Reverse a Linked List Python (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 21 Feb, 2025
Given pointer to the head node of a linked list, the task is to reverse the linked list. We need to reverse the list by changing links between nodes.
**Examples:
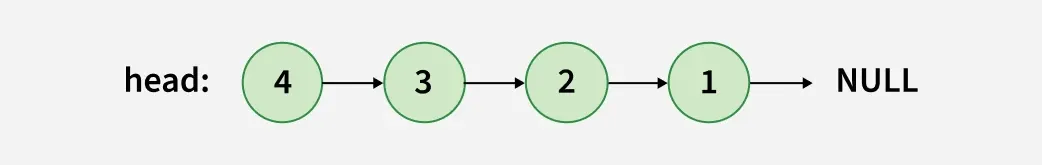
Input: head: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> NULL
Output: head: 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> NULL
Explanation: Reversed Linked List:
Reversed Linked List
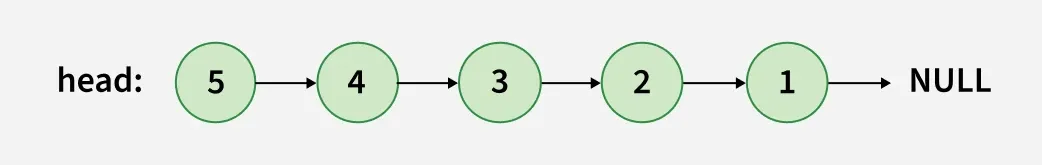
Input: head: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL
Output: head: 5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> NULL
Explanation: Reversed Linked List:
Reversed Linked List
Input : NULL
Output : NULLInput : 1->NULL
Output : 1->NULL
**1. Iterative Method
The idea is to reverse the links of all nodes using **three pointers:
- **prev: pointer to keep track of the previous node
- **curr: pointer to keep track of the current node
- **next: pointer to keep track of the next node
Starting from the first node, initialize **curr with the head of linked list and **next with the next node of curr. Update the next pointer of **curr with **prev. Finally, move the three pointer by updating **prev with **curr and **curr with **next.
Python `
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = Noneclass LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to reverse the linked list
def reverse(self):
prev = None
current = self.head
while(current is not None):
next = current.next
current.next = prev
prev = current
current = next
self.head = prev
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Utility function to print the LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print (temp.data,end=" ")
temp = temp.nextDriver program to test above functions
llist = LinkedList() llist.push(20) llist.push(4) llist.push(15) llist.push(85)
print ("Given Linked List") llist.printList() llist.reverse() print ("\nReversed Linked List") llist.printList()
`
Output
Given Linked List 85 15 4 20 Reversed Linked List 20 4 15 85
- **Time Complexity: O(N)
- **Auxiliary Space: O(1)
**2. A Simpler and Tail Recursive Method
The idea is to reach the last node of the linked list using recursion then start reversing the linked list from the last node.
Python `
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = Noneclass LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def reverseUtil(self, curr, prev):
# If last node mark it head
if curr.next is None:
self.head = curr
# Update next to prev node
curr.next = prev
return
# Save curr.next node for recursive call
next = curr.next
# And update next
curr.next = prev
self.reverseUtil(next, curr)
# This function mainly calls reverseUtil()
# with previous as None
def reverse(self):
if self.head is None:
return
self.reverseUtil(self.head, None)
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Utility function to print the LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print(temp.data,end=" ")
temp = temp.nextDriver program
llist = LinkedList() llist.push(8) llist.push(7) llist.push(6) llist.push(5) llist.push(4) llist.push(3) llist.push(2) llist.push(1)
print("Given linked list") llist.printList()
llist.reverse()
print("\nReverse linked list") llist.printList()
`
Output
Given linked list 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Reverse linked list 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
- **Time Complexity: O(N)
- **Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Please refer Reverse a linked list for more details!