ReactJS Data Binding (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 28 Feb, 2025
**Data binding is a technique that binds data sources from the provider and consumer together and synchronizes them. In other words, Data Binding means sharing data between components to view and view to component.
- Data binding in React can be achieved by using a controlled input.
- A controlled input is achieved by binding the value to a state variable and an onChange event to change the state as the input value changes.
How React Handles Data Binding?
React handles data binding by using a unidirectional data flow, where state and props manage component data, and controlled components enable real-time synchronization between the UI and state.
- Define a state to manage data.
- Set up event listeners to detect user interactions.
- Update the state when an event occurs.
- React automatically re-renders the component with updated data.
**There are two ways to achieve data binding in React
**One-way Data Binding
One-way data binding means data flows in a single direction, from the component's state to the UI. However, changes in the UI do not update the state directly.
One-way data binding is commonly used in React applications. When the state of a component changes, React updates the DOM to reflect the new state, ensuring that the UI is always in sync with the component’s data.
- Parent components pass data down to child components via props.
- Child components cannot directly modify the props they receive; they are read-only.
- The view automatically re-renders when the state or props change.
- The component controls the data, with user interactions updating the state explicitly via event handlers.
1. Model
- The model in React represents the data in your application. It can be stored in various places, such as in component state, props, or through more complex state management libraries like Redux.
- State: This holds the model data (i.e., variables that can change over time).
- Props: These are the values passed from parent components to child components.
2. View
- The view is the visual representation of the data.
- In React, the view is defined by the JSX (a syntax extension for JavaScript), which renders the UI based on the state and props.
Data Flow Process in One-Way Data Binding
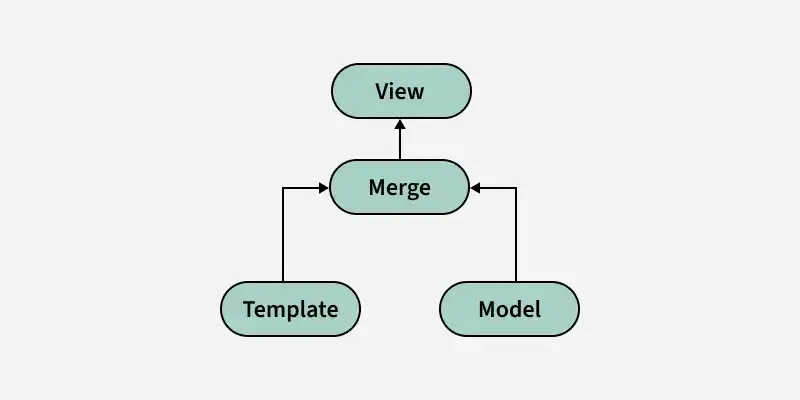
One-Way Data Binding
- Initial Rendering: When the component renders, React looks at the model (state or props), and based on the data, it renders the view (UI).
- **2. State/Props Change: If the model (state or props) changes, React re-renders the component and updates the UI accordingly.
- **3. User Interaction: If a user interacts with the UI (e.g., clicks a button, types in an input field), an event handler is triggered, which updates the state or model.
- **4. Re-render: React then triggers a re-render to update the view based on the new model values. JavaScript `
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function comp() { const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<h1>Count: {count}</h1>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>Incre</button>
</div>
);}
export default comp;
`
**Output

One Way Data Binding
**Implementing Component to View Data Binding
It is a process where the component's state is dynamically linked to the UI, such that any changes in the state automatically update the view.
