Secure Socket Layer (SSL) (original) (raw)
SSL or Secure Sockets Layer, is an Internet security protocol that encrypts data to keep it safe. It was created by Netscape in 1995 to ensure privacy, authentication, and data integrity in online communications. SSL is the older version of what we now call TLS (Transport Layer Security).
Websites using SSL/TLS have "HTTPS" in their URL instead of "HTTP."
Working of SSL
- **Encryption: SSL encrypts data transmitted over the web, ensuring privacy. If someone intercepts the data, they will see only a jumble of characters that is nearly impossible to decode.
- **Authentication: SSL starts an authentication process called a handshake between two devices to confirm their identities, making sure both parties are who they claim to be.
- **Data Integrity: SSL digitally signs data to ensure it hasn't been tampered with, verifying that the data received is exactly what was sent by the sender.
Importance of SSL
Originally, data on the web was transmitted in plaintext, making it easy for anyone who intercepted the message to read it. For example, if someone logged into their email account, their username and password would travel across the Internet unprotected.
SSL was created to solve this problem and protect user privacy. By encrypting data between a user and a web server, SSL ensures that anyone who intercepts the data sees only a scrambled mess of characters. This keeps the user's login credentials safe, visible only to the email service.
Additionally, SSL helps prevent cyber attacks by:
- **Authenticating Web Servers: Ensuring that users are connecting to the legitimate website, not a fake one set up by attackers.
- **Preventing Data Tampering: Acting like a tamper-proof seal, SSL ensures that the data sent and received hasn't been altered during transit.
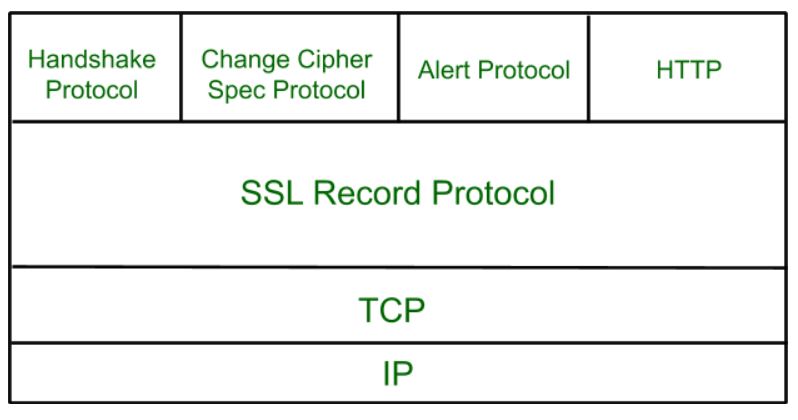
Secure Socket Layer Protocols
- SSL Record Protocol
- Handshake Protocol
- Change-Cipher Spec Protocol
- Alert Protocol
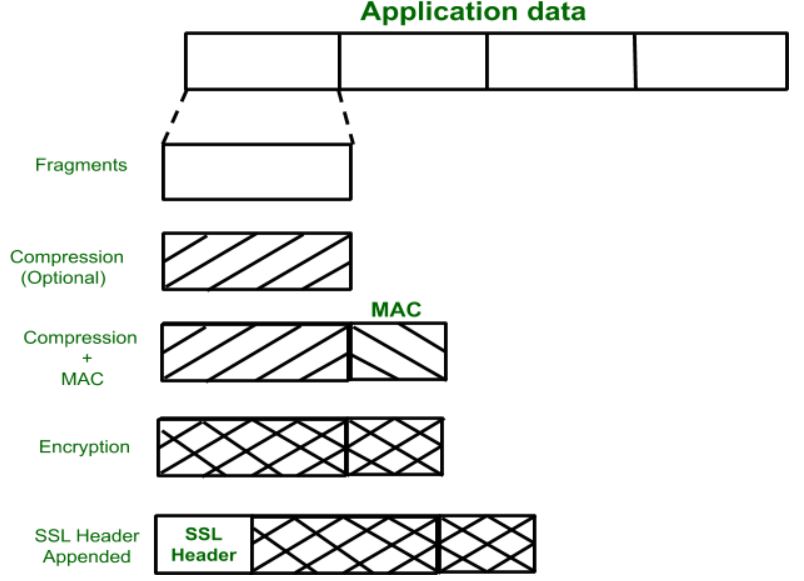
**SSL Record Protocol
SSL Record provides two services to SSL connection.
