Skewed Binary Tree (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 22 Jul, 2021
A skewed binary tree is a type of binary tree in which all the nodes have only either one child or no child.
Types of Skewed Binary trees
There are 2 special types of skewed tree:
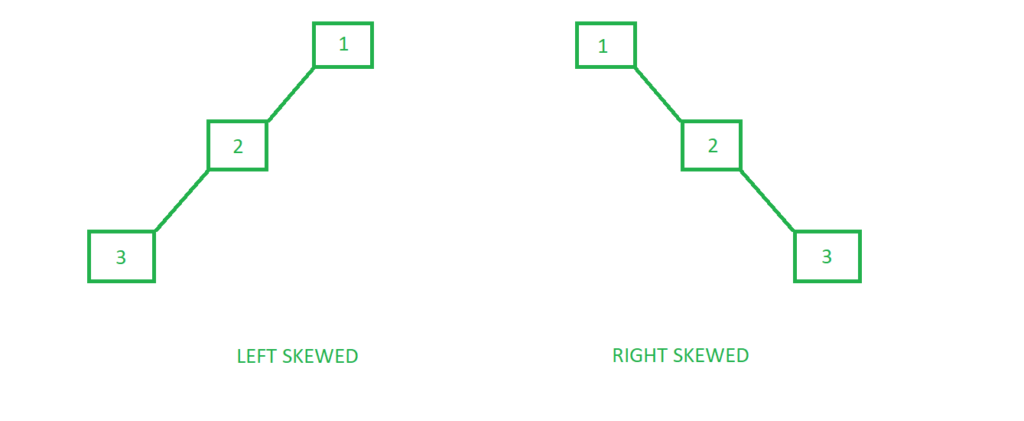
1. Left Skewed Binary Tree:
These are those skewed binary trees in which all the nodes are having a left child or no child at all. It is a left side dominated tree. All the right children remain as null.
Below is an example of a left-skewed tree:
C++ `
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
// A Tree node struct Node { int key; struct Node *left, *right; };
// Utility function to create a new node Node* newNode(int key) { Node* temp = new Node; temp->key = key; temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return (temp);}
// Driver code int main() { /* 1 / 2 / 3 / Node root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->left->left = newNode(3);
return 0;}
Java
// Java implementation of above approach import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// A Tree node static class Node { int key; Node left, right; };
// Utility function to create a new node static Node newNode(int key) { Node temp = new Node(); temp.key = key; temp.left = temp.right = null;
return (temp);}
// Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { /* 1 / 2 / 3 */ Node root = newNode(1); root.left = newNode(2); root.left.left = newNode(3); } }
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
Python3
Python3 implementation of the above approach
Class that represents an individual
node in a Binary Tree
class Node: def init(self, key):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.val = key
Driver code
""" 1 / 2 / 3 """ root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.left.left = Node(2)
This code is contributed by dhruvsantoshwar
C#
// C# implementation of above approach using System;
class GFG {
// A Tree node
public class Node
{
public int key;
public Node left, right;
};
// Utility function to create a new node
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return (temp);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
/*
1
/
2
/
3
*/
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.left.left = newNode(3);
} }
// This code is contributed by AnkitRai01
JavaScript
`
2. Right Skewed Binary Tree:
These are those skewed binary trees in which all the nodes are having a right child or no child at all. It is a right side dominated tree. All the left children remain as null.
Below is an example of a right-skewed tree:
C++ `
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
// A Tree node struct Node { int key; struct Node *left, *right; };
// Utility function to create a new node Node* newNode(int key) { Node* temp = new Node; temp->key = key; temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return (temp);}
// Driver code
int main()
{
/*
1
2
3
/
Node root = newNode(1);
root->right = newNode(2);
root->right->right = newNode(3);
return 0;}
Java
// Java implementation of above approach import java.util.*; class GFG {
// A Tree node static class Node { int key; Node left, right; };
// Utility function to create a new node static Node newNode(int key) { Node temp = new Node(); temp.key = key; temp.left = temp.right = null;
return (temp);}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
/*
1
2
3
*/
Node root = newNode(1);
root.right = newNode(2);
root.right.right = newNode(3);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
Python3
Python3 implementation of the above approach
A Tree node
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.val = key
Driver code
"""
1
2
3
"""
root = Node(1)
root.right = Node(2)
root.right.right = Node(3)
This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
C#
// C# implementation of above approach using System;
class GFG {
// A Tree node public class Node { public int key; public Node left, right; };
// Utility function to create a new node static Node newNode(int key) { Node temp = new Node(); temp.key = key; temp.left = temp.right = null;
return (temp);}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
/*
1
2
3
*/
Node root = newNode(1);
root.right = newNode(2);
root.right.right = newNode(3);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
JavaScript
`