random.gauss() function in Python (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 27 Mar, 2025
**random module is used to generate random numbers in Python. Not actually random, rather this is used to generate pseudo-random numbers. That implies that these randomly generated numbers can be determined. **gauss() is an inbuilt method of the random module. It is used to return a random floating point number with gaussian distribution.
**Example:
Python `
import random
mu = 100 sigma = 50
print(random.gauss(mu, sigma))
`
**Output :
127.80261974806497
**Explanation: This code generates and prints a random number from a Gaussian distribution with a mean (mu) of 100 and a standard deviation (sigma) of 50 using the random.gauss() function. The result will be a value close to 100 but can vary within a range due to the standard deviation.
Syntax
random.gauss(mu, sigma)
Parameters
- **mu: mean
- **sigma: standard deviation
Return Value
- Returns a random gaussian distribution floating number
Examples of random.gauss() function
1. Gaussian Distribution Plot
We can generate the number multiple times and plot a graph to observe the gaussian distribution.
Python `
import random import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
store the random numbers in a list
nums = [] mu = 100 sigma = 50
for i in range(100): temp = random.gauss(mu, sigma) nums.append(temp)
plotting a graph
plt.plot(nums) plt.show()
`
O**utput :
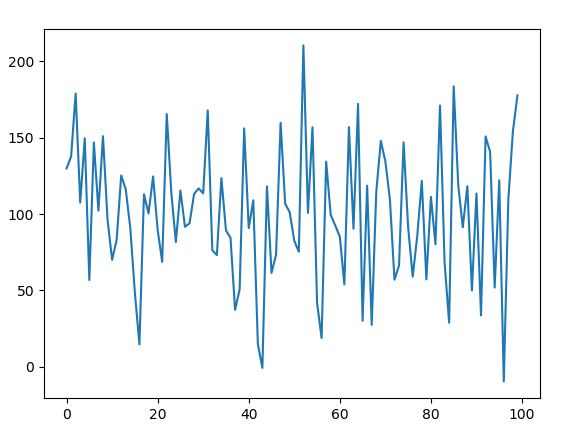
Gaussian Distribution Plot
**Explanation: This code generates 100 random numbers following a Gaussian distribution with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 50. It stores these numbers in a list and then plots the values using matplotlib to visualize the distribution.
2. Gaussian Distribution Histogram
We can create a histogram to observe the density of the gaussian distribution.
Python `
import random import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
store the random numbers in a list
nums = [] mu = 100 sigma = 50
for i in range(10000): temp = random.gauss(mu, sigma) nums.append(temp)
plotting a graph
plt.hist(nums, bins = 200) plt.show()
`
O**utput :
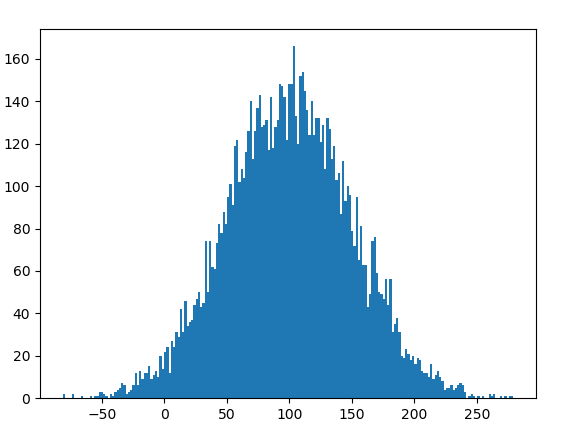
Gaussian Distribution Histogram
**Explanation: This code generates 10,000 random numbers following a Gaussian distribution with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 50. It stores the numbers in a list and then plots a histogram using matplotlib to visualize the distribution with 200 bins.