Adam Optimizer in Tensorflow (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 04 Oct, 2025
Adam (Adaptive Moment Estimation) is an optimizer that combines the best features of two optimizers i.e Momentum and RMSprop. Adam is used in deep learning due to its efficiency and adaptive learning rate capabilities.
To use Adam in TensorFlow we can pass the string value 'adam' to the optimizer argument of the model.compile() function. Here's a simple example of how to do this:
model.compile(optimizer="adam")
This method passes the Adam optimizer object to the function with default values for parameters like betas and learning rate. Alternatively we can use the Adam class provided in tf.keras.optimizers. Below is the syntax for using the Adam class directly:
Adam(learning_rate, beta_1, beta_2, epsilon, amsgrad, name)
Here is a description of the parameters in the Adam optimizer:
- **learning_rate: The learning rate to use in the algorithm (default value: 0.001).
- **beta_1: The exponential decay rate for the 1st moment estimates (default value: 0.9).
- **beta_2: The exponential decay rate for the 2nd moment estimates (default value: 0.999).
- **epsilon: A small constant for numerical stability (default value: 1e-7).
- **amsgrad: A boolean flag to specify whether to apply the AMSGrad variant (default value: False).
- **name: Optional name for the operations created when applying gradients (default value: 'Adam').
Using Adam Optimizer in TensorFlow
Let's now look at an example where we will create a simple neural network model using TensorFlow and compile it using the Adam optimizer.
**1. Creating the Model
We will create a simple neural network with 2 Dense layers for demonstration.
Python `
import tensorflow as tf
def createModel(input_shape): X_input = tf.keras.layers.Input(input_shape) X = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='relu')(X_input) X_output = tf.keras.layers.Dense(2, activation='softmax')(X) model = tf.keras.Model(inputs=X_input, outputs=X_output) return model
`
Now, we will create an instance of this model and print the summary to inspect the architecture.
Python `
model = createModel((10, 10)) print(model.summary())
`
**Output:

Output
2. Checking Initial Weights
Before training the model, let's print out the initial weights for the layers.
Python `
print('Initial Layer Weights') for i in range(1, len(model.layers)): print(f'Weight for Layer {i}:') print(model.layers[i].get_weights()[0]) print()
`
**Output:
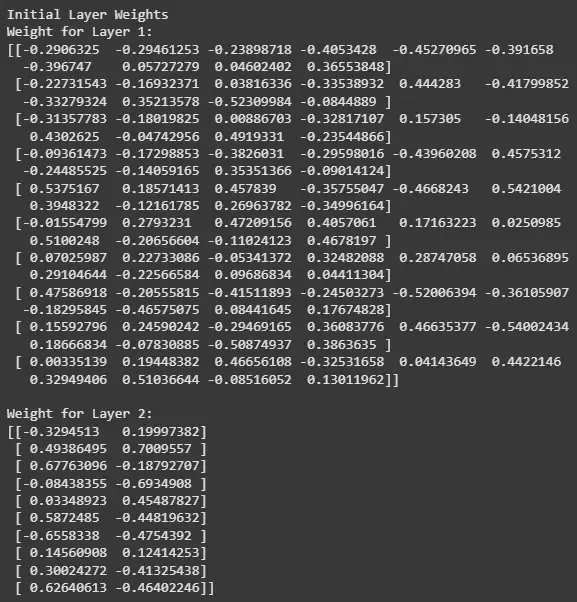
Output
3. Generating Dummy Data
For this example we will generate random data to train the model.
Python `
tf.random.set_seed(5)
X = tf.random.normal((2, 10, 10)) Y = tf.random.normal((2, 10, 2))
`
**4. Compiling Model
Now we compile the model using the Adam optimizer, the categorical cross-entropy loss function and accuracy as the evaluation metric.
Python `
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
print(model.optimizer.get_config())
`
**Output:
{'name': 'adam', 'learning_rate': 0.0010000000474974513, 'weight_decay': None, 'clipnorm': None, 'global_clipnorm': None, 'clipvalue': None, 'use_ema': False, 'ema_momentum': 0.99, 'ema_overwrite_frequency': None, 'loss_scale_factor': None, 'gradient_accumulation_steps': None, 'beta_1': 0.9, 'beta_2': 0.999, 'epsilon': 1e-07, 'amsgrad': False}
The output shows the default configuration of the Adam Optimizer. Now, let's train the model using the dummy data we generated and check the weights of the model after training.
Python `
model.fit(X, Y)
print('Final Layer Weights') for i in range(1, len(model.layers)): print(f'Weight for Layer {i}:') print(model.layers[i].get_weights()[0]) print()
`
**Output:
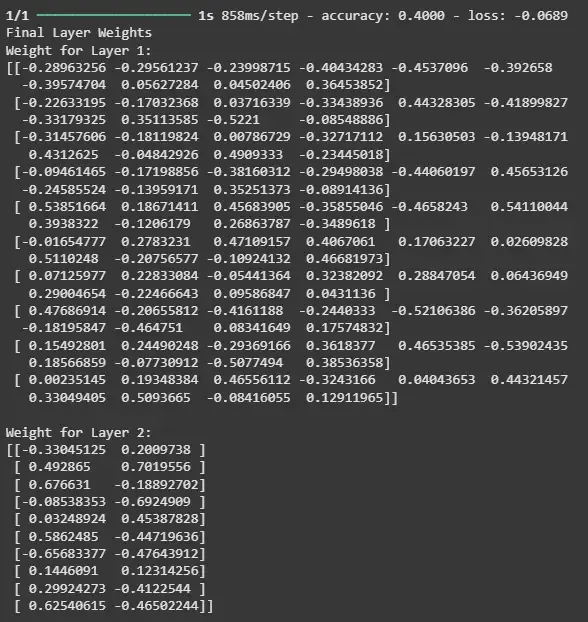
Output
The output shows how well the model is performing on the training data based on the loss and accuracy and also allows you to observe how the model's weights have changed as a result of the training process.
Which two optimization techniques does Adam combine?
- SGD and AdaGrad
- Momentum and RMSprop
- AdaDelta and Nadam
- RMSprop and SGD
Explanation:
Adam merges the advantages of **Momentum (uses moving averages of gradients) and **RMSprop (adaptive learning rate).
What is the default learning rate of the Adam optimizer in TensorFlow as mentioned in the content?
- 0.1
- 0.01
- 0.001
- 0.0001
Explanation:
The content clearly states that the default learning rate for Adam is 0.001.
Which argument is used in model.compile() to apply Adam using default settings?
- optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam()
- optimizer="default_adam"
- optimizer="adam"
- optimizer="adaptive"

Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/3
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/3
1/3 < Previous Next >