Right view of Binary Tree using Queue (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 26 Sep, 2024
Given a Binary Tree, the task is to print the Right view of it. The right view of a Binary Tree is a set of **rightmost nodes for every level.
**Examples:
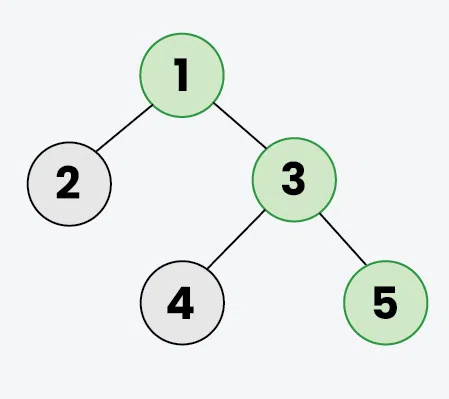
_Example 1: The **Green _colored nodes (1, 3, 5) represents the Right view in the below Binary tree.
_Example 2: The **Green _colored nodes (1, 3, 4, 5) represents the Right view in the below Binary tree.
**Approach:
The idea is to traverse the treelevel by leveland print the last node at each level (**the rightmost node). A simple solution is to do level order traversal and print the last node in every level.
Follow the steps below to implement the idea:
- Perform a level order traversal of the binary tree.
- For each level, print the **last node in it's level order traversal.
- Move to the **next level and repeat until all levels are processed.
Below is the implementation of above approach:
C++ `
// C++ program to print right view of Binary // tree using Level order Traversal #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
class Node { public: int data; Node* left; Node* right;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = right = nullptr;
}};
// Function to return the right view of the binary tree vector rightView(Node* root) { vector result;
if (root == nullptr) return result;
// Queue for level order traversal
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
// Number of nodes at current level
int levelSize = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
Node* curr = q.front();
q.pop();
// If it's the last node of the current level
if (i == levelSize - 1) {
result.push_back(curr->data);
}
// Enqueue left child
if (curr->left != nullptr) {
q.push(curr->left);
}
// Enqueue right child
if (curr->right != nullptr) {
q.push(curr->right);
}
}
}
return result;}
void printArray(vector& arr) { for (int val : arr) { cout << val << " "; } cout << endl; }
int main() {
// Representation of the input tree:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \
// 4 5
Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->right->left = new Node(4);
root->right->right = new Node(5);
vector<int> result = rightView(root);
printArray(result);
return 0;}
Java
// Java program to print right view of Binary // tree using Level order Traversal import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue;
class Node { int data; Node left, right;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = right = null;
}}
class GfG {
// Function to return the right view of the binary tree
static ArrayList<Integer> rightView(Node root) {
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return result;
}
// Queue for level order traversal
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
// Number of nodes at the current level
int levelSize = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
Node curr = q.poll();
// If it's the last node of the current level
if (i == levelSize - 1) {
result.add(curr.data);
}
// Enqueue left child
if (curr.left != null) {
q.add(curr.left);
}
// Enqueue right child
if (curr.right != null) {
q.add(curr.right);
}
}
}
return result;
}
static void printArray(ArrayList<Integer> arr) {
for (int val : arr) {
System.out.print(val + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Representation of the input tree:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \
// 4 5
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.right.left = new Node(4);
root.right.right = new Node(5);
ArrayList<Integer> result = rightView(root);
printArray(result);
}}
Python
Python program to print right view of Binary Tree
using Level Order Traversal
from collections import deque
class Node: def init(self, data): self.data = data self.left = None self.right = None
Function to return the right view of the binary tree
def rightView(root): result = []
if root is None:
return result
# Queue for level order traversal
q = deque([root])
while q:
# Number of nodes at the current level
level_size = len(q)
for i in range(level_size):
curr = q.popleft()
# If it's the last node of the
# current level
if i == level_size - 1:
result.append(curr.data)
# Enqueue left child
if curr.left is not None:
q.append(curr.left)
# Enqueue right child
if curr.right is not None:
q.append(curr.right)
return resultdef printArray(arr): for val in arr: print(val, end=" ") print()
if name == "main":
# Representation of the input tree:
# 1
# / \
# 2 3
# / \
# 4 5
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.right.left = Node(4)
root.right.right = Node(5)
result = rightView(root)
printArray(result)C#
// C# program to print right view of Binary Tree // using Level Order Traversal using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
class Node { public int data; public Node left, right;
public Node(int x) {
data = x;
left = right = null;
}}
class GfG {
// Function to return the right view of
// the binary tree
static List<int> rightView(Node root) {
List<int> result = new List<int>();
if (root == null) {
return result;
}
// Queue for level order traversal
Queue<Node> queue = new Queue<Node>();
queue.Enqueue(root);
while (queue.Count > 0) {
// Number of nodes at the current level
int levelSize = queue.Count;
for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
Node curr = queue.Dequeue();
// If it's the last node of
// the current level
if (i == levelSize - 1) {
result.Add(curr.data);
}
// Enqueue left child
if (curr.left != null) {
queue.Enqueue(curr.left);
}
// Enqueue right child
if (curr.right != null) {
queue.Enqueue(curr.right);
}
}
}
return result;
}
static void PrintList(List<int> arr) {
foreach (int val in arr) {
Console.Write(val + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void Main(string[] args) {
// Representation of the input tree:
// 1
// / \
// 2 3
// / \
// 4 5
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.right.left = new Node(4);
root.right.right = new Node(5);
List<int> result = rightView(root);
PrintList(result);
}}
JavaScript
// JavaScript program to print right view of Binary // tree using Level order Traversal
class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } }
// Function to return the right view of the binary tree function rightView(root) { let result = [];
if (root === null) {
return result;
}
// Queue for level order traversal
let queue = [root];
while (queue.length > 0) {
// Number of nodes at the current level
let levelSize = queue.length;
for (let i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
let curr = queue.shift();
// If it's the last node of the
// current level
if (i === levelSize - 1) {
result.push(curr.data);
}
// Enqueue left child
if (curr.left !== null) {
queue.push(curr.left);
}
// Enqueue right child
if (curr.right !== null) {
queue.push(curr.right);
}
}
}
return result;}
function printArray(arr) { console.log(arr.join(' ')); }
// Representation of the input tree:
// 1
// /
// 2 3
// / \
// 4 5
let root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.right.left = new Node(4);
root.right.right = new Node(5);
let result = rightView(root);
printArray(result);
`
**Time Complexity: O(n), We traverse all nodes of the binary tree exactly once, where **n is the number of nodes.
**Auxiliary Space: O(n) since using auxiliary space for queue.
**Related articles: