Sort an array after applying the given equation (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 16 May, 2025
Given an integer array **arr[] sorted in ascending order, along with three integers: **A, B, and C. The task is to transform each element **x in the array using the quadratic function **A*(x^2) + B*x + C. After applying this transformation to every element, return the modified array in sorted order.
**Examples:
**Input: arr[] = [-4, -2, 0, 2, 4], A = 1, B = 3, C = 5
**Output: [3, 5, 9, 15, 33]
**Explanation: After applying f(x) = 1*x2+ 3*x + 5 to each x, we get [9, 3, 5, 15, 33]. After sorting this array, the array becomes [3, 5, 9, 15, 33].**Input: arr[] = [-3, -1, 2, 4], A = -1, B = 0, C = 0
**Output: [-16, -9, -4, -1]
**Explanation: After applying f(x) = -1*x2 to each x, we get [-9, -1, -4, -16 ]. After sorting this array, the array becomes [-16, -9, -4, -1].**Input: arr[] = [-1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4], A = -1, B = 2, C = -1
**Output: [-9, -4, -4, -1, -1, 0]
Table of Content
- [Brute Force Approach] Apply the Equation and Sort - O(n*log(n)) Time and O(1) Space
- [Expected Approach] Using Two Pointers - O(n) Time and O(n) Space
[Brute Force Approach] Apply the Equation and Sort - O(n*log(n)) Time and O(1) Space
The **idea is to directly transform each element in the array, i.e. for each element **x in **arr[], apply the given equation **A*x 2 + B*x + C in-place and then simply **sort the array in **ascending order.
C++ `
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
// Function to apply quadratic transformation int evaluate(int x, int A, int B, int C) { return A * x * x + B * x + C; }
// Function to transform and sort the array in-place vector sortArray(vector &arr, int A, int B, int C) { int n = arr.size();
vector<int> transformed;
// Apply the transformation
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
transformed.push_back(evaluate(arr[i], A, B, C));
}
// Sort the transformed array
sort(transformed.begin(), transformed.end());
return transformed;}
int main() { vector arr = {-4, -2, 0, 2, 4}; int A = 1, B = 3, C = 5;
vector<int> res = sortArray(arr, A, B, C);
for (int val : res) {
cout << val << " ";
}
return 0;}
Java
import java.util.*;
class GfG {
// Function to apply quadratic transformation
static int evaluate(int x, int A, int B, int C) {
return A * x * x + B * x + C;
}
// Function to transform and sort the array (returns ArrayList<Integer>)
static ArrayList<Integer> sortArray(int[] arr, int A, int B, int C) {
int n = arr.length;
Integer[] transformed = new Integer[n];
// Apply the transformation and store in array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
transformed[i] = evaluate(arr[i], A, B, C);
}
// Sort the array
Arrays.sort(transformed);
// Convert to ArrayList and return
return new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(transformed));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {-4, -2, 0, 2, 4};
int A = 1, B = 3, C = 5;
ArrayList<Integer> res = sortArray(arr, A, B, C);
for (int val : res) {
System.out.print(val + " ");
}
}}
Python
Python Code to Sort array after applying
equation using Brute Force Approach
Function to apply quadratic transformation
def evaluate(x, A, B, C): return A * x * x + B * x + C
Function to transform and sort the array, returning a new list
def sortArray(arr, A, B, C): # Create a new array with the transformed values transformed = [evaluate(x, A, B, C) for x in arr]
# Sort the transformed array
transformed.sort()
return transformedif name == "main": arr = [-4, -2, 0, 2, 4] A, B, C = 1, 3, 5
res = sortArray(arr, A, B, C)
for val in res:
print(val, end=" ")C#
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
class GfG{ // Function to apply quadratic transformation static int evaluate(int x, int A, int B, int C){
return A * x * x + B * x + C;
}
// Function to transform and sort the array (returns List<int>)
static List<int> sortArray(int[] arr, int A, int B, int C){
int n = arr.Length;
int[] transformed = new int[n];
// Apply transformation
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
transformed[i] = evaluate(arr[i], A, B, C);
}
// Sort the transformed array
Array.Sort(transformed);
// Convert to List<int> and return
return new List<int>(transformed);
}
static void Main(){
int[] arr = { -4, -2, 0, 2, 4 };
int A = 1, B = 3, C = 5;
List<int> res = sortArray(arr, A, B, C);
foreach (int val in res){
Console.Write(val + " ");
}
}}
JavaScript
// JavaScript Code to Sort array after applying // equation using Brute Force Approach
// Function to apply quadratic transformation function evaluate(x, A, B, C) { return A * x * x + B * x + C; }
// Function to transform and sort the array in-place function sortArray(arr, A, B, C) { let n = arr.length;
let transformed = [];
// Apply the transformation in-place
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
transformed.push(evaluate(arr[i], A, B, C));
}
// Sort the transformed array
transformed.sort((a, b) => a - b);
return transformed;}
// Driver Code let arr = [-4, -2, 0, 2, 4]; let A = 1, B = 3, C = 5;
let res = sortArray(arr, A, B, C);
for (let val of res) { process.stdout.write(val + " "); }
`
**[Expected Approach] Using Two Pointers - O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The **idea is to use the fact that input array is sorted and apply a **Two-Pointer approach. After applying the quadratic transformation to each element, the smallest and largest values will always be at the **ends of the array (Why? The equation given is parabolic. So the result of applying it to a sorted array will result in an array that will have a maximum/minimum with the sub-arrays to its left and right sorted)
We process from both ends using **two pointers (left and right) moving towards each other. By comparing the transformed values of **arr[left] and **arr[right], we can fill a new array (newArr) starting either from the front or the back depending on whether the **coefficient A is positive or negative. The observation here is:
- if **A >= 0, the largest values will be at the end
- while if **A < 0, the largest values will be at the beginning.
