random.expovariate() function in Python (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 23 Dec, 2021
random module is used to generate random numbers in Python. Not actually random, rather this is used to generate pseudo-random numbers. That implies that these randomly generated numbers can be determined.
random.expovariate()
**expovariate()** is an inbuilt method of the random module. It is used to return a random floating point number with exponential distribution.
Syntax : random.expovariate(lambda)Parameters :lambda : a non zero valueReturns : a random exponential distribution floating number if the parameter is positive, the results range from 0 to positive infinity if the parameter is negative, the results range from 0 to negative infinity
Example 1:
Python3 1== `
import the random module
import random
determining the values of the parameter
lambda = 1.5
using the expovariate() method
print(random.expovariate(lambda))
`
Output :
0.22759592233982198
Example 2: We can generate the number multiple times and plot a graph to observe the exponential distribution.
Python3 1== `
import the required libraries
import random import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
store the random numbers in a
list
nums = [] alpha = 3
for i in range(100): temp = random.paretovariate(alpha) nums.append(temp)
plotting a graph
plt.plot(nums) plt.show()
`
Output : 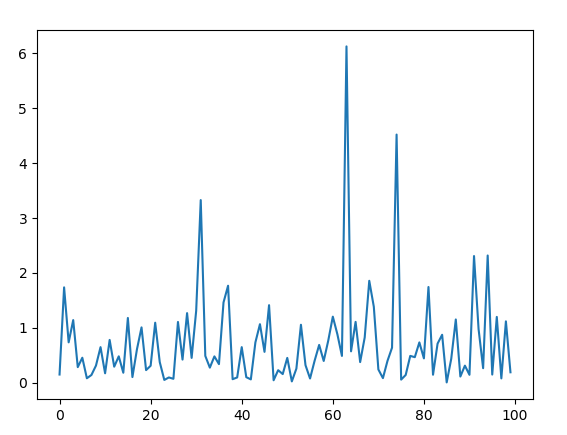 Example 3: We can create a histogram to observe the density of the exponential distribution.
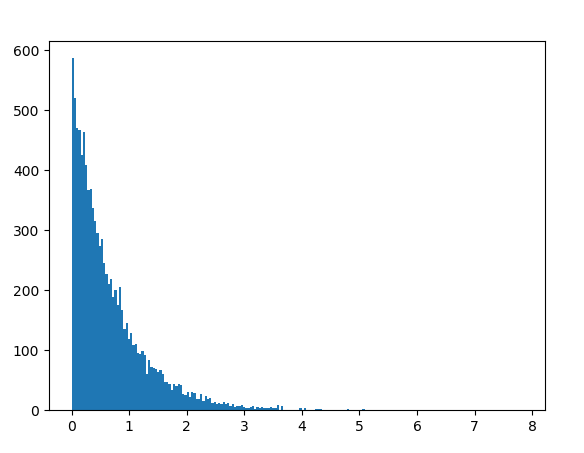
Example 3: We can create a histogram to observe the density of the exponential distribution.
Python3 1== `
import the required libraries
import random import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
store the random numbers in a list
nums = [] lambda = 1.5
for i in range(10000): temp = random.expovariate(lambda) nums.append(temp)
plotting a graph
plt.hist(nums, bins = 200) plt.show()
`
Output :