ReactJS State vs Props (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 05 Aug, 2025
In React, State allows components to manage and update internal data dynamically, while Props enables data to be passed from a parent component to a child component. Understanding their differences and use cases is essential for developing efficient React applications.
State in React
State is a built-in object in React components that holds data or information about the component. It is mutable, which means it can be updated within the component using the setState method in class components or the useState hook in functional components.
- State is local to the component and cannot be accessed by child components unless passed down as props.
- It is mutable, meaning it can change over time based on user interactions or API responses.
- When state updates, the component re-renders to reflect the changes.
- Managed using useState in functional components or this.setState in class components. JavaScript `
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function Counter() { const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<p>Count: {count}</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>Increment</button>
</div>
);}
export default Counter;
`
**Output
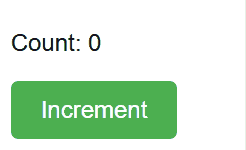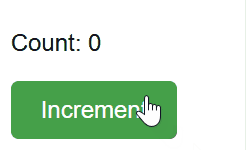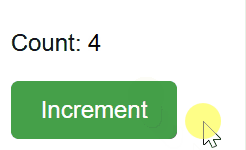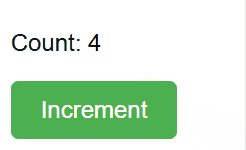
State in React
**In this example
- useState(0) initializes the state variable count with the value 0.
- The setCount function is used to update the state whenever the button is clicked. This triggers a re-render, updating the displayed count.
Props in React
Props (short for Properties) are used to pass data from a parent component to a child component. Unlike state, props are immutable, meaning they cannot be modified within the receiving component.
- Props allow components to be reusable and dynamic.
- Props are read-only and cannot be changed by the child component.
- They help in data communication between components.
- Passed as attributes in JSX elements. JavaScript `
import React from 'react';
function Greeting({ name }) { return
Hello, {name}!
; }function App() { return ; }
export default App;
`
**Output

Props in React
Here, the Greeting component receives a prop named name and displays a personalized message. The App component passes the value "Jiya" as a prop.
Difference between State and Props in React
| Aspect | State | Props |
|---|---|---|
| Modification | Can be changed by the component itself. | Cannot be changed by the receiving component; props are read-only. |
| Communication | Facilitates communication within a component. | Facilitates communication between components (from parent to child). |
| Re-rendering | Changes in state trigger a re-render of the component where the state is modified. | Changes in props cause a re-render of the child component that receives them, but the parent manages them. |
| Component Type | State is used in **class components (via this.state and this.setState) or **functional components (via useState). | Props are used in both class and functional components. |
| Effect on Parent | Changing state only affects the component where the state is defined. | Changing props doesn't affect the parent component directly; the parent controls the props passed to the child. |
| Responsibility | Managed by the component itself. | Managed by the parent component. |
| Examples | const [count, setCount] = useState(0); (functional component with hook) | (passing props to a child component) |
When to Use State and Props?
- **Use State when you need to manage data that can change over time within a component (e.g., form inputs, counters, UI toggles).
- **Use Props when you need to pass data from a parent component to a child component to make components reusable.