C# Switch Statement (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 11 Jan, 2025
In C#, Switch statement is a multiway branch statement. It provides an efficient way to transfer the execution to different parts of a code based on the value of the expression. The switch expression is of integer type such as int, char, byte, or short, or of an enumeration type, or of string type. The expression is checked for different cases and the one match is executed.
**Syntax:
switch (expression)
{
case value1: // statement sequence
break;
case value2: // statement sequence
break;
.
.
.
case valueN: // statement sequence
break;
default: // default statement sequence }
**Flow Chart:
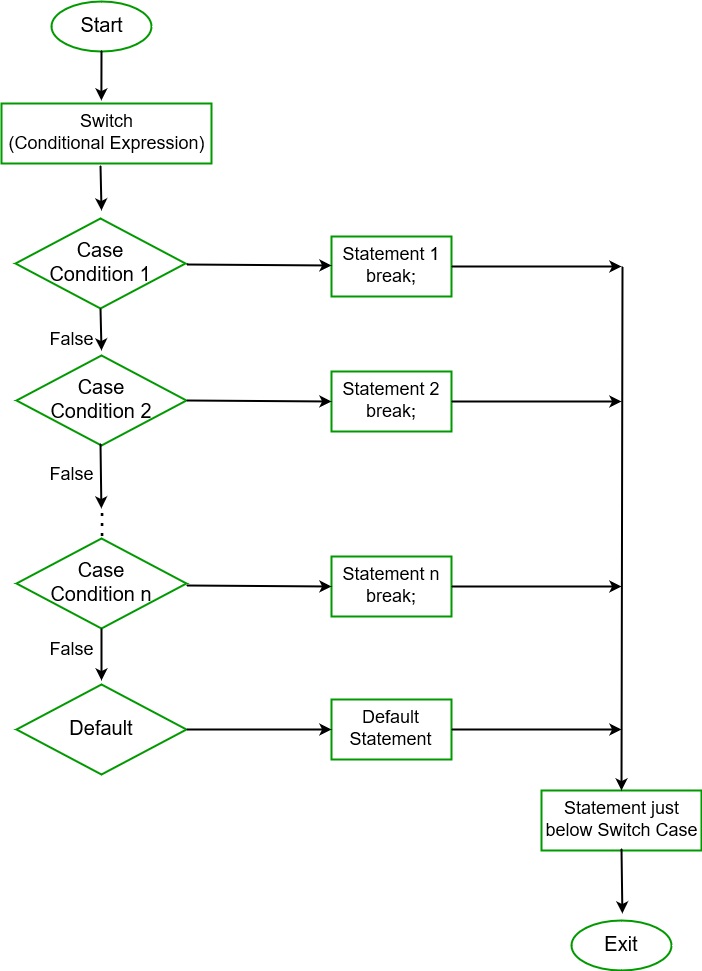
**Important Points to Remember:
- **No Duplicate Case Values: In C#, duplicate case values are not allowed.
- **Data Type Matching: The data type of the variable in the switch and value of a case must be of the same type.
- **Constant Values: The value of a case must be a constant or a literal. Variables are not allowed.
- **Break Statement: The break in switch statement is used to terminate the current sequence.
- **Optional Default Case: The default statement is optional and it can be used anywhere inside the switch statement.
- **Multiple Default Statements: Multiple default statements are not allowed.
**Example:
C# `
// Using Switch Case Statement using System;
public class Geeks { // Main Method public static void Main(String[] args) { int nitem = 5; switch (nitem) {
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("Case 1");
break;
case 5:
Console.WriteLine("Case 5");
break;
case 9:
Console.WriteLine("Case 9");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("No match found");
break;
}
} }
`
Why do we use switch statements instead of if-else statements?
We use a switch statement instead of if-else statements because if-else statement only works for a small number of logical evaluations of a value. If you use if-else statement for a larger number of possible conditions then, it takes more time to write and also become difficult to read.
**Example 1: Using if-else-if statement
C# `
// Using if-else statement using System;
class Geeks { // Main Method public static void Main(String[] args) { // taking two strings value string topic; string category;
// taking topic name
topic = "Inheritance";
// using compare function of string class
if ((String.Compare(topic, "Introduction to C#") == 0) ||
(String.Compare(topic, "Variables") == 0) ||
(String.Compare(topic, "Data Types") == 0)) {
category = "Basic";
}
// using compare function of string class
else if ((String.Compare(topic, "Loops") == 0) ||
(String.Compare(topic, "If Statements") == 0) ||
(String.Compare(topic, "Jump Statements") == 0)) {
category = "Control Flow";
}
// using compare function of string class
else if ((String.Compare(topic, "Class & Object") == 0) ||
(String.Compare(topic, "Inheritance") == 0) ||
(String.Compare(topic, "Constructors") == 0)) {
category = "OOPS Concept";
}
else{
category = "Not Mentioned";
}
System.Console.Write("Category is " + category);
} }
`
Output
Category is OOPS Concept
**Example 2: Using Switch Statement
C# `
// Using switch statement using System;
class Geeks { // Main Method public static void Main(String[] args) { // taking two strings value string topic; string category;
// taking topic name
topic = "Inheritance";
// using switch Statement
switch(topic)
{
case "Introduction to C#":
case "Variables":
case "Data Types":
category = "Basic";
break;
case "Loops":
case"If Statements":
case"Jump Statements":
category = "Control Flow";
break;
case "Class & Object":
case "Inheritance":
case "Constructors":
category = "OOPS Concept";
break;
// default case
default:
category = "Not Mentioned";
break;
}
System.Console.Write("Category is " + category);
} }
`
Output
Category is OOPS Concept
Using goto in the Switch Statement
You can also use **goto statement in place of the break in the switch statement. Generally, we use a break statement to exit from the switch statement. But in some situations, the default statement is required to be executed, so we use the goto statement. It allows executing default condition in the switch statement. The goto statement is also used to jump to a labeled location in C# program.
**Example:
C# `
// Use of goto in switch statement using System;
public class Geeks { // Main Method public static void Main(String[] args) { int greeting = 2;
switch (greeting) {
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("Hello");
goto default;
case 2:
Console.WriteLine("Bonjour");
goto case 3;
case 3:
Console.WriteLine("Namaste");
goto default;
default:
Console.WriteLine("Entered value is: " + greeting);
break;
}
} }
`
Output
Bonjour Namaste Entered value is: 2
**Note: You can also use continue in place of a break in switch statement if your switch statement is a part of a loop, then continue statement will cause execution to return instantly to the starting of the loop.