There are two distinct cases when working with a quadratic transformation of a sorted array, and the nature of the function depends on the coefficient **A.
**Case 1: A > 0 – Convex parabola (opens upwards) → **Has a valley (minimum point)
- The largest transformed values lie at the ends of the array.
- We fill the result array **from end to start using two pointers.
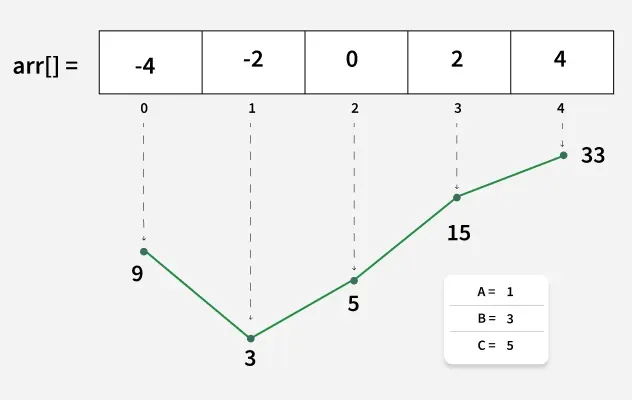
**Case 2: A < 0 – Concave parabola (opens downwards) → **Has a peak (maximum point)
- The smallest transformed values lie at the ends.
- We fill the result array **from start to end using two pointers.
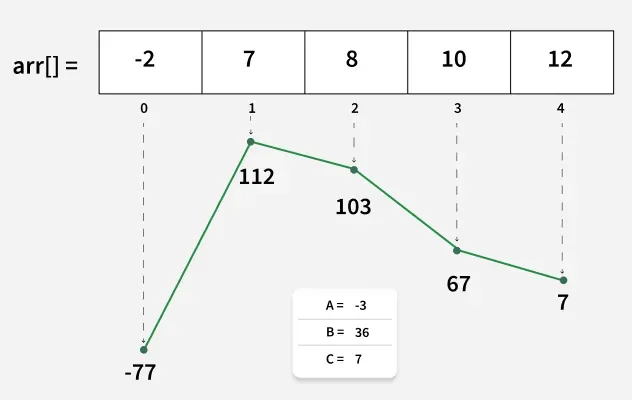
**Step-by-Step Implementation:
- Start by initializing two pointers: **left at the beginning and **right at the end of the array.
- Create a new array **newArr of the same size to store the transformed and sorted values.
- Determine the **index where you will start filling **newArr based on whether **A is positive or negative.
- Loop through the array using the **left and **right pointers, comparing the transformed values of **arr[left] and **arr[right].
- Depending on the sign of **A, place the larger of the two values at the appropriate position in **newArr.
- After processing all elements, copy the sorted values from **newArr back to the original **arr.
- Finally, return the modified **arr containing the transformed and sorted values.
