Pandas DataFrame mean() Method (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 17 May, 2024
Python is a great language for doing data analysis, primarily because of the fantastic ecosystem of data-centric Python packages. **Pandasis one of those packages and makes importing and analyzing data much easier.
Pandas DataFrame mean()
Pandas dataframe.mean() function returns the mean of the values for the requested axis. If the method is applied on a pandas series object, then the method returns a scalar value which is the mean value of all the observations in the Pandas Dataframe. If the method is applied on a Pandas Dataframe object, then the method returns a Pandas series object which contains the mean of the values over the specified axis.
**Syntax: DataFrame.mean(axis=0, skipna=True, level=None, numeric_only=False, **kwargs)
**Parameters :
- **axis : _{index (0), columns (1)}
- **skipna : Exclude NA/null values when computing the result
- **level : If the axis is a MultiIndex (hierarchical), count along a particular level, collapsing into a Series
- **numeric_only : Include only float, int, boolean columns. If None, will attempt to use everything, then use only numeric data. Not implemented for Series.
**Returns : mean : Series or DataFrame (if level specified)
Pandas DataFrame.mean() Examples
**Example 1:
Use mean() function to find the mean of all the observations over the index axis.
Python `
importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
Creating the dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[12, 4, 5, 44, 1], "B":[5, 2, 54, 3, 2], "C":[20, 16, 7, 3, 8], "D":[14, 3, 17, 2, 6]})
Print the dataframe
df
`
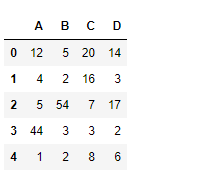
Let’s use the Dataframe.mean() function to find the mean over the index axis.
Python `
Even if we do not specify axis = 0,
the method will return the mean over
the index axis by default
df.mean(axis = 0)
`
**Output:

**Example 2:
Use mean() function on a Dataframe that has None values. Also, find the mean over the column axis.
Python `
importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
Creating the dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[12, 4, 5, None, 1], "B":[7, 2, 54, 3, None], "C":[20, 16, 11, 3, 8], "D":[14, 3, None, 2, 6]})
skip the Na values while finding the mean
df.mean(axis = 1, skipna = True)
`
**Output:
