Queue Linked List Implementation (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 25 Mar, 2025
In this article, the Linked List implementation of the queue data structure is discussed and implemented. Print '-1' if the queue is empty.
**Approach: To solve the problem follow the below idea:
we maintain two pointers, **front and **rear. The frontpoints to the first item of the queue andrearpoints to the last item.
- **enQueue(): This operation adds a new node after the rearand moves the rearto the next node.
- **deQueue(): This operation removes the front node and moves the frontto the next node.
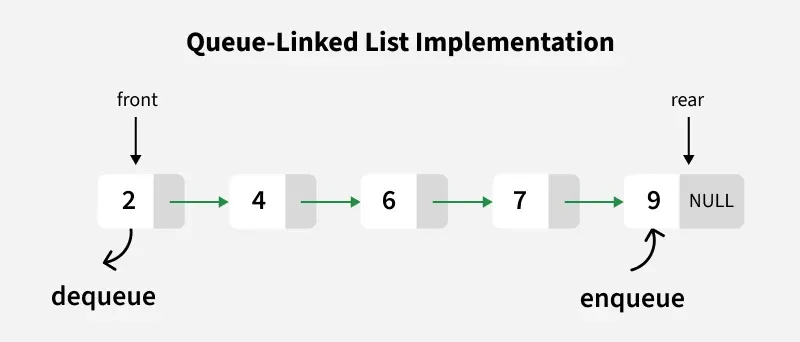
Queue using Linked List
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Create a class Node with data members integer data and Node* next
- A parameterized constructor that takes an integer x value as a parameter and sets data equal to xand next as NULL
- Create a class Queue with data members Node frontand rear
- Enqueue Operation with parameter x:
- Initialize Node* tempwith data = x
- If the rear is set to NULL then set the front and rear to tempand return(Base Case)
- Else set rear next totemp and then move rear to temp
- Dequeue Operation:
- If the front is set to NULL return(Base Case)
- Initialize Node tempwith front and set front to its next
- If the front is equal to NULLthen set the rear to NULL
- Delete temp from the memory
Below is the Implementation of the above approach:
C++ `
#include using namespace std;
// Node class definition class Node { public: int data; Node* next; Node(int new_data) { data = new_data; next = nullptr; } };
// Queue class definition class Queue { private: Node* front; Node* rear; public: Queue() { front = rear = nullptr; }
// Function to check if the queue is empty
bool isEmpty() {
return front == nullptr;
}
// Function to add an element to the queue
void enqueue(int new_data) {
Node* new_node = new Node(new_data);
if (isEmpty()) {
front = rear = new_node;
printQueue();
return;
}
rear->next = new_node;
rear = new_node;
printQueue();
}
// Function to remove an element from the queue
void dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return;
}
Node* temp = front;
front = front->next;
if (front == nullptr) rear = nullptr;
delete temp;
printQueue();
}
// Function to print the current state of the queue
void printQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Queue is empty" << endl;
return;
}
Node* temp = front;
cout << "Current Queue: ";
while (temp != nullptr) {
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
cout << endl;
}};
// Driver code to test the queue implementation int main() { Queue q;
// Enqueue elements into the queue
q.enqueue(10);
q.enqueue(20);
// Dequeue elements from the queue
q.dequeue();
q.dequeue();
// Enqueue more elements into the queue
q.enqueue(30);
q.enqueue(40);
q.enqueue(50);
// Dequeue an element from the queue (this should print 30)
q.dequeue();
return 0;}
C
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
// Node structure definition struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; };
// Queue structure definition struct Queue { struct Node* front; struct Node* rear; };
// Function to create a new node struct Node* newNode(int new_data) { struct Node* node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); node->data = new_data; node->next = NULL; return node; }
// Function to initialize the queue struct Queue* createQueue() { struct Queue* q = (struct Queue*)malloc(sizeof(struct Queue)); q->front = q->rear = NULL; return q; }
// Function to check if the queue is empty int isEmpty(struct Queue* q) { return q->front == NULL; }
// Function to add an element to the queue void enqueue(struct Queue* q, int new_data) { struct Node* new_node = newNode(new_data); if (isEmpty(q)) { q->front = q->rear = new_node; printQueue(q); return; } q->rear->next = new_node; q->rear = new_node; printQueue(q); }
// Function to remove an element from the queue void dequeue(struct Queue* q) { if (isEmpty(q)) { return; } struct Node* temp = q->front; q->front = q->front->next; if (q->front == NULL) q->rear = NULL; free(temp); printQueue(q); }
// Function to print the current state of the queue void printQueue(struct Queue* q) { if (isEmpty(q)) { printf("Queue is empty\n"); return; } struct Node* temp = q->front; printf("Current Queue: "); while (temp != NULL) { printf("%d ", temp->data); temp = temp->next; } printf("\n"); }
// Driver code to test the queue implementation int main() { struct Queue* q = createQueue();
// Enqueue elements into the queue
enqueue(q, 10);
enqueue(q, 20);
// Dequeue elements from the queue
dequeue(q);
dequeue(q);
// Enqueue more elements into the queue