**Illustration:
C++ `
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
// Function to apply quadratic transformation int evaluate(int x, int A, int B, int C) { return A * x * x + B * x + C; }
// Function to transform and sort the array vector sortArray(vector &arr, int A, int B, int C) { int n = arr.size(); vector newArr(n);
int left = 0, right = n - 1;
int index = (A >= 0) ? n - 1 : 0;
// Two-pointer approach to fill newArr
while (left <= right) {
int leftVal = evaluate(arr[left], A, B, C);
int rightVal = evaluate(arr[right], A, B, C);
if (A >= 0) {
if (leftVal > rightVal) {
newArr[index--] = leftVal;
left++;
} else {
newArr[index--] = rightVal;
right--;
}
} else {
if (leftVal < rightVal) {
newArr[index++] = leftVal;
left++;
} else {
newArr[index++] = rightVal;
right--;
}
}
}
return newArr;}
int main() { vector arr = {-4, -2, 0, 2, 4}; int A = 1, B = 3, C = 5;
vector<int> res = sortArray(arr, A, B, C);
for (int val : res) {
cout << val << " ";
}
return 0;}
Java
import java.util.*;
class GfG {
// Function to apply quadratic transformation
public static int evaluate(int x, int A, int B, int C) {
return A * x * x + B * x + C;
}
// Function to transform and sort the array
public static ArrayList<Integer> sortArray(int[] arr, int A, int B, int C) {
int n = arr.length;
int[] newArr = new int[n];
int left = 0, right = n - 1;
int index = (A >= 0) ? n - 1 : 0;
// Two-pointer approach to fill newArr from end or start
while (left <= right) {
int leftVal = evaluate(arr[left], A, B, C);
int rightVal = evaluate(arr[right], A, B, C);
if (A >= 0) {
if (leftVal > rightVal) {
newArr[index--] = leftVal;
left++;
} else {
newArr[index--] = rightVal;
right--;
}
} else {
if (leftVal < rightVal) {
newArr[index++] = leftVal;
left++;
} else {
newArr[index++] = rightVal;
right--;
}
}
}
// Convert array to ArrayList and return
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int val : newArr) {
result.add(val);
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {-4, -2, 0, 2, 4};
int A = 1, B = 3, C = 5;
ArrayList<Integer> res = sortArray(arr, A, B, C);
for (int val : res) {
System.out.print(val + " ");
}
}}
Python
Python Code to Sort array after applying
equation using Two Pointer Approach
Function to apply quadratic transformation
def evaluate(x, A, B, C): return A * x * x + B * x + C
Function to transform and sort the array
def sortArray(arr, A, B, C): n = len(arr) newArr = [0] * n
left, right = 0, n - 1
index = n - 1 if A >= 0 else 0
# Two-pointer approach to fill newArr
# from end or start
while left <= right:
leftVal = evaluate(arr[left], A, B, C)
rightVal = evaluate(arr[right], A, B, C)
if A >= 0:
# Fill from end
if leftVal > rightVal:
newArr[index] = leftVal
left += 1
index -= 1
else:
newArr[index] = rightVal
right -= 1
index -= 1
else:
# Fill from start
if leftVal < rightVal:
newArr[index] = leftVal
left += 1
index += 1
else:
newArr[index] = rightVal
right -= 1
index += 1
return newArrif name == "main": arr = [-4, -2, 0, 2, 4] A = 1 B = 3 C = 5
res = sortArray(arr, A, B, C)
print(*res)C#
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
class GfG {
// Function to apply quadratic transformation
public static int evaluate(int x, int A, int B, int C) {
return A * x * x + B * x + C;
}
// Function to transform and sort the array
public static List<int> sortArray(int[] arr, int A, int B, int C) {
int n = arr.Length;
int[] newArr = new int[n];
int left = 0, right = n - 1;
int index = (A >= 0) ? n - 1 : 0;
// Two-pointer approach to fill newArr
while (left <= right) {
int leftVal = evaluate(arr[left], A, B, C);
int rightVal = evaluate(arr[right], A, B, C);
if (A >= 0) {
if (leftVal > rightVal) {
newArr[index--] = leftVal;
left++;
} else {
newArr[index--] = rightVal;
right--;
}
} else {
if (leftVal < rightVal) {
newArr[index++] = leftVal;
left++;
} else {
newArr[index++] = rightVal;
right--;
}
}
}
return new List<int>(newArr);
}
public static void Main(string[] args) {
int[] arr = {-4, -2, 0, 2, 4};
int A = 1, B = 3, C = 5;
List<int> res = sortArray(arr, A, B, C);
foreach (int val in res) {
Console.Write(val + " ");
}
}}
JavaScript
// JavaScript Code to Sort array after applying // equation using Two Pointer Approach
// Function to apply quadratic transformation function evaluate(x, A, B, C) { return A * x * x + B * x + C; }
// Function to transform and sort the array function sortArray(arr, A, B, C) { let n = arr.length; let newArr = new Array(n);
let left = 0, right = n - 1;
let index = (A >= 0) ? n - 1 : 0;
// Two-pointer approach to fill newArr
// from end or start
while (left <= right) {
let leftVal = evaluate(arr[left], A, B, C);
let rightVal = evaluate(arr[right], A, B, C);
if (A >= 0) {
// Fill from end
if (leftVal > rightVal) {
newArr[index] = leftVal;
left++;
index--;
} else {
newArr[index] = rightVal;
right--;
index--;
}
} else {
// Fill from start
if (leftVal < rightVal) {
newArr[index] = leftVal;
left++;
index++;
} else {
newArr[index] = rightVal;
right--;
index++;
}
}
}
// Assign values back to arr
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = newArr[i];
}
return arr;}
// Driver Code let arr = [-4, -2, 0, 2, 4]; let A = 1, B = 3, C = 5;
let res = sortArray(arr, A, B, C);
console.log(res.join(' '));
`
