Ruby | Case Statement (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 26 Oct, 2018
The case statement is a multiway branch statement just like a switch statement in other languages. It provides an easy way to forward execution to different parts of code based on the value of the expression. There are 3 important keywords which are used in the case statement:
- case: It is similar to the switch keyword in another programming languages. It takes the variables that will be used by when keyword.
- when: It is similar to the case keyword in another programming languages. It is used to match a single condition. There can be multiple when statements into a single case statement.
- else: It is similar to the default keyword in another programming languages. It is optional and will execute when nothing matches.
Syntax:
case expression
when expression 1
your code
when expression 2
your code
. .
else
your code
end
Flow Chart: 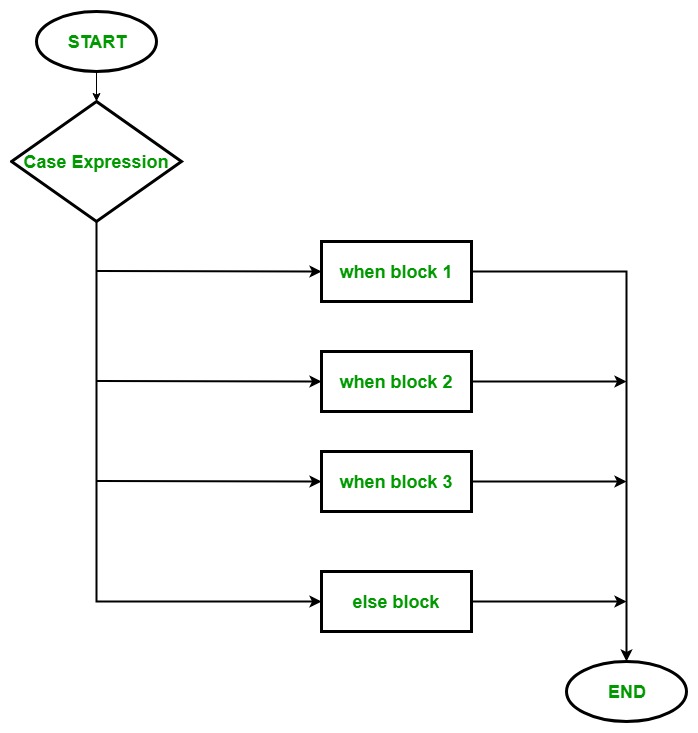 Example 1:
Example 1:
Ruby `
Ruby program to illustrate the
concept of case statement
#!/usr/bin/ruby
print "Input from one, two, three, four: "
taking input from user
str = gets.chomp
hardcoded input
str = "two"
using case statement
case str
using when
when "one"
puts 'Input is 1'
when "two"
puts 'Input is 2'
when "three"
puts 'Input is 3'
when "four"
puts 'Input is 4'
else
puts "Default!"
end
`
Output:
Input from one, two, three, four: Input is 2
Example 2:
Ruby `
Ruby program to illustrate
case statement
#!/usr/bin/ruby
marks = 70
marks is the input
for case statement
case marks
using range operators ..
when 0..32 puts "You fail!"
when 33..40 puts "You got C grade!"
when 41..60 puts "You got B grade!"
else puts "You got A grade!"
end
`
Output:
You got A grade!
Important Points:
- In case statement the when statement can contain multiple values and range(see above example).Example: Ruby `
Ruby program to illustrate
how to use multiple values
in when statement
choice = "5"
using 'case' statement
case choice
# here 'when' statement contains
# the two values
when "1","2"
puts "You order Espresso!"
when "3","4"
puts "You order Short Macchiato!"
when "5","6"
puts "You order Ristretto!"
when "7","8"
puts "You order Cappuccino!"
else
"No Order!"
end
` Output:
You order Ristretto!
- You can also use case statement without any value.Example: Ruby `
Ruby program to illustrate no
value in case statement
str = "GeeksforGeeks"
here case statement
has no value
case
# using match keyword to check
when str.match(/\d/)
puts 'String contains numbers'
when str.match(/[a-zA-Z]/)
puts 'String contains letters' else
puts 'String does not contain numbers & letters'
end
` Output:
String contains letters
- You can use case statement in method call. Like method call, a case statement will always return a single object.Example: Ruby `
Ruby program to illustrate case
statement in a method call
str = "1234"
here case statement
has no value & used as
in puts method call
puts case
# using match keyword to check
when str.match(/\d/)
'String contains numbers'
when str.match(/[a-zA-Z]/)
'String contains letters' else
'String does not contain numbers & letters' end
` Output:
String contains numbers
Explanation: Here we are using the case statement in a puts method call. The benefit of doing this that we can omit the puts from the when statement.