ReactJS Reconciliation (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 13 Aug, 2025
**Reconciliation is the process React uses to figure out how to efficiently update the DOM (Document Object Model) when changes occur in the UI. React's goal is to update the page as efficiently as possible, without unnecessary re-rendering or slow performance.
**Reconciliation helps in the following ways:
- Minimizes unnecessary updates: React only changes the parts of the UI that actually need to be updated, rather than re-rendering the entire page.
- Improves performance:By optimizing the update process, React reduces the number of changes to the actual DOM, which improves the performance of your application.
- **Ensures consistency: React ensures that the UI always matches the current state of your application, even as it changes over time.
How ReactJS Reconciliation Works
**The reconciliation process involves the following steps:
**1. Render Phase
- React calls the render() method of a component to generate a new virtual DOM representation.
- This new Virtual DOM is compared with the previous Virtual DOM snapshot.
**2. Diffing Algorithm
- React compares the old and new virtual DOM trees to determine the differences.
- Instead of re-rendering the entire UI, React updates only the changed nodes.
**3. Commit Phase
- Once the differences are determined, React applies the updates to the real DOM in the most efficient way.
- React batches updates and minimizes reflows and repaints for better performance.
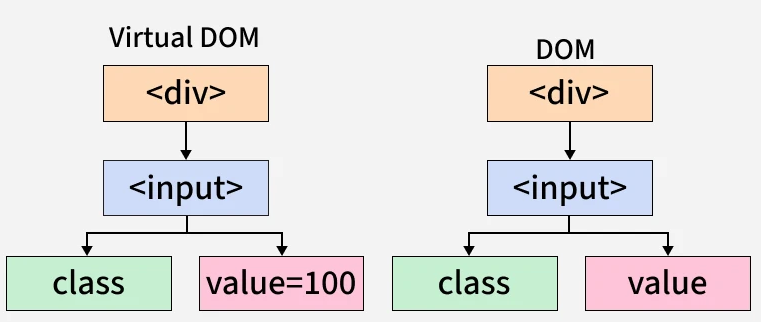
Virtual DOM in React
virtual Dom
The Virtual DOM (VDOM) is a lightweight, in-memory representation of the actual DOM elements.
- It allows React to perform DOM updates more efficiently by updating only the necessary elements, avoiding full re-renders of the entire UI.
- The Virtual DOM is a concept borrowed from the idea of "virtualization" in computing, where operations are performed on a virtual version of an object (like the DOM) before applying those changes to the actual object. This results in a more optimized and less resource-intensive approach.
How Virtual DOM Works
- **Initial Rendering: React creates an initial Virtual DOM tree when the components are first rendered. React then compares the Virtual DOM with the actual DOM and updates the actual DOM only where necessary.
- **State/Props Changes: When the state or props of a component change, React creates a new Virtual DOM tree. React then compares the new Virtual DOM with the previous one, determining what parts of the actual DOM need to be updated.
- **Efficient DOM Updates: React uses the diffing algorithm to identify the differences between the new and previous Virtual DOM trees, updating only the parts of the DOM that have changed.
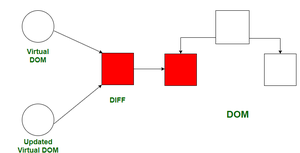
Virtual DOM in React
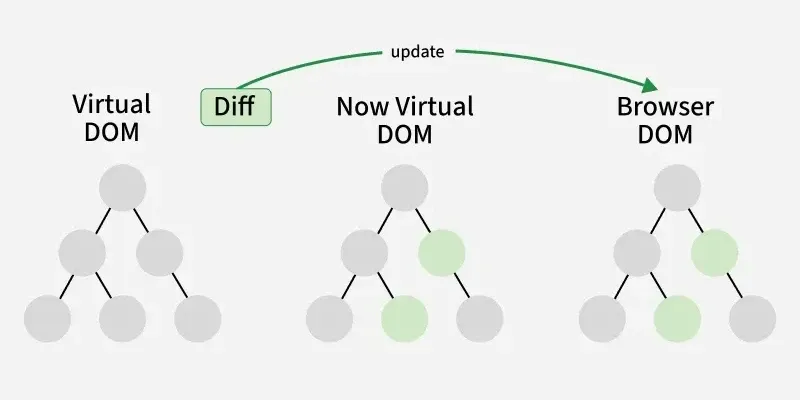
Diffing Algorithm and Its Role in Reconciliation
The Diffing Algorithm plays a crucial role in the Reconciliation process. It is responsible for
- **Identifying Differences: The diffing algorithm identifies the differences between the old and new Virtual DOM trees by comparing each element.
