Sorting a dynamic 2dimensional array of Strings (original) (raw)
Sorting a dynamic 2-dimensional array of Strings
Last Updated : 27 Mar, 2023
Prerequisite: How to dynamically allocate a 2D array in C?
Double pointer: A pointer pointing to another pointer is known as a Double pointer. To represent the double pointer ' ** ' is used. Double pointer is also called as pointer to pointer. Example:
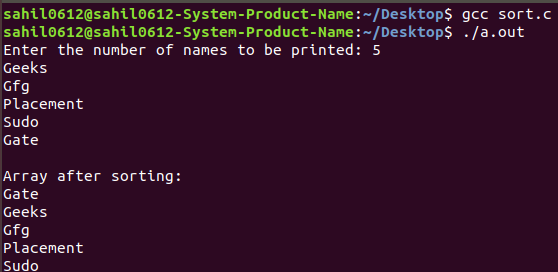
Input: Geeks, Gfg, Placement, Sudo, Gate Output: Gate, Geeks, Gfg, Placement, Sudo
The idea is to dynamically allocate memory and values to the strings in a form of a 2-D array. Then apply bubble sort using strcmp and strcpy function.
Implementation:
C++ `
#include #include #include
// Function to sort the values void sort(char** names, int n) { int i, j; // Perform sort operation using bubble sort for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) for (j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) if (strcmp(names[j], names[j + 1]) > 0) { char* temp; temp = (char*)calloc(30, sizeof(char)); strcpy(temp, names[j]); strcpy(names[j], names[j + 1]); strcpy(names[j + 1], temp); } }
// Driver code int main() { char** names; int n, i; std::cout << "Enter the number of names to be printed: "; std::cin >> n; // allocating memory for 1st dimension names = (char**)calloc(n, sizeof(char*));
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
// allocating memory for 2nd dimension
{
names[i] = (char*)calloc(30, sizeof(char));
std::cin >> names[i];
}
sort(names, n);
std::cout << "\nArray after sorting:\n";
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
std::cout << names[i] << std::endl;
return 0;}
//code contributed by dhanshriborse
C
// C program to sort an array of strings #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h>
// Function to sort the values void sort(char** names, int n) { int i, j;
// Perform sort operation using bubble sort
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
for (j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++)
if (strcmp(names[j], names[j + 1]) > 0) {
char* temp;
temp = (char*)calloc(30, sizeof(char));
strcpy(temp, names[j]);
strcpy(names[j], names[j + 1]);
strcpy(names[j + 1], temp);
}}
// Driver code int main() { char** names; int n, i; printf("Enter the number of names to be printed: "); scanf("%d\n", &n);
// allocating memory for 1st dimension
names = (char**)calloc(n, sizeof(char*));
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
// allocating memory for 2nd dimension
{
names[i] = (char*)calloc(30, sizeof(char));
scanf("%s", names[i]);
}
sort(names, n);
printf("\nArray after sorting:\n");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%s\n", names[i]);
return 0;}
Java
// Java code import java.util.Scanner;
// Function to sort the values class GFG { public static void sort(String names[], int n) { for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) { if (names[j].compareTo(names[j + 1]) > 0) { // swap arr[j+1] and arr[i] String temp = names[j]; names[j] = names[j + 1]; names[j + 1] = temp; } } } }
// Driver code public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); Sort ob = new Sort(); String names[] = new String[10]; int n = scanner.nextInt(); scanner.nextLine();
// Input names
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
names[i] = scanner.nextLine();
}
ob.sort(names, n);
System.out.println("\nArray after sorting:\n");
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
System.out.println(names[i]);
}} }
// This code is contributed by akashish__
Python3
Python code
Function to sort the values
def sort(names, n): for i in range(n-1): for j in range(n-i-1): if (names[j] > names[j+1]): temp = names[j] names[j] = names[j+1] names[j+1] = temp
Driver code
if name == 'main': names = [] n = int(input("Enter the number of names to be printed: ")) for i in range(0, n): names.append(input()) sort(names, n) print("\nArray after sorting:\n") for i in range(n): print(names[i])
This code is contributed by akashish__
JavaScript
// JavaScript code // Function to sort the values function sort(names, n){ for(let i=0; i<n-1; i++){ for(let j=0; j<n-i-1; j++){ if(names[j] > names[j+1]){ let temp = names[j]; names[j] = names[j+1]; names[j+1] = temp; } } } }
// Driver code
let names = [];
let n = parseInt(prompt("Enter the number of names to be printed: "));
for(let i=0; i<n; i++){
names.push(prompt());
}
sort(names, n);
console.log("\nArray after sorting:\n");
for(let i=0; i<n; i++){
console.log(names[i]);
}// This code is contributed by akashish__
C#
using System;
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { string[] names; int n, i;
Console.Write("Enter the number of names to be printed: ");
string input = Console.ReadLine();
while (!int.TryParse(input, out n)) {
Console.Write("Invalid input. Please enter a valid integer: ");
input = Console.ReadLine();
}
// allocating memory for 1st dimension
names = new string[n];
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) // allocating memory for 2nd dimension
{
names[i] = Console.ReadLine();
}
Sort(names, n);
Console.WriteLine("\nArray after sorting:");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.WriteLine(names[i]);
}
static void Sort(string[] names, int n) {
int i, j;
// Perform sort operation using bubble sort
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
for (j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++)
if (string.Compare(names[j], names[j + 1]) > 0) {
string temp;
temp = names[j];
names[j] = names[j + 1];
names[j + 1] = temp;
}
}}
`
Output: