Python Program for Array Rotation (original) (raw)
Here we are going to see how we can rotate array with Python code.
Array Rotation:

Python Program for Array Rotation Example
Partitioning the sub arrays and reversing them
Approach:
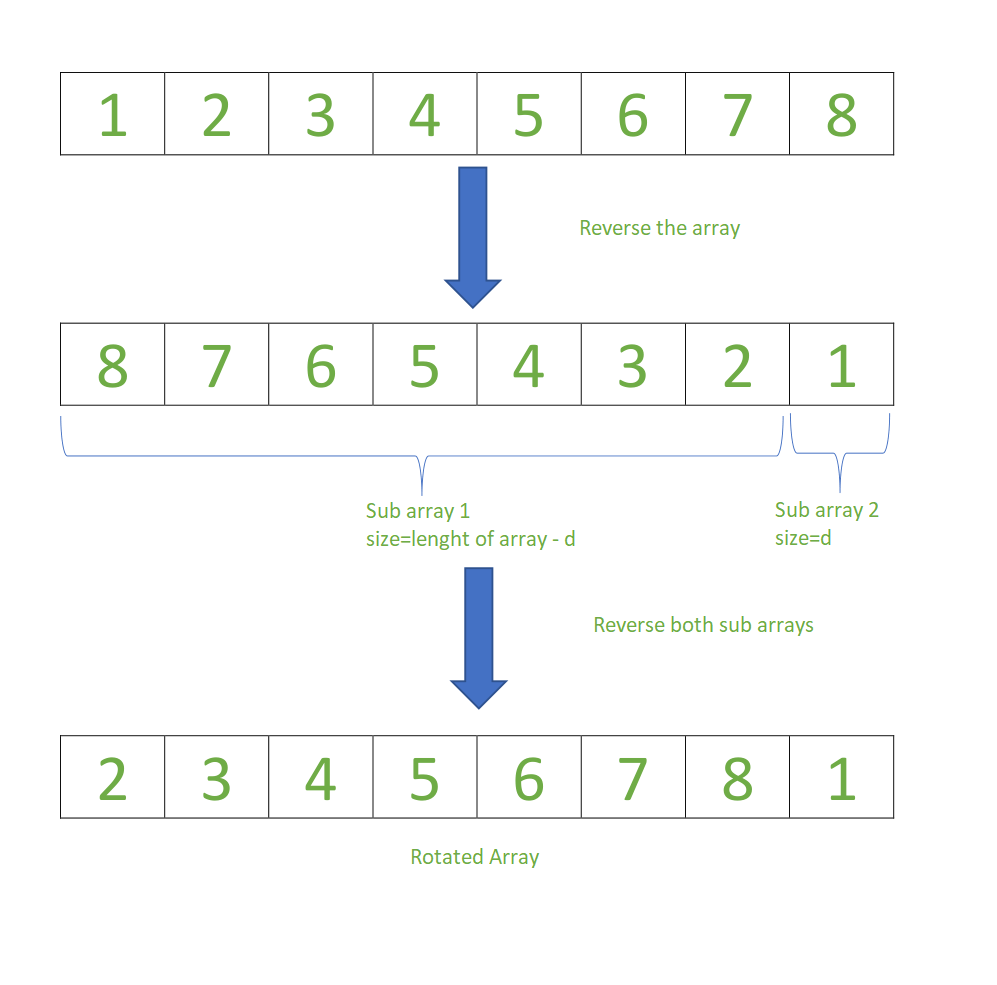
Input arr[] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], d = 1, size = 8
- Reverse the entire list by swapping first and last numbers
i.e start=0, end=size-1
- Partition the first subarray and reverse the first subarray, by swapping first and last numbers.
i.e start=0, end=size-d-1
- Partition the second subarray and reverse the second subarray, by swapping first and last numbers.
i.e start=size-d, end=size-1
Example:
Python3
def reverse(start, end, arr):
`` no_of_reverse = end - start + 1
`` count = 0
`` while ((no_of_reverse) / / 2 ! = count):
`` arr[start + count], arr[end - count] = arr[end - count], arr[start + count]
`` count + = 1
`` return arr
def left_rotate_array(arr, size, d):
`` start = 0
`` end = size - 1
`` arr = reverse(start, end, arr)
`` start = 0
`` end = size - d - 1
`` arr = reverse(start, end, arr)
`` start = size - d
`` end = size - 1
`` arr = reverse(start, end, arr)
`` return arr
arr = [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 ]
size = 8
d = 1
print ( 'Original array:' , arr)
if (d < = size):
`` print ( 'Rotated array: ' , left_rotate_array(arr, size, d))
else :
`` d = d % size
`` print ( 'Rotated array: ' , left_rotate_array(arr, size, d))
Output
Original array: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8] Rotated array: [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 1]
Time Complexity: O(log10(Half no of elements presents in the given array)).
