b)
`
Output
Addition: 19 Subtraction: 11 Multiplication: 60 Division: 3.75 Floor Division: 3 Modulus: 3 Exponentiation: 50625
**Note: Refer to Differences between / and // for some interesting facts about these two Python operators.
Comparison of Python Operators
In Python Comparison of Relational operators compares the values. It either returns **True or **False according to the condition.
**Example of Comparison Operators in Python
Let’s see an example of Comparison Operators in Python.
Python `
a = 13 b = 33
print(a > b) print(a < b) print(a == b) print(a != b) print(a >= b) print(a <= b)
`
Output
False True False True False True
**Logical Operators in Python
Python Logical operators perform **Logical AND, **Logical OR and Logical NOT operations. It is used to combine conditional statements.
The precedence of Logical Operators in Python is as follows:
- Logical not
- logical and
- logical or
**Example of Logical Operators in Python:
Python `
a = True b = False print(a and b) print(a or b) print(not a
`
**Bitwise Operators in Python
Python Bitwise operators act on bits and perform bit-by-bit operations. These are used to operate on binary numbers.
Bitwise Operators in Python are as follows:
- Bitwise NOT
- Bitwise Shift
- Bitwise AND
- Bitwise XOR
- Bitwise OR
**Example of Bitwise Operators in Python:
Python `
a = 10 b = 4
print(a & b) print(a | b) print(~a) print(a ^ b) print(a >> 2) print(a << 2)
`
**Assignment Operators in Python
Python Assignment operators are used to assign values to the variables. This operator is used to assign the value of the right side of the expression to the left side operand.
**Example of Assignment Operators in Python:
Python `
a = 10 b = a print(b) b += a print(b) b -= a print(b) b *= a print(b) b <<= a print(b)
`
Output
10 20 10 100 102400
**Identity Operators in Python
In Python, **is and **is not are the identity operators both are used to check if two values are located on the same part of the memory. Two variables that are equal do not imply that they are identical.
**is True if the operands are identical
**is not True if the operands are not identical
**Example of Identity Operators in Python:
Python `
a = 10 b = 20 c = a
print(a is not b) print(a is c)
`
**Membership Operators in Python
In Python, **in and **not in are the membership operators that are used to test whether a value or variable is in a sequence.
**in True if value is found in the sequence
**not in True if value is not found in the sequence
**Examples of Membership Operators in Python:
Python `
x = 24 y = 20 list = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
if (x not in list): print("x is NOT present in given list") else: print("x is present in given list")
if (y in list): print("y is present in given list") else: print("y is NOT present in given list")
`
Output
x is NOT present in given list y is present in given list
**Ternary Operator in Python
in Python, Ternary operators also known as conditional expressions are operators that evaluate something based on a condition being true or false. It was added to Python in version 2.5.
It simply allows testing a condition in a **single line replacing the multiline if-else making the code compact.
**Syntax : [on_true] if [expression] else [on_false]
Examples of Ternary Operator in Python:
Python `
a, b = 10, 20 min = a if a < b else b
print(min)
`
Precedence and Associativity of Operators in Python
In Python, Operator precedence and associativity determine the priorities of the operator.
**Operator Precedence in Python
This is used in an expression with more than one operator with different precedence to determine which operation to perform first.
**Example:
Python `
expr = 10 + 20 * 30 print(expr) name = "Alex" age = 0
if name == "Alex" or name == "John" and age >= 2: print("Hello! Welcome.") else: print("Good Bye!!")
`
Output
610 Hello! Welcome.
**Operator Associativity in Python
If an expression contains two or more operators with the same precedence then Operator Associativity is used to determine. It can either be Left to Right or from Right to Left.
**Example:
Python `
print(100 / 10 * 10) print(5 - 2 + 3) print(5 - (2 + 3)) print(2 ** 3 ** 2)
`
To try your knowledge of Python Operators, you can take out the quiz on Operators in Python.
Python Operator Exercise Questions
Below are two Exercise Questions on Python Operators. We have covered arithmetic operators and comparison operators in these exercise questions. For more exercises on Python Operators visit the page mentioned below.
**Q1. Code to implement basic arithmetic operations on integers
Python `
num1 = 5 num2 = 2
sum = num1 + num2 difference = num1 - num2 product = num1 * num2 quotient = num1 / num2 remainder = num1 % num2
print("Sum:", sum) print("Difference:", difference) print("Product:", product) print("Quotient:", quotient) print("Remainder:", remainder)
`
Output
Sum: 7 Difference: 3 Product: 10 Quotient: 2.5 Remainder: 1
**Q2. Code to implement Comparison operations on integers
Python `
num1 = 30 num2 = 35
if num1 > num2: print("The first number is greater.") elif num1 < num2: print("The second number is greater.") else: print("The numbers are equal.")
`
Output
The second number is greater.
Quiz:
**Related Posts:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Identity Operators and Membership Operators
- Modulo Operator
- Division Operator
- Ternary Operator
- Operator Overloading
- OR operator
- Why are there no ++ and – Operator in Python
- How to do Math in Python 3 with Operators
- Difference between == and is Operator in Python
**Recommended Problems:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- The Modulo Task
- Last Digit of a number
- Sum of N Numbers
- GCD
- LCM
- Armstrong Number
- Count Set Bits
- Evaluate Formulae
- AP Term
- Geometric Progression
- Celsius to Fahrenheit Conversion
- Sum of AP series
- LCM And GCD
- Factorial of Large number
- Count trailing zeroes
- Last Non-Zero digit
**Explore more Exercises: **Practice Exercise on Operators in Python