App.js `
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
subject: "ReactJS"
};
}
render() {
return (
<div style={{ textAlign: "center" }}>
<h4 style={{ color: "#68cf48" }}>GeeksForGeeks</h4>
<p><b>{this.state.subject}</b> Tutorial</p>
</div>
)
}}
export default App;
`
**Output
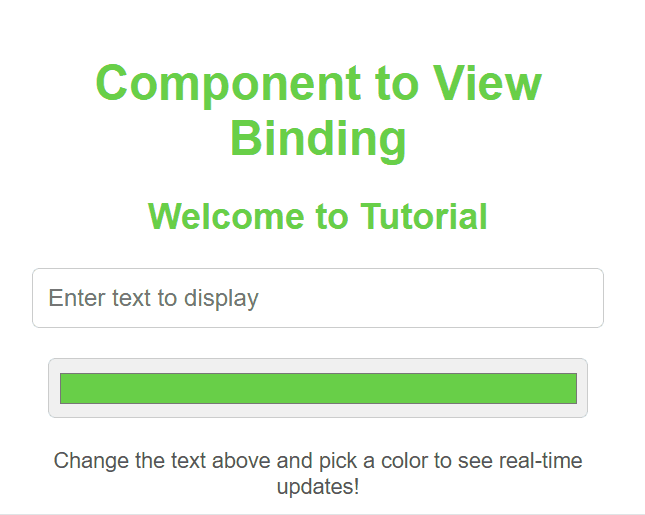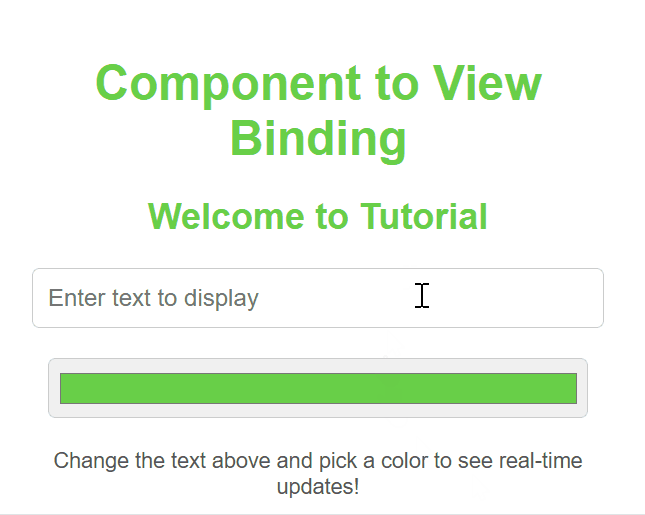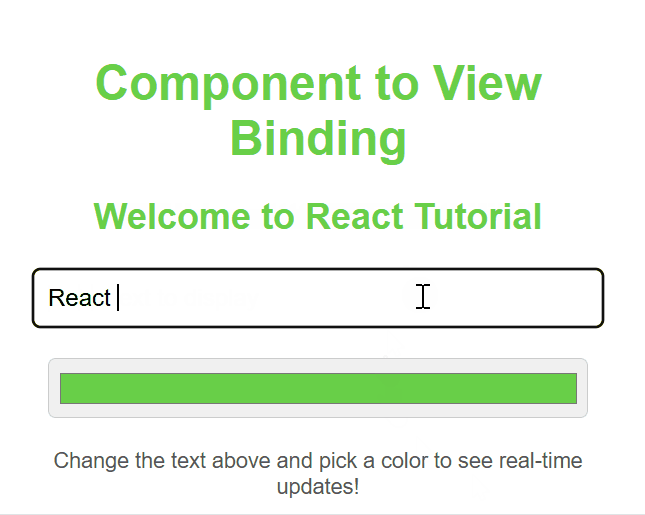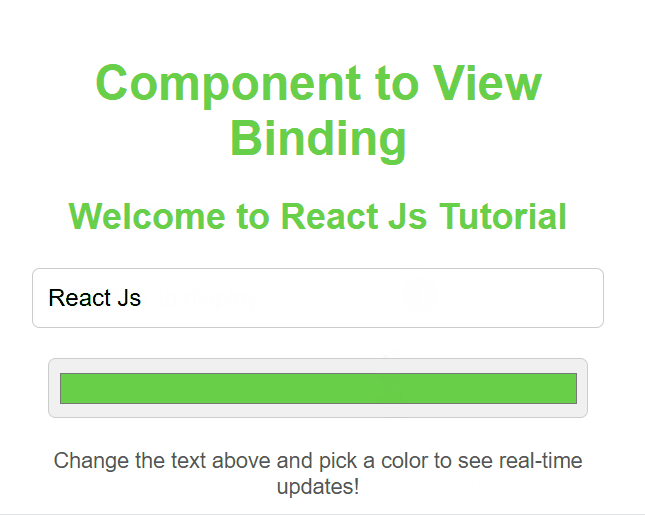
Component to View Data Binding
**In this example
- **Initializes state with subject: "ReactJS" in the constructor.
- **Renders JSX displaying the state value (subject) inside a
tag and a styled
heading.
- **Uses inline styles to center the content and change the heading color.
- **Exports the App component for use in other files.
Implementing View to Component Data Binding
It refers to handling user interactions, such as events (like button clicks), to update the component's state or trigger actions.
App.js `
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
subject: ""
};
}
handleChange = event => {
this.setState({
subject: event.target.value
})
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h4 style={{ color: "#68cf48" }}>GeeksForGeeks</h4>
<input placeholder="Enter Subject"
onChange={this.handleChange}></input>
<p><b>{this.state.subject}</b> Tutorial</p>
</div>
)
}}
export default App;
`
**In this example
- **State Initialization: Initializes subject in the state as an empty string ("").
- **Event Handling: Defines a handleChange method to update the subject state based on user input (event.target.value).
- **Two-Way Binding: Displays the updated subject dynamically in a paragraph (
) whenever the user types in the input field ().
