Java StringBuilder Class (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 08 Apr, 2025
In Java, the **StringBuilder class is a part of the java.lang package that provides a mutable sequence of characters. Unlike String (which is immutable), StringBuilder allows in-place modifications, making it memory-efficient and faster for frequent string operations.
**Declaration:
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Initial String");
**Key points of the StringBuilder class:
The key features of the StringBuilder class are listed below:
- StringBuilder in Java represents a mutable sequence of characters.
- String Class in Java creates an immutable sequence of characters, whereas StringBuilder creates a mutable sequence of characters, offering an alternative.
- The functionality of StringBuilder is similar to the StringBuffer class, as both provide mutable sequences of characters.
- StringBuilder does not guarantee synchronization, while StringBuffer does. It is a high-performance and low-overhead non thread non-thread-safe alternative to StringBuffer, suitable for single-threaded applications, while StringBuffer is used for synchronization in multithreaded applications.
- StringBuilder is faster than StringBuffer in most implementations.
**Example: Demonstration of a StringBuilder class in Java.
Java `
// Demonstrating the usage of StringBuilder class public class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a new StringBuilder with the // initial content "GeeksforGeeks" StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("GeeksforGeeks"); System.out.println("Initial StringBuilder: " + sb);
// Append a string to the StringBuilder
sb.append(" is awesome!");
System.out.println("After append: " + sb);
}}
`
Output
Initial StringBuilder: GeeksforGeeks After append: GeeksforGeeks is awesome!
**Explanation:
- In the above code, we first create a StringBuilder with the object **sb and put the initial string as "GeeksforGeeks"
- Then we use the **append() method from StringBuilder class to add the " is awesome!" string in end of current StringBuilder object.
Syntax of Java StringBuilder Class
The syntax of the StringBuilder class is listed below:
public final class StringBuilder extends Object implements Serializable, CharSequence
StringBuilder Class Hierarchy
java.lang.Object
↳ java.lang
↳ Class StringBuilder
Why Use StringBuilder in Java?
Using the StringBuilder class in Java has many benefits, which are listed below:
- **Mutable: Unlike String, which creates a new object every time it's modified, StringBuilder allows you to change the string without creating new objects. This makes it more efficient for repeated modifications.
- **Faster than String: StringBuilder doesn't create new objects for every change, it avoids unnecessary memory allocations, which makes it faster than String when performing many string manipulations.
- **More Efficient than StringBuffer: In single-threaded environments, StringBuilder is more efficient than StringBuffer because it doesn't have the overhead of thread safety, which makes StringBuilder a better choice when we don't need synchronization.
StringBuilder vs String vs StringBuffer
The table below demonstrates the difference between String, StringBuilder and StringBuffer:
| Features | String | StringBuilder | StringBuffer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mutability | String are immutable(creates new objects on modification) | StringBuilder are mutable(modifies in place) | StringBuffer are mutable (modifies in place) |
| Thread-Safe | It is thread-safe | It is not thread-safe | It is thread-safe |
| Performance | It is slow because it creates an object each time | It is faster (no object creation) | it is slower due to synchronization overhead |
| use Case | Fixed, unchanging strings | Single-threaded string manipulation | Multi-threaded string manipulation |
StringBuilder Constructors
The StringBuilder class provides several constructors, which are listed below:
| Constructor | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| StringBuilder() | Creates an empty StringBuilder with a default initial capacity of 16. | StringBuilder strbldr = new StringBuilder(); |
| StringBuilder(int capacity) | Creates a StringBuilder with the specified initial capacity. | StringBuilder strbldr = new StringBuilder(50); |
| StringBuilder(String str) | Creates a StringBuilder initialized with the contents of the given string. | StringBuilder strbldr = new StringBuilder("Geeks"); |
| StringBuilder(CharSequence cs) | Creates a StringBuilder initialized with the contents of the given CharSequence object. | CharSequence strbldr = "Geeks"; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(cs); |
**Example: Creating a string using the StringBuilder Constructor **StringBuilder(String str).
Java `
// Creating a String using StringBuilder constructor // StringBuilder(String str) public class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a String using StringBuilder constructor
// StringBuilder(String str)
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("GeeksforGeeks");
// Converting StringBuilder to String
String str = sb.toString();
// Printing the String
System.out.println(str);
}}
`
Methods of StringBuilder class
The StringBuilder class provides several methods for creating and manipulating strings, which are listed below:
| Method | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| append(String str) | Appends the specified string to the end of the StringBuilder. | sb.append("Geeks"); |
| insert(int offset, String) | Inserts the specified string at the given position in the StringBuilder. | sb.insert(5, " Geeks"); |
| replace(int start, int end, String) | Replaces characters in a substring with the specified string. | sb.replace(6, 11, "Geeks"); |
| delete(int start, int end) | Removes characters in the specified range. | sb.delete(5, 11); |
| reverse() | Reverses the sequence of characters in the StringBuilder. | sb.reverse(); |
| capacity() | Returns the current capacity of the StringBuilder. | int cap = sb.capacity(); |
| length() | Returns the number of characters in the StringBuilder. | int len = sb.length(); |
| charAt(int index) | Returns the character at the specified index. | char ch = sb.charAt(4); |
| setCharAt(int index, char) | Replaces the character at the specified position with a new character. | sb.setCharAt(0, 'G'); |
| substring(int start, int end) | Returns a new String that contains characters from the specified range. | String sub = sb.substring(0, 5); |
| ensureCapacity(int minimum) | Ensures the capacity of the StringBuilder is at least equal to the specified minimum. | sb.ensureCapacity(50); |
| deleteCharAt(int index) | Removes the character at the specified position. | sb.deleteCharAt(3); |
| indexOf(String str) | Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified string. | int idx = sb.indexOf("Geeks"); |
| lastIndexOf(String str) | Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified string. | int idx = sb.lastIndexOf("Geeks"); |
| toString() | Converts the StringBuilder object to a String. | String result = sb.toString(); |
**Example: Performing different String manipulation operations using StringBuilder methods such as appending, inserting, replacing, deleting, reversing, and accessing characters.