Auxiliary Space: O(1).
Python Program for Array Rotation Using temp array
Write a function rotate(ar[], d, n) that rotates arr[] of size n by d elements.
Rotation of the above array by 2 will make array

Input arr[] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], d = 2, n =7
- Store d elements in a temp array temp[] = [1, 2]
- Shift rest of the arr[] arr[] = [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 6, 7]
- Store back the d elements arr[] = [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2]
Python3
def rotateArray(arr, n, d):
`` temp = []
`` i = 0
`` while (i < d):
`` temp.append(arr[i])
`` i = i + 1
`` i = 0
`` while (d < n):
`` arr[i] = arr[d]
`` i = i + 1
`` d = d + 1
`` arr[:] = arr[: i] + temp
`` return arr
arr = [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 ]
print ( "Array after left rotation is: " , end = ' ' )
print (rotateArray(arr, len (arr), 2 ))
Output
Array after left rotation is: [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2]
Time complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(d)
Python Program for Array Rotation Using Rotate one by one
leftRotate(arr[], d, n) start For i = 0 to i < d Left rotate all elements of arr[] by one end
To rotate by one, store arr[0] in a temporary variable temp, move arr[1] to arr[0], arr[2] to arr[1] …and finally temp to arr[n-1]
Let us take the same example arr[] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], d = 2
Rotate arr[] by one 2 times We get [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1] after first rotation and [ 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2] after second rotation.
Python3
def leftRotate(arr, d, n):
`` for i in range (d):
`` leftRotatebyOne(arr, n)
def leftRotatebyOne(arr, n):
`` temp = arr[ 0 ]
`` for i in range (n - 1 ):
`` arr[i] = arr[i + 1 ]
`` arr[n - 1 ] = temp
def printArray(arr,size):
`` for i in range (size):
`` print ( "%d" % arr[i],end = " " )
arr = [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 ]
leftRotate(arr, 2 , 7 )
printArray(arr, 7 )
Time complexity : O(n * d)
Auxiliary Space : O(1)
Python Program for Array Rotation Using 4 Juggling Algorithm
This is an extension of method 2. Instead of moving one by one, divide the array in different sets
where number of sets is equal to GCD of n and d and move the elements within sets.
If GCD is 1 as is for the above example array (n = 7 and d =2), then elements will be moved within one set only, we just start with temp = arr[0] and keep moving arr[I+d] to arr[I] and finally store temp at the right place.
Here is an example for n =12 and d = 3. GCD is 3 and
Let arr[] be {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}
a) Elements are first moved in first set – (See below diagram for this movement
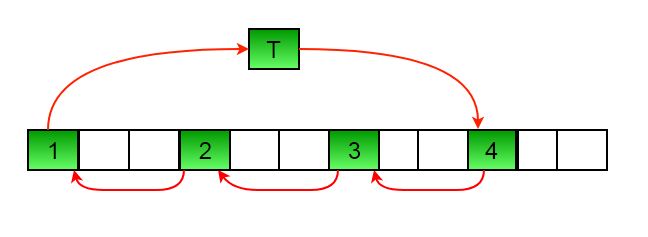
arr[] after this step --> {4 2 3 7 5 6 10 8 9 1 11 12}b) Then in second set. arr[] after this step --> {4 5 3 7 8 6 10 11 9 1 2 12}
c) Finally in third set. arr[] after this step --> {4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3}
Python3
def leftRotate(arr, d, n):
`` for i in range (gcd(d, n)):
`` temp = arr[i]
`` j = i
`` while 1 :
`` k = j + d
`` if k > = n:
`` k = k - n
`` if k = = i:
`` break
`` arr[j] = arr[k]
`` j = k
`` arr[j] = temp
def printArray(arr, size):
`` for i in range (size):
`` print ( "%d" % arr[i], end = " " )
def gcd(a, b):
`` if b = = 0 :
`` return a
`` else :
`` return gcd(b, a % b)
arr = [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 ]
leftRotate(arr, 2 , 7 )
printArray(arr, 7 )
Time complexity : O(n)
Auxiliary Space : O(1)
Another Approach : Using List slicing
Python3
def rotateList(arr,d,n):
`` arr[:] = arr[d:n] + arr[ 0 :d]
`` return arr
arr = [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 ]
print (arr)
print ( "Rotated list is" )
print (rotateList(arr, 2 , len (arr)))
Output
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] Rotated list is [3, 4, 5, 6, 1, 2]
If array needs to be rotated by more than its length then mod should be done.
For example: rotate arr[] of size n by d where d is greater than n. In this case d%n should be calculated and rotate by the result after mod.
Time complexity : O(n) where n is size of given array
Auxiliary Space : O(1)
Please refer complete article on Program for array rotation for more details!