**Output

View to Component Data Binding
Two way Data Binding
In two-way data binding, data flows in both directions. This means that the changes in the UI (like user input) are reflected in the component’s state, and changes in the state are automatically reflected in the UI. It allows the component’s state to be updated from the UI and vice versa.
React, by default, does not have built-in two-way data binding as part of its core functionality. However, developers can easily implement it using controlled components (in forms, for instance), where both the state and the input field are tied together.
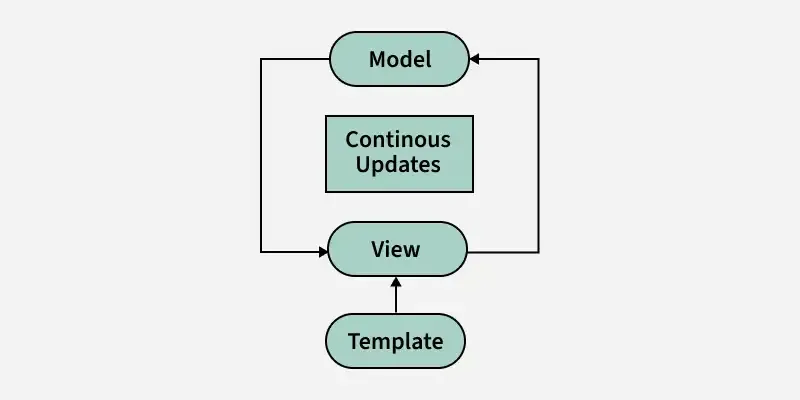
Two-Way Data Binding
- **Bidirectional Flow: Data flows both from the component to the view and from the view to the component.
- **Automatic Sync: Changes in the view (e.g., input fields) automatically update the state, and vice versa.
- **Common in Forms: Often used for form inputs where both UI and data need to stay in sync.
- **React Implementation: Mimicked via controlled components with state and event handlers JavaScript `
import React, { useState } from 'react'; import './App.css';
function App() { const [subject, setSubject] = useState("");
const handleInputChange = (event) => {
setSubject(event.target.value);
};
return (
<div className="container">
<h1>Two-Way Data Binding Example</h1>
<div className="content">
<input
type="text"
placeholder="Enter a subject..."
value={subject}
onChange={handleInputChange} // Update state on change
className="input-field"
/>
<p>Your selected subject is: <b>{subject || "___"}</b></p>
</div>
</div>
);}
export default App;
`
**Output :
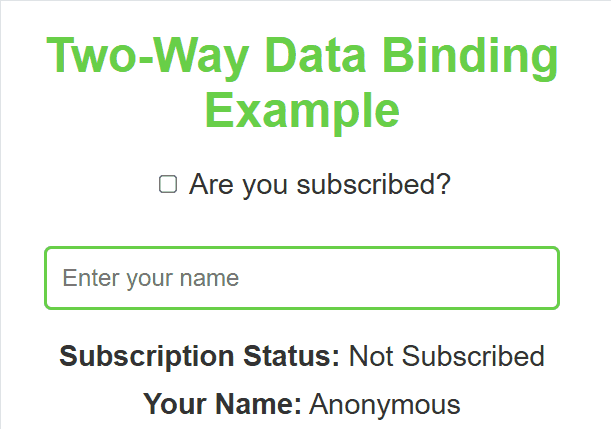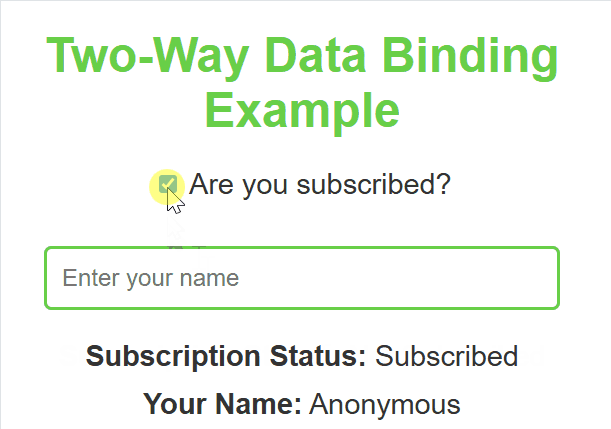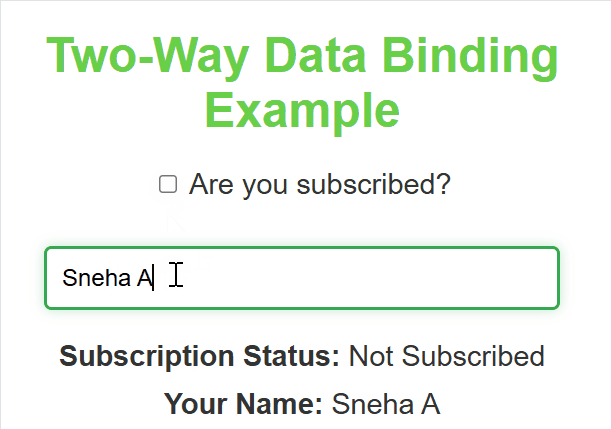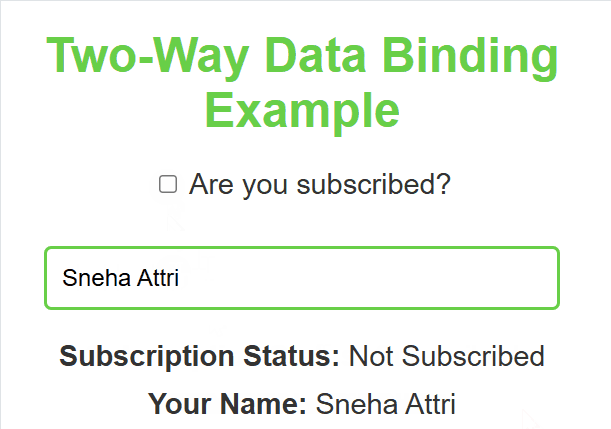
Two Way Data Binding
**In this example
- **useState hook: Initializes a state variable subject with an empty string, and provides a function setSubject to update it.