- **Minimizing DOM Changes: The algorithm ensures that only the minimal number of changes are applied to the actual DOM.
- **Optimization: The diffing algorithm optimizes updates by reusing elements where possible and only making necessary changes.
Diffing Algorithm
Strategies for Optimizing ReactJS Reconciliation
1. Use shouldComponentUpdate
In class components, React provides the shouldComponentUpdate() lifecycle method, which allows us to prevent re-renders if the component’s state or props haven’t changed.
index.js `
import React from 'react';
class Counter extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { count: 0, }; }
// Only re-render if count is an even number shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) { console.log('shouldComponentUpdate called'); if (nextState.count % 2 === 0) { return true; // Allow re-render } return false; // Skip re-render }
increment = () => { this.setState((prevState) => ({ count: prevState.count + 1 })); };
render() { console.log('Render called'); return (
Count: {this.state.count}
Incrementexport default Counter;
`
Output:
shouldComponentUpdate()
2. Use React.memo
React.memo is a higher-order component for functional components that prevents re-renders if the props haven't changed. It’s similar to shouldComponentUpdate but easier to use with functional components.
index.js `
import React, { useState } from 'react';
// Child component wrapped in React.memo const DisplayCounter = React.memo(({ count }) => { console.log('DisplayCounter rendered'); return
Count: {count}
; });function App() { const [count, setCount] = useState(0); const [text, setText] = useState('');
return (
export default App;
`
Output:
output
3. Use key Prop Efficiently in Lists
When rendering lists of elements, always use a unique key for each item. This helps React efficiently track and update individual elements without reordering or re-rendering the entire list.
JavaScript `
import React from 'react'; const users = [ { id: 101, name: 'Alice' }, { id: 102, name: 'Bob' }, { id: 103, name: 'Charlie' }, ];
function UserList() { return (
-
{users.map((user) => (
- {user.name} ))}
export default UserList;
`
Output
output
4. Avoid Inline Functions and Objects in JSX
Inline functions and objects in JSX create a new instance on every render, which can cause unnecessary re-renders. Instead, define functions and objects outside of the render cycle or use useCallback to memoize them.
5. Use React.PureComponent
React.PureComponent is a base class for class components that implements shallow comparison of props and state to prevent unnecessary re-renders.
JavaScript `
import React from 'react'; // PureComponent to avoid re-rendering if props haven't changed class Display extends React.PureComponent { render() { console.log('Display re-rendered'); return
Count: {this.props.count}
; } }cclass App extends React.Component { state = { count: 0, dummy: '', };
increment = () => { this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 }); };
updateDummy = () => { this.setState({ dummy: 'Changed' }); // Won't affect Display if count doesn't change };
render() { return (
export default App;
`
Output
output
What is Reconciliation in React?
- A method to style components efficiently
- The process React uses to update the DOM efficiently when UI changes
- A data storage mechanism in React
- A feature to handle server-side rendering only
Explanation:
Reconciliation refers to **how React determines what needs to change in the DOM, updating only modified parts for better performance.
Which algorithm is responsible for comparing old and new Virtual DOM trees during Reconciliation?
- Sorting Algorithm
- Searching Algorithm
- Diffing Algorithm
- Parsing Algorithm
Explanation:
React uses the **Diffing Algorithm to compare previous and new Virtual DOM trees and apply minimal updates to the real DOM.
Which method helps prevent unnecessary re-renders in class components?
- useState()
- shouldComponentUpdate()
- useMemo()
- createContext()
Explanation:
The article states that **shouldComponentUpdate() is used in class components to stop a re-render if props/state haven't changed.
What is the main benefit of using keys in a list during Reconciliation?
- Helps identify elements uniquely for efficient updates
- Automatically handles state management
- Makes JSX compile faster
Explanation:
Unique keys help React **track list items individually, improving performance by avoiding unnecessary re-renders or reordering.

Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/4
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/4
1/4 < Previous Next >