Pandas DataFrame duplicated() Method Python (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 26 Jul, 2025
The duplicated() method in Pandas helps us to find these duplicates in our data quickly and returns True for duplicates and False for unique rows. It is used to clean our dataset before going into analysis. In this article, we'll see how the duplicated() method works with some examples.
**Lets see an example:
Python `
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Alice', 'Charlie'], 'Age': [25, 32, 25, 37] }) duplicates = df[df.duplicated()] print(duplicates)
`
**Output:
Name Age
2 Alice 25
**Syntax:
DataFrame.duplicated(subset=None, keep='first')
**Parameters:
**1. subset: (Optional) Specifies which columns to check for duplicates. By default, it checks all columns.
**2. keep: Finds which duplicates to mark as True:
- '**first' (default): Marks duplicates after the first occurrence as True.
- '**last': Marks duplicates after the last occurrence as True.
- **False: Marks all occurrences of duplicates as True.
**Returns: A Boolean series where each value corresponds to whether the row is a duplicate (True) or unique (False).
Let's look at some examples of the duplicated method in Pandas library used to identify duplicated rows in a DataFrame. Here we will be using custom dataset.
You can download the dataset from Here.
**Example 1: Returning a Boolean Series
In this example we will identify duplicate values in the First Name column using the default **keep='first' parameter.. This keeps the first occurrence of each duplicate and marks the rest as duplicates.
Python `
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_csv("/content/employees.csv") data.sort_values("First Name", inplace = True) bool_series = data["First Name"].duplicated() data.head() data[bool_series]
`
**Output:
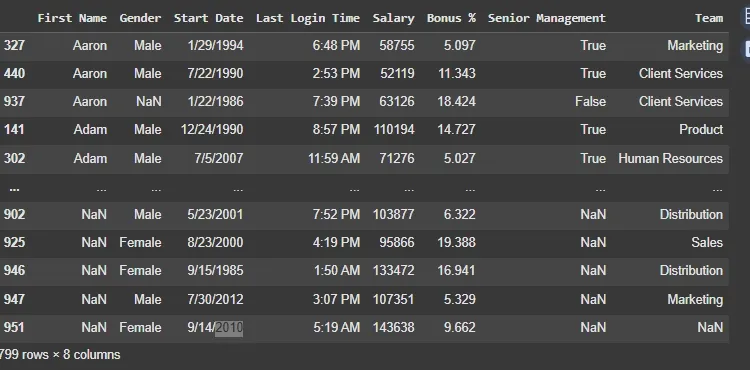
Output
**Example 2: Removing duplicates
In this example we'll remove all duplicates from the DataFrame. By setting keep=False we remove every instance of a duplicate.
Python `
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_csv("/content/employees.csv") data.sort_values("First Name", inplace = True) bool_series = data["First Name"].duplicated(keep = False) bool_series data = data[~bool_series] data.info() data
`
**Output:
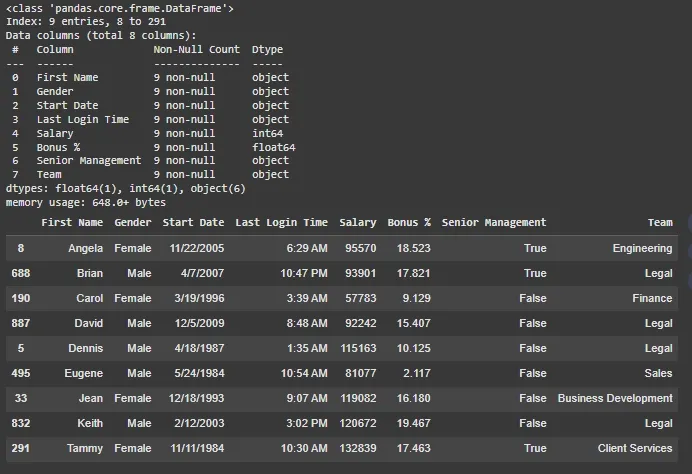
Output
Example 3: Keeping the Last Occurrence of Duplicates
In this example, we will keep the last occurrence of each duplicate and mark the rest as duplicates. This is done using the **keep='last' arguments.
Python `
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_csv("/content/employees.csv") data.sort_values("First Name", inplace=True) bool_series_last = data["First Name"].duplicated(keep='last') data_last = data[~bool_series_last] data_last.info() print(data_last)
`
**Output:
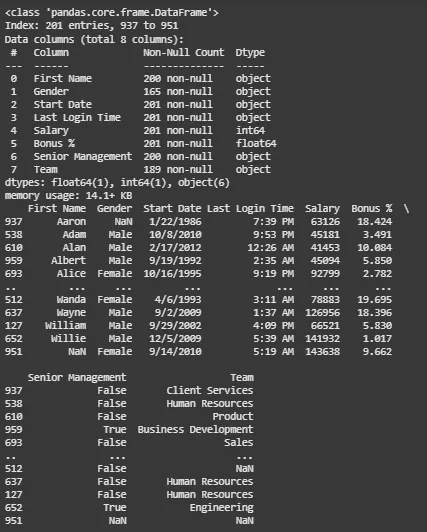
Output
What does the duplicated() method in Pandas return?
- A DataFrame with duplicates removed
- The number of duplicate rows
- A Boolean Series marking duplicate rows
- The last duplicate row only
Explanation:
duplicated() returns a Boolean Series where True marks rows that are duplicates.
Which row is marked as duplicate when using duplicated()?
- The first occurrence
- The last occurrence
- All matching rows
- All except the first occurrence
Explanation:
By default, duplicated() marks all duplicate rows as True except for the first one.
How can you mark the first occurrence as duplicate in duplicated()?
- duplicated(first=True)
- duplicated(last=True)
- duplicated(keep='first')
- duplicated(keep='none')
Explanation:
keep='none' marks all duplicates (including the first occurrence) as True.
What is the default behavior of duplicated() in Pandas?
- Keeps the first duplicate
- Marks only the last duplicate
- Ignores duplicates
- Marks all but the first as
True
Explanation:
By default, it marks all duplicate rows except the first one.

Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/4
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/4
1/4 < Previous Next >