- Confidentiality
- Message Integrity
In the SSL Record Protocol application data is divided into fragments. The fragment is compressed and then encrypted MAC (Message Authentication Code) generated by algorithms like SHA (Secure Hash Protocol) and MD5 (Message Digest) is appended. After that encryption of the data is done and in last SSL header is appended to the data.
 Handshake Protocol
Handshake Protocol
Handshake Protocol is used to establish sessions. This protocol allows the client and server to authenticate each other by sending a series of messages to each other. Handshake protocol uses four phases to complete its cycle.
- **Phase-1: In Phase-1 both Client and Server send hello-packets to each other. In this IP session, cipher suite and protocol version are exchanged for security purposes.
- **Phase-2: Server sends it certificate and Server-key-exchange. The server end phase-2 by sending the Server-hello-end packet.
- **Phase-3: In this phase, Client replies to the server by sending it certificate and Client-exchange-key.
- **Phase-4: In Phase-4 Change Cipher Spec occurs and after this the Handshake Protocol ends.

SSL Handshake Protocol Phases diagrammatic representation
Change-Cipher Protocol
This protocol uses the SSL record protocol. Unless Handshake Protocol is completed, the SSL record Output will be in a pending state. After the handshake protocol, the Pending state is converted into the current state.
Change-cipher protocol consists of a single message which is 1 byte in length and can have only one value. This protocol's purpose is to cause the pending state to be copied into the current state.

Alert Protocol
This protocol is used to convey SSL-related alerts to the peer entity. Each message in this protocol contains 2 bytes.
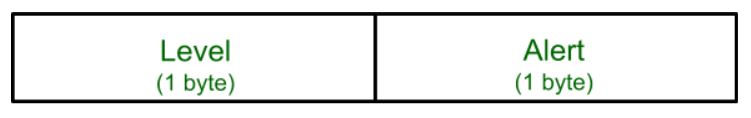
The level is further classified into two parts:
**Warning (level = 1)
This Alert has no impact on the connection between sender and receiver. Some of them are:
- **Bad Certificate: When the received certificate is corrupt.
- **No Certificate: When an appropriate certificate is not available.
- **Certificate Expired: When a certificate has expired.
- **Certificate Unknown: When some other unspecified issue arose in processing the certificate, rendering it unacceptable.
- **Close Notify: It notifies that the sender will no longer send any messages in the connection.
- **Unsupported Certificate: The type of certificate received is not supported.
- **Certificate Revoked: The certificate received is in revocation list.
**Fatal Error (level = 2):
This Alert breaks the connection between sender and receiver. The connection will be stopped, cannot be resumed but can be restarted. Some of them are :
- **Handshake Failure: When the sender is unable to negotiate an acceptable set of security parameters given the options available.
- **Decompression Failure: When the decompression function receives improper input.
- **Illegal Parameters: When a field is out of range or inconsistent with other fields.
- **Bad Record MAC: When an incorrect MAC was received.
- **Unexpected Message: When an inappropriate message is received.
The second byte in the Alert protocol describes the error.
Salient Features of Secure Socket Layer
- The advantage of this approach is that the service can be tailored to the specific needs of the given application.
- Secure Socket Layer was originated by Netscape.
- SSL is designed to make use of TCP to provide reliable end-to-end secure service.
- This is a two-layered protocol.
**Versions of SSL
SSL 1 - Never released due to high insecurity
SSL 2 - Released in 1995
SSL 3 - Released in 1996
TLS 1.0 - Released in 1999
TLS 1.1 - Released in 2006
TLS 1.2 - Released in 2008
TLS 1.3 - Released in 2018
SSL Certificate
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate is a digital certificate used to secure and verify the identity of a website or an online service. The certificate is issued by a trusted third-party called a Certificate Authority (CA), who verifies the identity of the website or service before issuing the certificate.
The SSL certificate has several important characteristics that make it a reliable solution for securing online transactions :
- **Encryption: The SSL certificate uses encryption algorithms to secure the communication between the website or service and its users. This ensures that the sensitive information, such as login credentials and credit card information, is protected from being intercepted and read by unauthorized parties.
