SQL Statistical Functions (original) (raw)
SQL **statistical functions are essential tools for extracting meaningful insights from databases. These functions, enable users to perform statistical calculations on numeric data. Whether determining **averages, **sums, counts, or measures of variability, these functions empowerefficient data analysis within the SQL environment.
In this article, we’ll explore the most commonly used SQL statistical functions such as **AVG(), SUM(), COUNT(), MIN(), **MAX(), STDDEV(), VAR(), and more. We will also provide practical examples to demonstrate their usage.
What is SQL Statistical Functions?
**Statistics is a branch of mathematics that deals with **data collection, analysis, interpretation, presentation, and organization. It involves the use of mathematical techniques to extract meaningful information from data. Statistics is widely used in various fields such as **business, economics, social science, medicine, and **engineering
A Statistical function is a **mathematical function that helps us to process and analyze data to provide meaningful information about the dataset. For example mean, sum, min, max, standard deviation, etc.
Statistical Functions in SQL
Here are Some Common Statistical Functions in SQL:
| Function | Output |
|---|---|
| AVG() | Calculates the average value of a numeric column. |
| SUM() | Calculates the sum of values in a numeric column. |
| COUNT() | Counts the number of rows in a result set or the number of non-null values in a column. |
| MIN() | Returns the minimum value in a column. |
| MAX() | Returns the maximum value in a column. |
| VAR() / VARIANCE() | Calculates the population variance of a numeric column. |
| STDDEV() / STDDEV_POP() | Calculates the population standard deviation of a numeric column. |
| CORR() | Calculates the correlation coefficient between two numeric columns. |
| COVAR_POP() | Calculates the population covariance between two numeric columns. |
| PERCENTILE_CONT() | Calculates a specified percentile value for a numeric column |
Statistical Functions With Exmaple
We have four tables in our database: 'studentDetails,' 'employees,' 'sales_data,' and 'financial_data.' (The pictures are displayed below.)
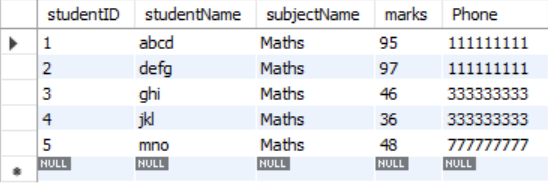
Table : StudentDetails
**employees Table:

Table:Employees
**sales_data:

Table:Sales_data
**financial_data:
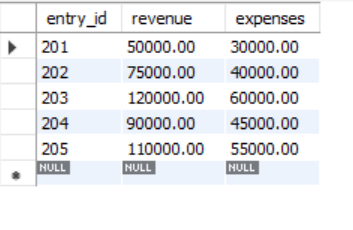
Table: financial_data
1. AVG() **Function
Calculate the average or arithmetic mean for a group of numbers or a numeric column.
**Syntax:
SELECT AVG(column_name) FROM table_name;
**Example Query:
SELECT AVG(marks) AS average_marks FROM studentDetails;
**Output:
.png)
AVG_MARKS
2. SUM() **Function
The total of all numeric values in a group i.e. Calculates the total sum of values in a numeric column.
**Syntax:
SELECT SUM(column_name) FROM table_name;
**Example Query:
SELECT SUM(marks) AS total_marks FROM studentDetails;
**Output:
.png)
Sum of marks
**3. Count() Function
The number of cell locations in a range that contain a numeric character i.e Counts the number of rows in a result set or the number of non-null values in a column.
**Syntax:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM table_name;
SELECT COUNT(column_name) FROM table_name;
**Example Query:
SELECT COUNT(studentID) AS total_students FROM studentDetails;
**Output:
.png)
Count of Student
**Example Query:
select count(*) from studentdetails;
**Output:
Return the count of rows that meet a specified condition .
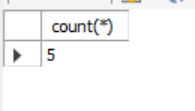
count all rows
4. Max() **Function
Returns the highest numeric value in a group of numbers.
**Syntax:
SELECT MAX(column_name) FROM table_name;
**Example Query:
SELECT MAX(marks) AS highest_marks FROM studentDetails;
**Output:
.png)
Maximum marks
**5. MIN() Function
Returns the lowest numeric value in a group of numbers.
**Syntax:
SELECT MIN(column_name) FROM table_name;
**Example Query:
SELECT MIN(marks) AS lowest_marks FROM studentDetails;
**Output:
.png)
Minimum marks
**6. VAR() / VARIANCE() Function
Calculates the population variance of a numeric column
**Syntax:
SELECT VAR(column_name) FROM table_name;
**Example Query:
SELECT VARIANCE(marks) AS variance_marks FROM studentDetails;
**Output:
.png)
Variance marks
**7. STDDEV() / STDDEV_POP() Function
The standard deviation for a group of numbers based on a sample
**Syntax:
SELECT STDDEV(column_name) FROM table_name;
**Example Query:
SELECT STDDEV(marks) AS stddev_marks FROM studentDetails;
**Output:
.png)
Standrad deviation for marks
**8. PERCENTILE_CONT() Function
Calculates a specified percentile value for a numeric column.
**Syntax:
SELECT PERCENTILE_CONT(0.5) WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY column_name) FROM table_name;
**Example Query:
SELECT PERCENTILE_CONT(0.5) WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY salary) AS median_salary FROM employees;
**Output:
.png)
Median salary of employee's
**9. CORR() Function
Calculates the correlation coefficient between two numeric columns.
**Syntax:
SELECT CORR(column1, column2) FROM table_name;
**Example Query:
SELECT CORR(sales, profit) AS correlation_coefficient FROM sales_data;
**Output:
.png)
correlation coefficient between 'sales' and 'profit'
**10 .COVAR_POP() Function
Calculates the population covariance between two numeric columns.
**Syntax:
SELECT COVAR_POP(column1, column2) FROM table_name;
**Example Query:
SELECT COVAR_POP(revenue, expenses) AS population_covariance FROM financial_data;
**Output:
.png)
Population Covariance between revenue and expenses
**Conclusion
In SQL, **statistical functions help to analyze and summarise data in the database. These functions assist in extracting meaningful information from the given datasets. For determining the number of occurrences , calculating totals , finding averages or calculating the variance in the dataset statistical functions plays a vital role .Overall, the integration of Statistical Functions elevates SQL's capabilities, making it an invaluable asset for businesses and analysts seeking actionable intelligence from their relational databases.