random.weibullvariate() function in Python (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 26 May, 2020
random module is used to generate random numbers in Python. Not actually random, rather this is used to generate pseudo-random numbers. That implies that these randomly generated numbers can be determined.
random.weibullvariate()
**weibullvariate()** is an inbuilt method of the random module. It is used to return a random floating point number with Weibull distribution.
Syntax : random.weibullvariate(alpha, beta)
Parameters :
alpha : scale parameter
beta : shape parameterReturns : a random Weibull distribution floating number
Example 1:
import random
alpha = 1
beta = 1.5
print (random.weibullvariate(alpha, beta))
Output :
0.7231214446591137
Example 2: We can generate the number multiple times and plot a graph to observe the Weibull distribution.
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
nums = []
alpha = 1
beta = 1.5
for i in range ( 100 ):
`` temp = random.weibullvariate(alpha, beta)
`` nums.append(temp)
plt.plot(nums)
plt.show()
Output :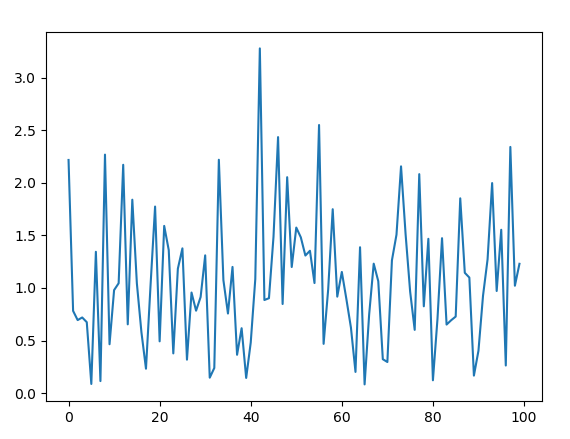
Example 3: We can create a histogram to observe the density of the Weibull distribution.
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
nums = []
alpha = 1
beta = 1.5
for i in range ( 10000 ):
`` temp = random.weibullvariate(alpha, beta)
`` nums.append(temp)
plt.hist(nums, bins = 200 )
plt.show()
Output :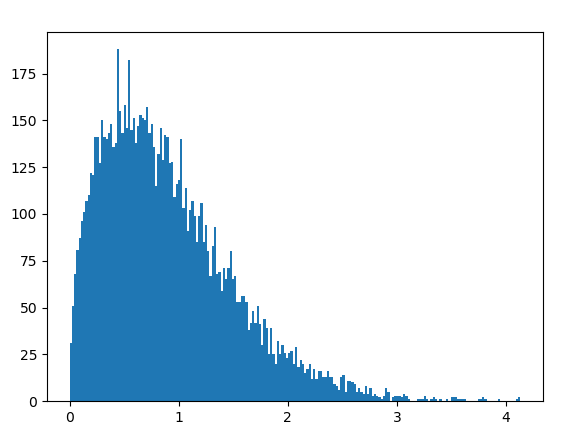
Similar Reads
- Python Random Module Python Random module generates random numbers in Python. These are pseudo-random numbers means they are not truly random. This module can be used to perform random actions such as generating random numbers, printing random a value for a list or string, etc. It is an in-built function in Python. Appl 7 min read
- Python - random.seed( ) method random.seed() method in Python is used to initialize the random number generator, ensuring the same random numbers on every run. By default, Python generates different numbers each time, but using .seed() allows result reproducibility. It's most commonly used in: Machine Learning- to ensure model co 4 min read
- random.getstate() in Python random() module is used to generate random numbers in Python. Not actually random, rather this is used to generate pseudo-random numbers. That implies that these randomly generated numbers can be determined. random.getstate() The getstate() method of the random module returns an object with the curr 1 min read
- random.setstate() in Python Random module is used to generate random numbers in Python. Not actually random, rather this is used to generate pseudo-random numbers. That implies that these randomly generated numbers can be determined. random.setstate() The setstate() method of the random module is used in conjugation with the g 2 min read
- random.getrandbits() in Python random module is used to generate random numbers in Python. Not actually random, rather this is used to generate pseudo-random numbers. That implies that these randomly generated numbers can be determined. random.getrandbits() The getrandbits() method of the random module is used to return an intege 1 min read
- randrange() in Python The randrange() function in Python's random module is used to generate a random number within a specified range. It allows defining a start, stop, and an optional step value to control the selection of numbers. Unlike randint(), which includes the upper limit, randrange() excludes the stop value. Ex 4 min read
- randint() Function in Python randint() is an inbuilt function of the random module in Python3. The random module gives access to various useful functions one of them being able to generate random numbers, which is randint(). In this article, we will learn about randint in Python. Python randint() Method SyntaxSyntax: randint(st 6 min read
- Python Numbers | choice() function choice() is an inbuilt function in Python programming language that returns a random item from a list, tuple, or string. Syntax: random.choice(sequence) Parameters: sequence is a mandatory parameter that can be a list, tuple, or string. Returns: The choice() returns a random item. Note:We have to im 1 min read
- Python - random.choices() method The choices() method returns multiple random elements from the list with replacement. Unlike random.choice(), which selects a single item, random.choices() allows us to select multiple items making it particularly useful for tasks like sampling from a population or generating random data. Example: [ 3 min read
- random.sample() function - Python sample() is an built-in function of random module in Python that returns a particular length list of items chosen from the sequence i.e. list, tuple, string or set. Used for random sampling without replacement. Example: [GFGTABS] Python from random import sample a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] print(sample(a,3) 2 min read