- **Authentication: The SSL certificate verifies the identity of the website or service, ensuring that users are communicating with the intended party and not with an impostor. This provides assurance to users that their information is being transmitted to a trusted entity.
- **Integrity: The SSL certificate uses message authentication codes (MACs) to detect any tampering with the data during transmission. This ensures that the data being transmitted is not modified in any way, preserving its integrity.
- **Non-repudiation: SSL certificates provide non-repudiation of data, meaning that the recipient of the data cannot deny having received it. This is important in situations where the authenticity of the information needs to be established, such as in e-commerce transactions.
- **Public-key cryptography: SSL certificates use public-key cryptography for secure key exchange between the client and server. This allows the client and server to securely exchange encryption keys, ensuring that the encrypted information can only be decrypted by the intended recipient.
- **Session management: SSL certificates allow for the management of secure sessions, allowing for the resumption of secure sessions after interruption. This helps to reduce the overhead of establishing a new secure connection each time a user accesses a website or service.
- **Certificates issued by trusted CAs: SSL certificates are issued by trusted CAs, who are responsible for verifying the identity of the website or service before issuing the certificate. This provides a high level of trust and assurance to users that the website or service they are communicating with is authentic and trustworthy.
In addition to these key characteristics, SSL certificates also come in various levels of validation, including Domain Validation (DV), Organization Validation (OV), and Extended Validation (EV). The level of validation determines the amount of information that is verified by the CA before issuing the certificate, with EV certificates providing the highest level of assurance and trust to users. For more information about SSL certificates for each Validation level type, please refer to Namecheap.
Overall, the SSL certificate is an important component of online security, providing encryption, authentication, integrity, non-repudiation, and other key features that ensure the secure and reliable transmission of sensitive information over the internet.
Types of SSL Certificates
There are different types of SSL certificates, each suited for different needs:
- **Single-Domain SSL Certificate: This type covers only one specific domain. A domain is the name of a website, like www.geeksforgeeks.org. For instance, if you have a single-domain SSL certificate for www.geeksforgeeks.org, it won't cover any other domains or subdomains.
- **Wildcard SSL Certificate: Similar to a single-domain certificate, but it also covers all subdomains of a single domain. For example, if you have a wildcard certificate for *.geeksforgeeks.org, it would cover www.geeksforgeeks.org, blog.www.geeksforgeeks.org, and any other subdomain under example.com.
- **Multi-Domain SSL Certificate: This type can secure multiple unrelated domains within a single certificate.
These certificates vary in scope and flexibility, allowing website owners to choose the appropriate level of security coverage based on their needs.
SSL certificates have different validation levels, which determine how thoroughly a business or organization is vetted:
- **Domain Validation (DV): This is the simplest and least expensive level. To get a DV certificate, a business just needs to prove it owns the domain (like www.geeksforgeeks.org).
- **Organization Validation (OV): This involves a more hands-on verification process. The Certificate Authority (CA) directly contacts the organization to confirm its identity before issuing the certificate. OV certificates provide more assurance to users about the legitimacy of the organization.
- **Extended Validation (EV): This is the most rigorous level of validation. It requires a comprehensive background check of the organization to ensure it's legitimate and trustworthy. EV certificates are recognized by the green address bar in web browsers, indicating the highest level of security and trustworthiness.
These validation levels help users understand the level of security and trust they can expect when visiting websites secured with SSL certificates.
Are SSL and TLS the Same thing?
SSL is the direct predecessor of TLS (Transport Layer Security). In 1999, the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) proposed an update to SSL. Since this update was developed by the IETF without Netscape's involvement, the name was changed to TLS. The changes between the last version of SSL (3.0) and the first version of TLS were not significant; the name change mainly signified new ownership.
Because SSL and TLS are so similar, people often use the terms interchangeably. Some still call it SSL, while others use "SSL/TLS encryption" since SSL is still widely recognized.
Check SSL Version
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) hasn't been updated since SSL 3.0 back in 1996 and is now considered outdated. It has known vulnerabilities, so security experts advise against using it. Most modern web browsers no longer support SSL.
TLS (Transport Layer Security) is the current encryption protocol used online. Despite this, many still refer to it as "SSL encryption," causing confusion when people look for security solutions. Nowadays, any vendor offering "SSL" is likely providing TLS protection, which has been the standard for over 20 years. The term "SSL protection" is still used widely on product pages because many users still search for it.