Pandas Dataframe.pop() (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 11 Jul, 2025
The pop() method in Pandas is used to remove a column from a DataFrame and return it as a Series. This is similar in concept to the dictionary pop() method in Python, but specifically designed for use with **Pandas DataFrames. It's key features include:
- Removes a specified column from a DataFrame.
- Returns the removed column as a Pandas Series.
- Modifies the original DataFrame in-place.
**Example:
Python `
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'name': ['Alice', 'Bob'], 'age': [25, 30], 'city': ['New York', 'Paris'] }) a = df.pop('age')
print(a) print(df)
`
**Output

Using pop()
**Explanation: pop() removes the 'age' column and returns it as a Series. After the operation, **a holds the age values and **df retains only the name and city columns.
Syntax of Pandas Dataframe.pop()
DataFrame.pop(label)
**Parameters: label (str) is the name of the column to be removed.
**Returns: A Series containing the removed column values.
Note: This method raises KeyError if the column does not exist in the DataFrame.
Examples of Pandas Dataframe.pop()
**Example 1: This example shows that trying to pop a column which does not exist in the DataFrame will raise a KeyError.
Python `
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'product': ['Book', 'Pen'], 'price': [100, 10] })
df.pop('quantity')
`
**Output
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "...", line ...
df.pop('quantity')
File "...", line ...
raise KeyError(key) from err
KeyError: 'quantity'
**Explanation: Since the column 'quantity' does not exist in the DataFrame, calling pop('quantity') raises a **KeyError.
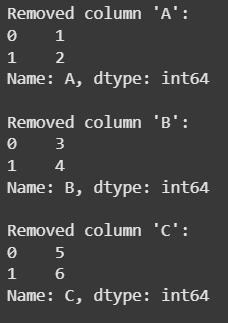
**Example 2: This example shows how you can use **pop() in a loop to remove and process columns until the DataFrame is empty.
Python `
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'A': [1, 2], 'B': [3, 4], 'C': [5, 6] })
while not df.empty: col = df.columns[0] val = df.pop(col) print(col, val)
`
**Output
Using pop()
**Explanation: Loop runs until the DataFrame is empty, removing the first column each time with **pop(), which deletes it in-place and returns it as a Series. The column name and values are printed until all columns are processed.
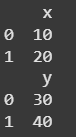
**Example 3: This example demonstrates how to pop a column from one DataFrame and assign it to another DataFrame.
Python `
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({ 'x': [10, 20], 'y': [30, 40] })
df2 = pd.DataFrame() df2['y'] = df1.pop('y')
print(df1) print(df2)
`
**Output
Using pop()
**Explanation: df1 is created with columns 'x' and 'y' and an empty **df2 is initialized. The pop() method removes 'y' from **df1 and assigns it to **df2['y']. As a result, df1 contains only 'x' and df2 contains the original 'y' values.