Matplotlib Pyplot (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 18 Jul, 2025
Matplotlib's pyplot module is a widely used interface that simplifies the process of creating visualizations in Python. It provides a MATLAB-like syntax, allowing users to generate line charts, bar graphs, scatter plots and other common visualizations with ease. With just a few lines of code analysts and developers can turn raw data into clear, informative charts for analysis and presentation.
This article will help you understand how to use Matplotlib’s Pyplot module to create simple charts.
Basic Plotting with Pyplot
Below are some of the most commonly used chart types in Pyplot, each demonstrated with a short example.
1. Line Plot
Line plots are simplest types of charts. The **plot() function takes two lists: one for x-axis and one for y-axis and connects the points in a linear path.
**Example:
Following code uses **plt.plot() to draw a basic line graph for the given **x and **y values using Pyplot module.
Python `
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x=[1, 2, 3, 4] y=[1, 4, 9, 16] plt.plot(x,y) plt.show()
`
**Output
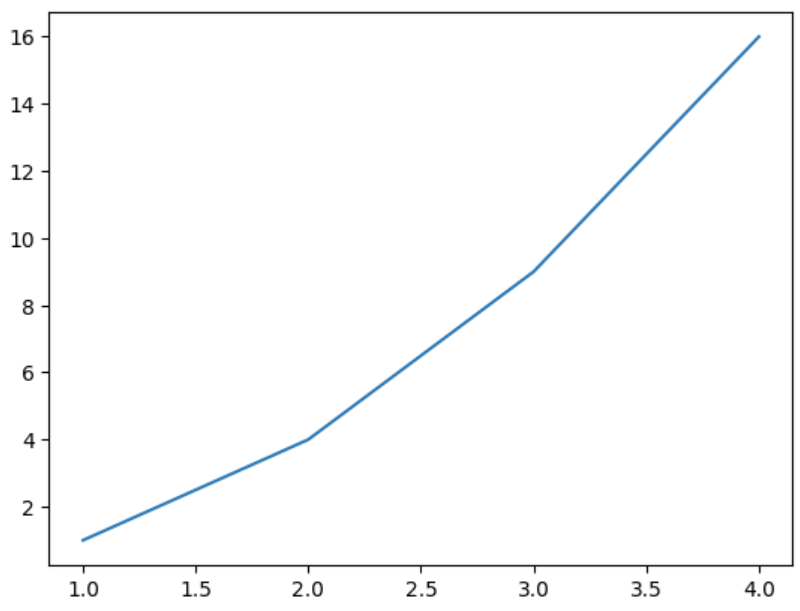
Plotting a line graph using pyplot
**Explanation:
- **plt.plot(x, y): creates a line plot by connecting **x and **y data points.
- **plt.show(): displays final plot window.
2. Pie Charts
Pie charts show the share of each category in a whole. The **pie() function takes a list of values and optional labels to represent each slice of the pie.
**Example:
This code creates a pie chart using **plt.pie() function to visualize the percentage share of different programming languages.
Python `
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt labels = ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'JavaScript'] sizes = [40, 30, 20, 10] plt.pie(sizes, labels=labels, autopct='%1.1f%%') plt.show()
`
**Output
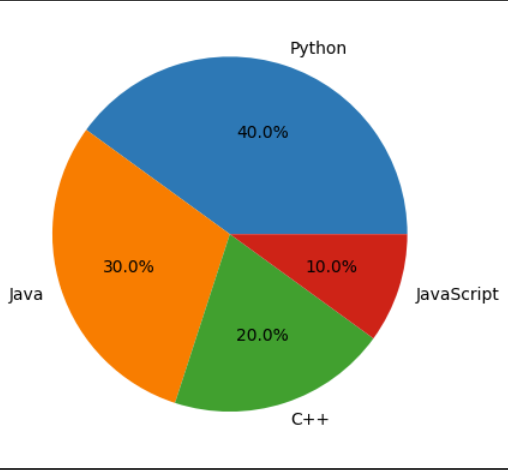
Pie chart using pyplot
**Explanation: plt.pie(sizes, labels=labels, autopct='%1.1f%%') creates a pie chart withslice sizes from sizes, labels for each sliceand **autopct shows percentage values with one decimal place.