enqueue(q, 30);
enqueue(q, 40);
enqueue(q, 50);
// Dequeue an element from the queue (this should print 30)
dequeue(q);
return 0;}
Java
// Node class definition class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int new_data) { data = new_data; next = null; } }
// Queue class definition class Queue { private Node front; private Node rear; public Queue() { front = rear = null; }
// Function to check if the queue is empty
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == null;
}
// Function to add an element to the queue
public void enqueue(int new_data) {
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
if (isEmpty()) {
front = rear = new_node;
printQueue();
return;
}
rear.next = new_node;
rear = new_node;
printQueue();
}
// Function to remove an element from the queue
public void dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return;
}
Node temp = front;
front = front.next;
if (front == null) rear = null;
temp = null;
printQueue();
}
// Function to print the current state of the queue
public void printQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty");
return;
}
Node temp = front;
System.out.print("Current Queue: ");
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}}
// Driver code to test the queue implementation public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Queue q = new Queue();
// Enqueue elements into the queue
q.enqueue(10);
q.enqueue(20);
// Dequeue elements from the queue
q.dequeue();
q.dequeue();
// Enqueue more elements into the queue
q.enqueue(30);
q.enqueue(40);
q.enqueue(50);
// Dequeue an element from the queue (this should print 30)
q.dequeue();
}}
Python
class Node: def init(self, new_data): self.data = new_data self.next = None
class Queue: def init(self): self.front = self.rear = None
# Function to check if the queue is empty
def isEmpty(self):
return self.front is None
# Function to add an element to the queue
def enqueue(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
if self.isEmpty():
self.front = self.rear = new_node
self.printQueue()
return
self.rear.next = new_node
self.rear = new_node
self.printQueue()
# Function to remove an element from the queue
def dequeue(self):
if self.isEmpty():
return
temp = self.front
self.front = self.front.next
if self.front is None:
self.rear = None
self.printQueue()
# Function to print the current state of the queue
def printQueue(self):
if self.isEmpty():
print("Queue is empty")
return
temp = self.front
queue_string = "Current Queue: "
while temp is not None:
queue_string += str(temp.data) + " "
temp = temp.next
print(queue_string)q = Queue()
Enqueue elements into the queue
q.enqueue(10) q.enqueue(20)
Dequeue elements from the queue
q.dequeue() q.dequeue()
Enqueue more elements into the queue
q.enqueue(30) q.enqueue(40) q.enqueue(50)
Dequeue an element from the queue
q.dequeue()
JavaScript
// Node class class Node { constructor(new_data) { this.data = new_data; this.next = null; } }
// Queue class class Queue { constructor() { this.front = this.rear = null; }
// Function to check if the queue is empty
isEmpty() {
return this.front === null;
}
// Function to add an element to the queue
enqueue(new_data) {
const new_node = new Node(new_data);
if (this.isEmpty()) {
this.front = this.rear = new_node;
this.printQueue();
return;
}
this.rear.next = new_node;
this.rear = new_node;
this.printQueue();
}
// Function to remove an element from the queue
dequeue() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
const temp = this.front;
this.front = this.front.next;
if (this.front === null) {
this.rear = null;
}
this.printQueue();
}
// Function to print the current state of the queue
printQueue() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log("Queue is empty");
return;
}
let temp = this.front;
let queue_string = "Current Queue: ";
while (temp !== null) {
queue_string += temp.data + " ";
temp = temp.next;
}
console.log(queue_string);
}}
const q = new Queue();
// Enqueue elements into the queue q.enqueue(10); q.enqueue(20);
// Dequeue elements from the queue q.dequeue(); q.dequeue();
// Enqueue more elements into the queue q.enqueue(30); q.enqueue(40); q.enqueue(50);
// Dequeue an element from the queue q.dequeue();
`
Output
Current Queue: 10 Current Queue: 10 20 Current Queue: 20 Queue is empty Current Queue: 30 Current Queue: 30 40 Current Queue: 30 40 50 Current Queue: 40 50
**Time Complexity: O(1), The time complexity of both operations enqueue() and dequeue() is O(1) as it only changes a few pointers in both operations
**Auxiliary Space: O(1), The auxiliary Space of both operations enqueue() and dequeue() is O(1) as constant extra space is required
Related Article: Array Implementation of Queue
