Python | Pandas DataFrame.set_index() (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 04 Dec, 2024
**Pandas DataFrame.set_index() method sets one or more columns as the index of a DataFrame. It can accept single or multiple column names and is useful for modifying or adding new indices to your DataFrame. By doing so, you can enhance data retrieval, indexing, and merging tasks.
**Syntax: DataFrame.set_index(keys, drop=True, append=False, inplace=False, verify_integrity=False)
**Parameters:
- **keys: A single column name or a list of column names to set as the index.
- **drop: A Boolean value (default=True). If True, the specified column(s) will be removed from the DataFrame.
- **append: A Boolean value (default=False). If True, the column(s) will be added to the existing index rather than replacing it.
- **inplace: A Boolean value (default=False). If True, the changes are applied directly to the DataFrame without returning a new one.
- **verify_integrity: A Boolean value (default=False). If True, checks whether the new index contains duplicates.
Examples of Using Pandas DataFrame.set_index()
1. Set a Single Column as Index
This example demonstrates how to set the **First Name column as the index in a DataFrame.
**Dataset Link: Employee.csv
Python `
import pandas as pd
Load DataFrame from CSV
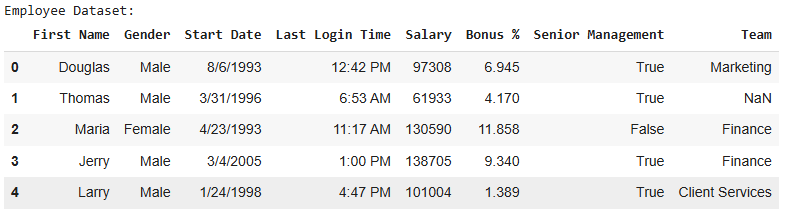
data = pd.read_csv("employees.csv") print("Employee Dataset:") display(data.head(5))
Set 'First Name' as the index column
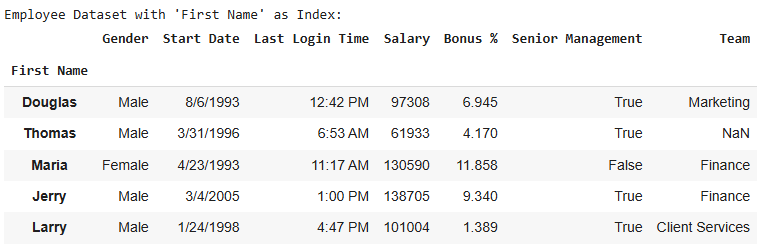
data.set_index("First Name", inplace=True) print("\nEmployee Dataset with 'First Name' as Index:") display(data.head(5))
`
**Output:
DataFrame uses a Default Integer Index
Index is replaced with the “First Name” column
Set Multiple Columns as Index (MultiIndex)
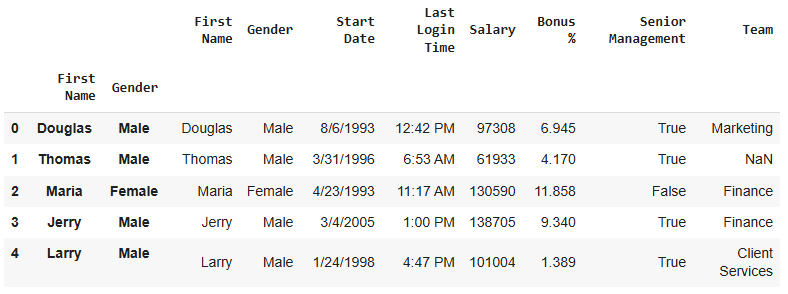
In this example, we set both First Name and Gender as the index columns using the **set_index() method with the append and drop parameters.
Python `
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_csv("employees.csv")
Set 'First Name' and 'Gender' as index columns
data.set_index(["First Name", "Gender"], inplace=True, append=True, drop=False) data.head()
`
**Output:
This results in a MultiIndex, with both “First Name” and “Gender” as part of the index.
3. Set a Float Column as Index
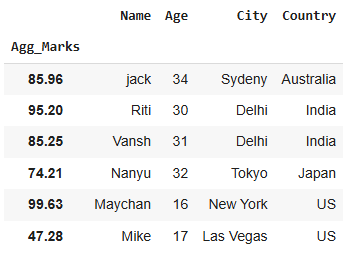
Here, we set the **Agg_Marks (a float column) as the index for a DataFrame containing student data.
Python `
import pandas as pd
students = [['jack', 34, 'Sydeny', 'Australia', 85.96], ['Riti', 30, 'Delhi', 'India', 95.20], ['Vansh', 31, 'Delhi', 'India', 85.25], ['Nanyu', 32, 'Tokyo', 'Japan', 74.21], ['Maychan', 16, 'New York', 'US', 99.63], ['Mike', 17, 'Las Vegas', 'US', 47.28]]
df = pd.DataFrame(students, columns=['Name', 'Age', 'City', 'Country', 'Agg_Marks'])
Set 'Agg_Marks' as the index
df.set_index('Agg_Marks', inplace=True) display(df)
`
**Output:
This will result in Agg_Marks being the index column, facilitating efficient lookups by student scores.
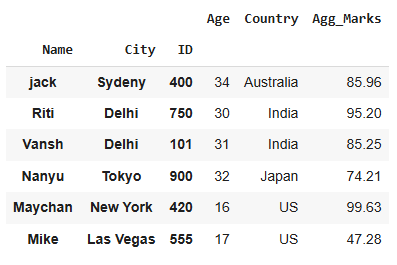
4. Set Multiple Columns as MultiIndex
This example demonstrates how to set Name, City, and ID as a multi-level index.
Python `
import pandas as pd
students = [['jack', 34, 'Sydeny', 'Australia', 85.96, 400], ['Riti', 30, 'Delhi', 'India', 95.20, 750], ['Vansh', 31, 'Delhi', 'India', 85.25, 101], ['Nanyu', 32, 'Tokyo', 'Japan', 74.21, 900], ['Maychan', 16, 'New York', 'US', 99.63, 420], ['Mike', 17, 'Las Vegas', 'US', 47.28, 555]]
df = pd.DataFrame(students, columns=['Name', 'Age', 'City', 'Country', 'Agg_Marks', 'ID'])
Set 'Name', 'City', and 'ID' as a MultiIndex
df.set_index(['Name', 'City', 'ID'], inplace=True) display(df)
`
**Output:
The resulting DataFrame will have a multi-level index, allowing for more complex data organization and retrieval.
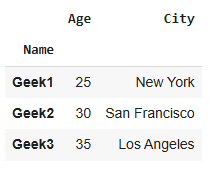
5. Set Index of Specific Column
In this example, the Name column is set as the index of a simple DataFrame.
Python `
import pandas as pd
data = {'Name': ['Geek1', 'Geek2', 'Geek3'], 'Age': [25, 30, 35], 'City': ['New York', 'San Francisco', 'Los Angeles']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
Set 'Name' column as index
df.set_index('Name', inplace=True) display(df)
`
**Output: