ReactJS Functional Components (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 17 Feb, 2025
In ReactJS, functional components are a core part of building user interfaces. They are simple, lightweight, and powerful tools for rendering UI and handling logic. Functional components can accept props as input and return JSX that describes what the component should render.
What are Reactjs Functional Components
ReactJS functional components are JavaScript functions that return a JSX element, which is a template used to define the component's structure. JSX looks similar to HTML, but it has a special syntax that lets it be converted into **JavaScript code.
- **Stateless (before hooks): Originally, functional components were stateless and used only for rendering UI based on props.
- **Simpler Syntax: They are defined as JavaScript functions, leading to cleaner and more readable code.
- **Return JSX: Functional components return JSX (a syntax extension that allows HTML-like code inside JavaScript).
- **No, this keyword: Unlike class components, functional components do not have a this context.
- **Hooks: With hooks, functional components can manage state and side effects, making them just as powerful as class components. JavaScript `
import React from 'react';
const MyComp = (props) => { return
export default MyComp;
`
**In the example above:
- MyComp is a functional component that takes props as an argument.
- It returns a JSX element (Hello, {props.name}!), which will be rendered to the screen.
How ReactJS Functional Components Work
When a functional component receives input and is rendered, React uses props and updates the virtual DOM to ensure the UI reflects the current state.
Here's a breakdown of how this process works:
- **Props: Functional components receive input data through props, which are objects containing key-value pairs.
- **Processing Props: After receiving props, the component processes them and returns a JSX element that defines the component's structure and content.
- **Virtual DOM: When the component is rendered, React creates a virtual DOM tree that represents the current state of the application.
- **Re-rendering: If the component's props or state change, React updates the virtual DOM tree accordingly and triggers the component to re-render.
**Implementation of functional component in ReactJS :
JavaScript `
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function App() { const [message, setMessage] = useState("Hello World!");
const changeMessage = () => { setMessage("Welcome to React!"); };
return ( <div style={{ textAlign: "center", marginTop: "50px" }}>
{message}
{/* Display the dynamic message */} <button onClick={changeMessage} style={{ padding: "10px 20px", fontSize: "16px", backgroundColor: "#4CAF50", color: "white", border: "none", borderRadius: "5px", cursor: "pointer" }} > Click Me! ); }export default App;
`
**Output
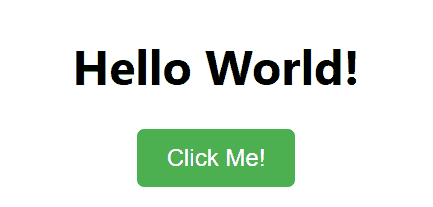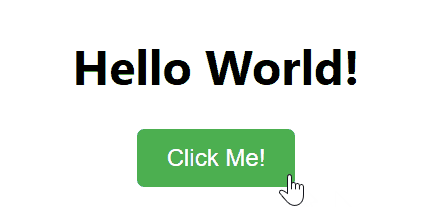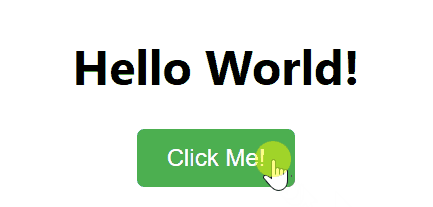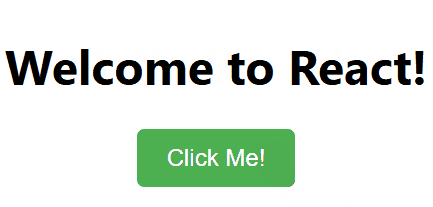
ReactJS Functional Component
Why use ReactJS Functional Components
ReactJS functional components offer several benefits over class components, including:
- **Simplicity: Functional components are simpler and easier to read than class components, making them ideal for small to medium-sized projects.
- **Performance: Functional components are faster than class components because they don’t use the this keyword, which can slow down rendering.
- **Testability: Functional components are easier to test because they are stateless and don’t rely on lifecycle methods.
- **Reusability: Functional components can be reused across multiple projects, making them a great choice for building component libraries.
When to Use ReactJS Functional Components
Functional components should be used whenever possible because they are simpler, easier to test, and more performant than class components. However, there are a few cases where functional components may not be suitable:
- **Stateful components: Functional components cannot hold state on their own. Therefore, if you need to maintain state within your component, you may need to use a class component.
- **Lifecycle methods: If you need to use lifecycle methods such as componentDidMount, componentDidUpdate, or componentWillUnmount, you will need to use a class component.
How to Pass Props to a ReactJS Functional Component
Props are used to pass data from a parent component to a child component. Props are read-only and allow you to make a component dynamic by passing different values into it.
**Passing a Single Prop to a React Functional Component:
App.js `
import React from 'react'; import Greeting from './components/Greeting';
function App() { return ( <div style={{ textAlign: "center", marginTop: "50px" }}> {/* Passing 'message' prop */} ); }
export default App;
Greeting.js
import React from 'react';
const Greeting = (props) => { return
{props.message}
;export default Greeting;
`
Output
Hello World!
**In this code
- In the App.js component, we are passing a name prop to the Greeting component.
- In Greeting.js, the name prop is accessed using props.name, and it is used to dynamically display the greeting message.
- When you render .
Advantages and Disadvantages of Functional Component.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simpler to write and understand. | No built-in lifecycle methods (without hooks). |
| Better performance without extra overhead. | May cause performance issues with frequent re-renders. |
| Supports React Hooks for managing state and effects. | Managing complex state can be harder |
| Easier to test due to predictable output | Difficult for beginners to understand hooks |
**React Functional Components vs. Class Components
| **Feature | **Functional Components | **Class Components |
|---|---|---|
| **Syntax | Simple function with Hooks | ES6 classes extending React.Component. |
| **State Management | Requires Hooks like useState | Managed via this.state and this.setState. |
| **Lifecycle Methods | Managed via useEffect | Dedicated lifecycle methods like componentDidMount. |
| **Performance | Slightly faster due to fewer abstractions | Slightly slower due to more internal logic. |