Python | Pandas Series.mul() (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 01 Oct, 2018
Python is a great language for doing data analysis, primarily because of the fantastic ecosystem of data-centric Python packages. Pandas is one of those packages and makes importing and analyzing data much easier. Python Series.mul() is used to multiply series or list like objects with same length with the caller series.
Syntax: Series.mul(other, level=None, fill_value=None, axis=0)Parameters: other: other series or list type to be multiplied with caller seriesfill_value: Value to be replaced by NaN in series/list before multiplicationlevel: integer value of level in case of multi indexReturn type: Caller series with multiplied values
To download the data set used in following example, click here.In the following examples, the data frame used contains data of some NBA players. The image of data frame before any operations is attached below.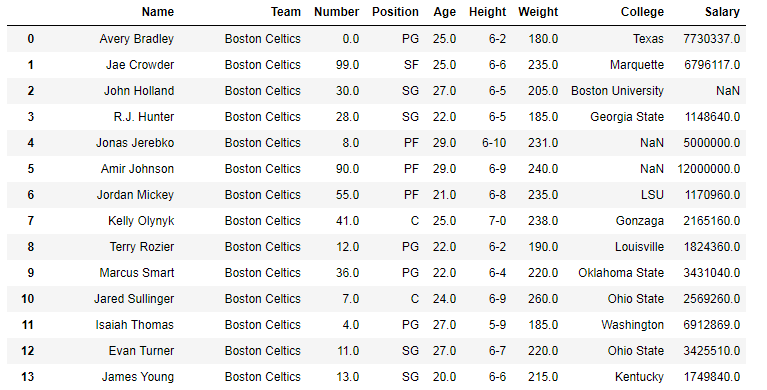 Example #1: Multiplying list with series In this example, the top 5 rows are stored in new variable using .head() method. After that a list of same length is created and multiplied with the Age column using .mul() method
Example #1: Multiplying list with series In this example, the top 5 rows are stored in new variable using .head() method. After that a list of same length is created and multiplied with the Age column using .mul() method
Python3 1== `
importing pandas module
import pandas as pd
reading csv file from url
data = pd.read_csv("https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/uploads/nba.csv")
creating short data of 5 rows
short_data = data.head()
creating list with 5 values
list =[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
multiplying list data
creating new column
short_data["Multiplied values"]= short_data["Age"].mul(list)
display
short_data
`
**Output:**As shown in the output image, it can be compared that the Multiplied values column is having the Multiplied values of (Age) x (list). Example #2: Multiplying series with series having null values In this example, the Salary column is multiplied with the Age column. Since the values in both Salary and Age column are large, product will be returned with high value. Hence just for demonstrating purposes, the age column is divided with 100 before doing the multiplication. Since the salary column contains null values too, by default it returns NaN no matter what is multiplied. In this example, 20 is passed to replace null values with 20.
Example #2: Multiplying series with series having null values In this example, the Salary column is multiplied with the Age column. Since the values in both Salary and Age column are large, product will be returned with high value. Hence just for demonstrating purposes, the age column is divided with 100 before doing the multiplication. Since the salary column contains null values too, by default it returns NaN no matter what is multiplied. In this example, 20 is passed to replace null values with 20.
Python3 1== `
importing pandas module
import pandas as pd
reading csv file from url
data = pd.read_csv("https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/uploads/nba.csv")
dividing age series
data["Age"]= data["Age"]/100
age = data["Age"]
na replacement
na = 20
Multiplying values
storing to new column
data["Multiplied values"]= data["Salary"].mul(other = age, fill_value = na)
display
data
`
**Output:**As shown in the output image, the Multiplicated value column has multiplied age column with 20 in case of Null values.