- **handleInputChange function: Updates the subject state whenever the user types into the input field, using the onChange event.
- **Input field: The input field’s value is bound to the subject state, reflecting the current value in real-time.
- **Displaying the input value: The paragraph dynamically shows the value of subject or a placeholder (___) if the subject is empty.
Difference Between One-Way Data Binding and Two-Way Data Binding
| Aspect | One-Way Data Binding | Two-Way Data Binding |
|---|---|---|
| **Data Flow | Data flows in one direction: from the component to the view (UI). | Data flows in both directions: from the component to the view and vice versa. |
| **State Update | Only the component updates the view (UI). | Both the component and the view (UI) can update each other. |
| **View to Component | The view (UI) doesn't directly update the component’s state; it only reflects changes in the state. | The view (UI) updates the component's state, and the state updates the view. |
| **Example | Button click triggering state changes (e.g., incrementing a counter). | Input field reflecting and modifying the state (e.g., text input). |
| **Complexity | Simpler to implement. | More complex because it involves synchronization between the view and component. |
| **Usage | Typically used for displaying data from the component. | Typically used for forms, inputs, and interactive elements where the UI and state must stay in sync. |
| **Performance | More efficient for read-only data or one-time updates. | May require more resources since it continuously syncs both directions. |
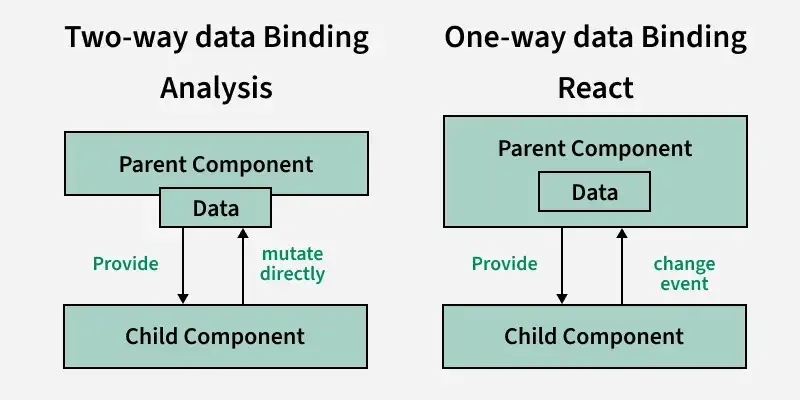
Difference between One-way Data Binding and two-way Data Binding
**Why One-way Data Binding is Preferred in React
- **Predictability: One-way data binding ensures that the flow of data is predictable. You know exactly where data is coming from (the state) and how it affects the UI.
- **Debugging: One-way data flow makes it easier to debug because you can track the state and understand how it affects the UI.
- **State Management: React’s state and props system encourages a structured way to manage data, reducing complexity when working with large applications.
- **Performance: With one-way data binding, React can optimize rendering by re-rendering only components whose state has changed, improving the overall performance of the application.
**When to Use Two-way Data Binding
Two-way data binding is useful when building forms, where user input should be reflected in the component’s state and vice versa. For example, when handling text input or selection changes, two-way data binding makes it easier to keep the UI and state in sync.
**Conclusion
ReactJS uses both one-way and two-way data binding, with one-way data binding being the default and the most common in React applications. **One-way data binding makes data flow predictable and easier to manage, while **two-way data binding allows for seamless interaction between the user and the component state, which is especially useful in forms.