3. Bar Charts
Bar charts are ideal for comparing quantities across categories. The bar() function takes two lists one for **category labels (x-axis) and one for their corresponding **values (y-axis).
**Example:
This Example creates a bar chart using **bar() function to display values for different categories.
Python `
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt categories = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'] values = [3, 7, 2, 5] plt.bar(categories, values) plt.show()
`
**Output
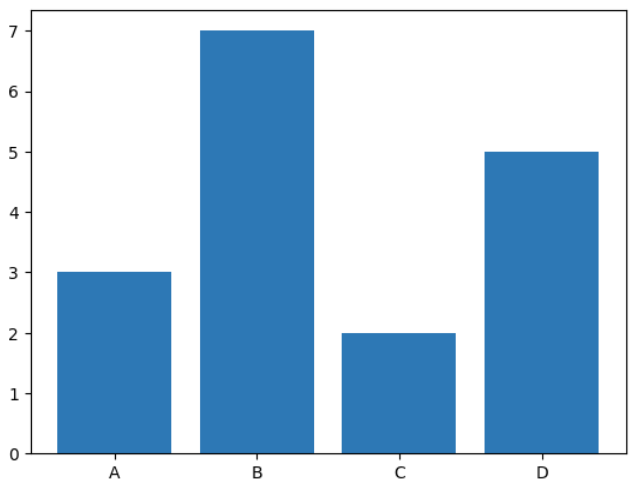
Bar Chart using Pyplot
**Explanation: **plt.bar(categories, values) draws a vertical bar chart using given categories and values.
4. Scatter Plots
Scatter plots are used for displaying individual data points and showing relationship between two variables. The scatter() function takes two lists like plot(), but it only plots the individual points without connecting them.
**Example:
Here, scatter plot is plotted using **scatter() function to visualize individual data points.
Python `
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] y = [5, 7, 9, 11, 13] plt.scatter(x, y) plt.show()
`
**Output
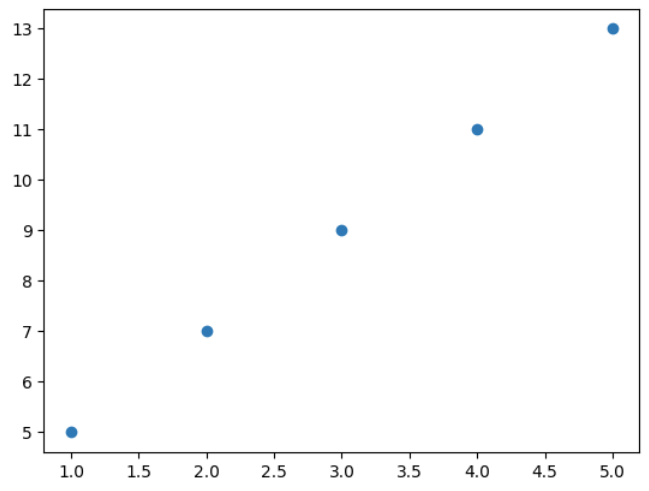
Scatter Plot using Pyplot
**Explanation: **plt.scatter(x, y) plots individual data points as dots at specified ****(x, y)** coordinates.
5. Histograms
Histograms are used to visualize distribution of a dataset. The **hist() function takes a list or array of numerical data and divides it into bins.
**Example:
A histogram is plotted using **hist() function to visualize the distribution of 1000 random data points.
Python `
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np data = np.random.randn(1000) plt.hist(data, bins=30) plt.show()
`
**Output
Histogram Using Pyplot
**Explanation:
- **np.random.randn(1000): generates **1000 random numbers from a standard normal distribution.
- **plt.hist(data, bins=30): creates a histogram of the data with 30 bins (intervals).
**Related Articles: