Pandas isnull() and notnull() Method (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 31 Oct, 2025
Missing or null values are common in real-world datasets. Pandas provides isnull() and notnull() to detect such values in a DataFrame or Series.
- **isnull(): Returns True for missing (NaN) values and False for non-missing values.
- **notnull(): Returns True for non-missing values and False for missing values.
These methods are essential for locating, filtering, or counting missing values during data cleaning.
To download the csv file used in this article, click here
Detecting Missing Values with isnull()
isnull() identifies NULL or NaN values and returns a boolean Series or DataFrame.
**Syntax:
pd.isnull(obj)
**Parameters:
- **obj: can be a Series, DataFrame, or scalar value.
- **Returns: Boolean Series/DataFrame with True for missing values.
**Example:
Python `
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_csv(r'enter the path to dataset here')
bool_series = pd.isnull(data["Team"]) missing_values_count = bool_series.sum() filtered_data = data[bool_series]
print("Count of missing values in 'Team':", missing_values_count) print("Rows with missing 'Team':") print(filtered_data)
`
**Output
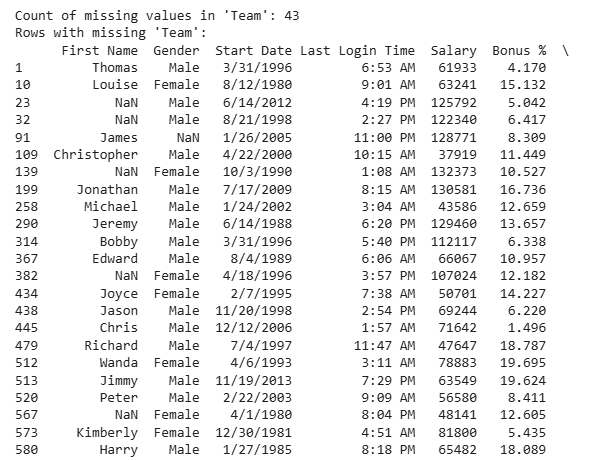
**Explanation:
- **pd.isnull(data["Team"]): Creates a boolean Series marking missing values
- **bool_series.sum(): Counts missing entries.
- **data[bool_series]: Filters rows with missing values in the Team column
Detecting Non-Missing Values with notnull()
notnull() method is the inverse of isnull(). It identifies non-missing (valid) values.
**Syntax:
pd.notnull(obj)
**Parameters:
- **obj: can be a scalar, Series, or DataFrame.
- **Returns: Boolean Series/DataFrame where True indicates non-null values.
**Example:
Python `
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_csv(r'enter path to dataset here') bool_series = pd.notnull(data["Gender"]) filtered_data = data[bool_series]
print(filtered_data)
`
**Output
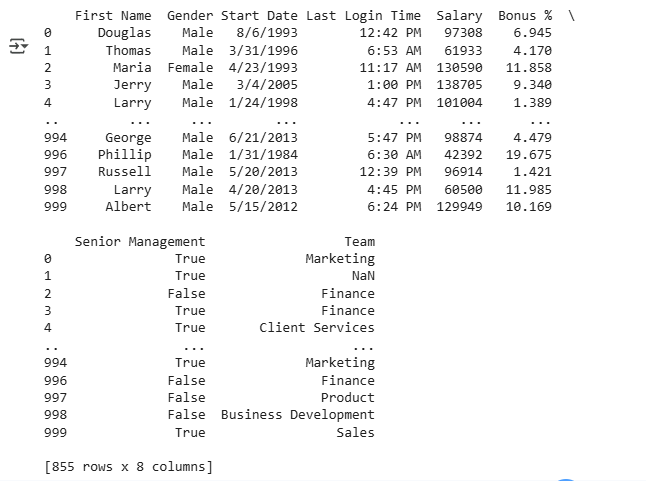
**Explanation:
- **pd.notnull(data["Gender"]): marks all non-missing values as True.
- ****data[bool_series]:**Filters rows that have non-null values in Gender
Filtering Data Based on Null Values
You can combine isnull() and notnull() for efficient filtering in data cleaning tasks.
**Syntax:
pd.notnull(obj)
**Parameters:
- **obj: Can be a scalar value, Series, or DataFrame. It is the input to check for non-missing (non-NaN) values.
- **Returns: A boolean Series or DataFrame of the same shape as the input, where True indicates non-null (valid) entries.
**Example:
Python `
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_csv("employees.csv") bool_series = pd.notnull(data["Gender"]) filtered_data = data[bool_series] print("Data with non-null 'Gender' values:") print(filtered_data)
`
**Output
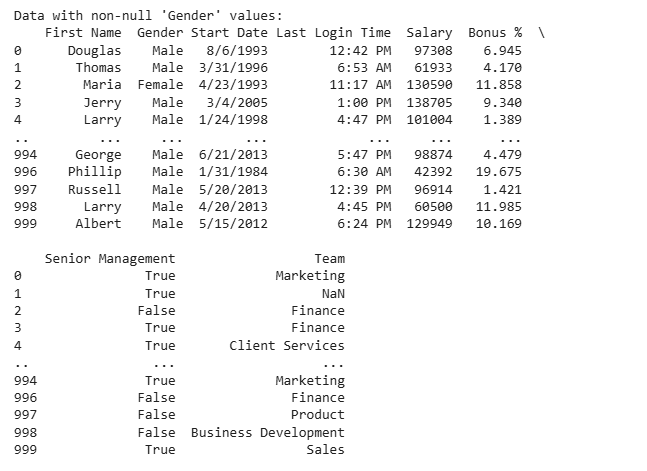
**Explanation:
- **bool_series = pd.notnull(data["Gender"]): Creates a Boolean Series; True for non-missing "Gender" values.
- **filtered_data = data[bool_series]: Filters rows where "Gender" is not null.