Java `
// Demonstrating the usage of multiple StringBuilder methods like // append(), insert(), replace(), delete(), reverse(), public class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new StringBuilder with the
// initial content "GeeksforGeeks"
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("GeeksforGeeks");
System.out.println("Initial StringBuilder: " + sb);
// 1. Append a string to the StringBuilder
sb.append(" is awesome!");
System.out.println("After append: " + sb);
// 2. Insert a substring at a specific position
sb.insert(13, " Java");
System.out.println("After insert: " + sb);
// 3. Replace a substring with another string
sb.replace(0, 5, "Welcome to");
System.out.println("After replace: " + sb);
// 4. Delete a substring from the StringBuilder
sb.delete(8, 14);
System.out.println("After delete: " + sb);
// 5. Reverse the content of the StringBuilder
sb.reverse();
System.out.println("After reverse: " + sb);
// 6. Get the current capacity of the StringBuilder
int capacity = sb.capacity();
System.out.println("Current capacity: " + capacity);
// 7. Get the length of the StringBuilder
int length = sb.length();
System.out.println("Current length: " + length);
// 8. Access a character at a specific index
char charAt5 = sb.charAt(5);
System.out.println("Character at index 5: " + charAt5);
// 9. Set a character at a specific index
sb.setCharAt(5, 'X');
System.out.println("After setCharAt: " + sb);
// 10. Get a substring from the StringBuilder
String substring = sb.substring(5, 10);
System.out.println("Substring (5 to 10): " + substring);
// 11. Find the index of a specific substring
sb.reverse(); // Reversing back to original order for search
int indexOfGeeks = sb.indexOf("Geeks");
System.out.println("Index of 'Geeks': " + indexOfGeeks);
// 12. Delete a character at a specific index
sb.deleteCharAt(5);
System.out.println("After deleteCharAt: " + sb);
// 13. Convert the StringBuilder to a String
String result = sb.toString();
System.out.println("Final String: " + result);
}}
`
**Output:
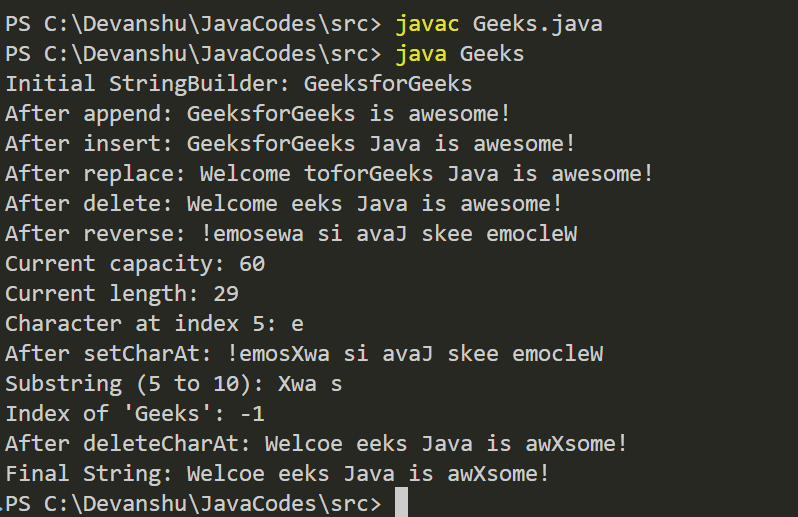
**Explanation: In the above program, we use different methods of the StringBuilder class to perform different string manipulation operations such as **append(), insert(), reverse(), and **delete().
Advantages
The advantages of the StringBuilder class are listed below:
- It is more efficient than String when performing multiple string manipulations (like concatenation) since it modifies the string in place.
- It avoids creating new objects on every modification, reducing memory overhead.
- Unlike String, StringBuilder allows the modification of strings without creating new instances.
- It dynamically adjusts its capacity as needed, minimizing the need for resizing.
- Great for scenarios where strings are modified repeatedly inside loops.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of the StringBuilder class are listed below:
- It is not synchronized, making it unsuitable for use in multi-threaded environments.
- If not used properly, StringBuilder may allocate excess memory, especially if the initial capacity is set too large.
- For multi-threaded scenarios, you must handle synchronization manually, unlike StringBuffer.