SQL Functions (Aggregate and Scalar Functions) (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 17 May, 2024
**SQL Functions are built-in programs that are used to perform different operations on the database.
There are **two **types of functions in SQL:
- Aggregate Functions
- Scalar Functions
SQL Aggregate Functions
**SQL Aggregate Functions operate on a data group and return a singular output. They are mostly used with the **GROUP BY clause to summarize data.
Some common Aggregate functions with Syntax and description are shown in the table below.
| Aggregate Function | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| AVG() | Calculates the average value | SELECT AVG(column_name) FROM table_name; |
| COUNT() | Counts the number of rows | SELECT COUNT(column_name) FROM table_name |
| FIRST() | Returns the first value in an ordered set of values | SELECT FIRST(column_name) FROM table_name; |
| LAST() | Returns the last value in an ordered set of values | SELECT LAST(column_name) FROM table_name; |
| MAX() | Retrieves the maximum value from a column | SELECT MAX(column_name) FROM table_name; |
| MIN() | Retrieves the minimum value from a column | SELECT MIN(column_name) FROM table_name; |
| SUM() | Calculates the total sum of values in a numeric column | SELECT SUM(column_name) FROM table_name; |
**SQL Scalar functions
**SQL Scalar Functions are built-in functions that operate on a single value and return a single value.
Scalar functions in SQL helps in efficient data manipulation and simplification of complex calculations in SQL queries.
| Scalar function | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| UCASE() | Converts a string to uppercase | SELECT UCASE(column_name) FROM table_name; |
| LCASE() | Converts a string to lowercase | SELECT LCASE(column_name) FROM table_name; |
| MID() | Extracts a substring from a string | SELECT MID(column_name, start, length) FROM table_name; |
| LEN() | Returns the length of a string | SELECT LEN(column_name) FROM table_name; |
| ROUND() | Rounds a number to a specified number of decimals | SELECT ROUND(column_name, decimals) FROM table_name; |
| NOW() | Returns the current date and time | SELECT NOW(); |
| FORMAT() | Formats a value with the specified format | SELECT FORMAT(column_name, format) FROM table_name; |
SQL Functions Examples
Let’s look at some examples of SQL Functions. We will cover examples of SQL aggregate functions and scalar functions.
We will perform queries on the given SQL table:
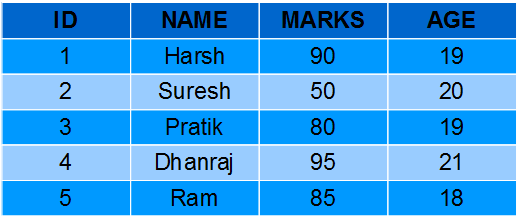
**Aggregate Functions Examples
Let’s look at the examples of each aggregate function in SQL.
**AVG() Function Example
Computing average marks of students.
**Query:
**SELECT AVG(MARKS) **AS AvgMarks **FROM Students;
**Output:
| **AvgMarks |
|---|
| 80 |
**COUNT() Function Example
Computing total number of students.
**Query:
*SELECT COUNT() **AS NumStudents **FROM Students;
**Output:
| **NumStudents |
|---|
| 5 |
**FIRST() Function Example
Fetching marks of first student from the Students table.
**Query:
**SELECT FIRST(MARKS) **AS MarksFirst **FROM Students;
**Output:
| **MarksFirst |
|---|
| 90 |
**LAST() **Function Example
Fetching marks of last student from the Students table.
**Query:
**SELECT LAST(MARKS) **AS MarksLast **FROM Students;
**Output:
| **MarksLast |
|---|
| 85 |
**MAX() Function Example
Fetching maximum marks among students from the Students table.
**Query:
**SELECT MAX(MARKS) **AS MaxMarks **FROM Students;
**Output:
| **MaxMarks |
|---|
| 95 |
**MIN() Function Example
Fetching minimum marks among students from the Students table.
**Query:
**SELECT MIN(MARKS) **AS MinMarks **FROM Students;
**Output:
| **MinMarks |
|---|
| 50 |
**SUM() Function Example
Fetching summation of total marks among students from the Students table.
**Query:
SELECT SUM(MARKS) AS TotalMarks FROM Students;
**Output:
| **TotalMarks |
|---|
| 400 |
**Scalar Functions Examples
Let’s look at some examples of each Scalar Function in SQL.
**UCASE() Function Example
Converting names of students from the table Students to uppercase.
**Query:
**SELECT UCASE(NAME) **FROM Students;
**Output:
| **NAME |
|---|
| HARSH |
| SURESH |
| PRATIK |
| DHANRAJ |
| RAM |
**LCASE() Function Example
Converting names of students from the table Students to lowercase.
**Query:
**SELECT LCASE(NAME) **FROM Students;
Output:
| **NAME |
|---|
| harsh |
| suresh |
| pratik |
| dhanraj |
| ram |
**MID() Function Example
Fetching first four characters of names of students from the Students table.
**Query:
**SELECT MID(NAME,1,4) FROM Students;
**Output:
| **NAME |
|---|
| HARS |
| SURE |
| PRAT |
| DHAN |
| RAM |
**LEN() Function Example
Fetching length of names of students from Students table.
**Query:
**SELECT LENGTH(NAME) **FROM Students;
Output:
| **NAME |
|---|
| 5 |
| 6 |
| 6 |
| 7 |
| 3 |
**ROUND() Function Example
Fetching maximum marks among students from the Students table.
**Query:
**SELECT ROUND(MARKS,0) **FROM Students;
**Output:
| **MARKS |
|---|
| 90 |
| 50 |
| 80 |
| 95 |
| 85 |
**NOW() Function Example
Fetching current system time.
**Query:
SELECT NAME, NOW() AS DateTime FROM Students;
**Output:
| **NAME | **DateTime |
|---|---|
| HARSH | 1/13/2017 1:30:11 PM |
| SURESH | 1/13/2017 1:30:11 PM |
| PRATIK | 1/13/2017 1:30:11 PM |
| DHANRAJ | 1/13/2017 1:30:11 PM |
| RAM | 1/13/2017 1:30:11 PM |
**FORMAT() Function Example
Formatting current date as ‘YYYY-MM-DD’.
**Query:
**SELECT NAME, **FORMAT(Now(),'YYYY-MM-DD') **AS Date **FROM Students;
**Output:
| **NAME | **Date |
|---|---|
| HARSH | 2017-01-13 |
| SURESH | 2017-01-13 |
| PRATIK | 2017-01-13 |
| DHANRAJ | 2017-01-13 |
| RAM | 2017-01-13 |
Important Points About SQL Functions
- SQL functions are built-in programs that are used to manipulate data in various ways.
- There are different types of SQL functions – Aggregate functions and Scalar functions.
- Aggregate functions perform calculations on a group of values and return a single value. Example SUM, AVG, COUNT.
- Scalar functions operate on a single value and return a single value. Example UPPER, LOWER, SUBSTRING.
- SQL functions can be used in different SQL statements, such as SELECT, WHERE, GROUP BY, and ORDER BY, to improve data processing and analysis.