Deletion at beginning (Removal of first node) in a Linked List (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 30 Aug, 2024
Given a **linked list, The task is to **remove the first node from the given **linked list.
**Examples:
**Input : head : 3 -> 12 -> 15 -> 18 -> NULL
**Output : 12 -> 15 -> 18 -> NULL**Input : head : 2 -> 4 -> 6 -> 8 -> 33 -> 67 -> NULL
**Output : 4 -> 6 -> 8 -> 33 -> 67 -> NULL
**By Shifting head node to next node of head - O(1) Time and O(1) Space
To remove the first node of a **linked list, store the current **head in a temporary variable ****(temp)**, move the **head pointer to the next node, **delete the temporary **head node and finally , return the new **head of the linked list.
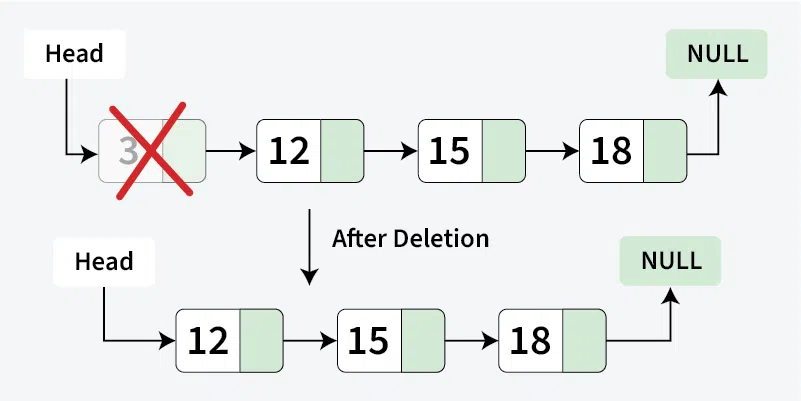
Deletion at beginning in a Linked List
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ `
// C++ program to delete the head node // from a linked list
#include using namespace std;
struct Node { int data; Node *next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = nullptr; } };
// Delete the head node and return the new head Node* deleteHead(Node* head) {
// Check if the list is empty
if (head == nullptr)
return nullptr;
// Store the current head in a
// temporary variable
Node* temp = head;
// Move the head pointer to the next node
head = head->next;
// Free the memory of the old head node
delete temp;
return head;}
void printList(Node* curr) { while (curr != nullptr) { cout << curr->data << " "; curr = curr->next; } }
int main() {
// Create a hard-coded linked list:
// 3 -> 12 -> 15 -> 18
Node* head = new Node(3);
head->next = new Node(12);
head->next->next = new Node(15);
head->next->next->next = new Node(18);
head = deleteHead(head);
printList(head);
return 0;}
C
// C program to delete the head node // from a linked list
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; };
// Delete the head node and return the new head struct Node* deleteHead(struct Node* head) {
// Check if the list is empty
if (head == NULL)
return NULL;
// Store the current head in a
// temporary variable
struct Node* temp = head;
// Move the head pointer to the next node
head = head->next;
// Free the memory of the old head node
free(temp);
return head;}
void printList(struct Node* curr) {
while (curr != NULL) {
printf("%d ", curr->data);
curr = curr->next;
}} struct Node *createNode(int new_data){ struct Node *new_node = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); new_node->data = new_data; new_node->next = NULL; return new_node; }
int main() {
// Create a hard-coded linked list:
// 3 -> 12 -> 15 -> 18
struct Node* head = createNode(3);
head->next = createNode(12);
head->next->next = createNode(15);
head->next->next->next = createNode(18);
head = deleteHead(head);
printList(head);
return 0;}
Java
// Java program to delete the head node // from a linked list
class Node { int data; Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}}
public class GfG {
// Delete the head node and return the new head
static Node deleteHead(Node head) {
// Check if the list is empty
if (head == null)
return null;
// Store the current head in a temporary variable
Node temp = head;
// Move the head pointer to the next node
head = head.next;
// Help the garbage collector by
// removing the reference
temp = null;
return head;
}
static void printList(Node curr) {
while (curr != null) {
System.out.print(curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a hard-coded linked list:
// 3 -> 12 -> 15 -> 18
Node head = new Node(3);
head.next = new Node(12);
head.next.next = new Node(15);
head.next.next.next = new Node(18);
head = deleteHead(head);
printList(head);
}}
Python
Python program to delete the head node
from a linked list
class Node: def init(self, data): self.data = data self.next = None
Delete the head node and return the new head
def delete_head(head):
# Check if the list is empty
if head is None:
return None
# Store the current head in a temporary variable
temp = head
# Move the head pointer to the next node
head = head.next
# Delete the old head by removing the reference
del temp
return headdef print_list(curr): while curr: print(curr.data, end=" ") curr = curr.next
if name == "main":
# Create a hard-coded linked list:
# 3 -> 12 -> 15 -> 18
head = Node(3)
head.next = Node(12)
head.next.next = Node(15)
head.next.next.next = Node(18)
head = delete_head(head)
print_list(head)C#
// C# program to delete the head node // from a linked list
using System;
class Node { public int data; public Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}}
class GfG {
// Delete the head node and return the new head
static Node DeleteHead(Node head) {
// Check if the list is empty
if (head == null)
return null;
// Move the head pointer to the next node
head = head.next;
return head;
}
static void PrintList(Node curr) {
while (curr != null) {
Console.Write(curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
}
static void Main() {
// Create a hard-coded linked list:
// 3 -> 12 -> 15 -> 18
Node head = new Node(3);
head.next = new Node(12);
head.next.next = new Node(15);
head.next.next.next = new Node(18);
head = DeleteHead(head);
PrintList(head);
}}
JavaScript
// JavaScript program to delete the head //node from a linked list
class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; } }
// Delete the head node and return the new head function deleteHead(head) {
// Check if the list is empty
if (head === null)
return null;
// Store the current head in a temporary variable
let temp = head;
// Move the head pointer to the next node
head = head.next;
// Free the memory of the old head node
temp = null;
return head;}
function printList(curr) { while (curr !== null) { console.log(curr.data + " "); curr = curr.next; }
}
// Create a hard-coded linked list: // 3 -> 12 -> 15 -> 18 let head = new Node(3); head.next = new Node(12); head.next.next = new Node(15); head.next.next.next = new Node(18);
head = deleteHead(head); printList(head);
`
**Time Complexity: O(1), because the operation to delete the head node is performed in constant time.
**Space Complexity: O(1)