Views In Django | Python (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 04 Apr, 2024
Django Views are one of the vital participants of the M**VT Structure of Django. As per Django Documentation, A view function is a Python function that takes a Web request and returns a Web response. This **response can be the HTML contents of a Web page, a redirect, a 404 error, an XML document, an image, or anything that a web browser can display.
Django Views
Django views are part of the user interface — they usually render the HTML/CSS/Javascript in your Template files into what you see in your browser when you render a web page. (Note that if you’ve used other frameworks based on the MVC (Model-View-Controller), do not get confused between Django views and views in the MVC paradigm. Django views roughly correspond to controllers in MVC, and Django templates to views in MVC.)
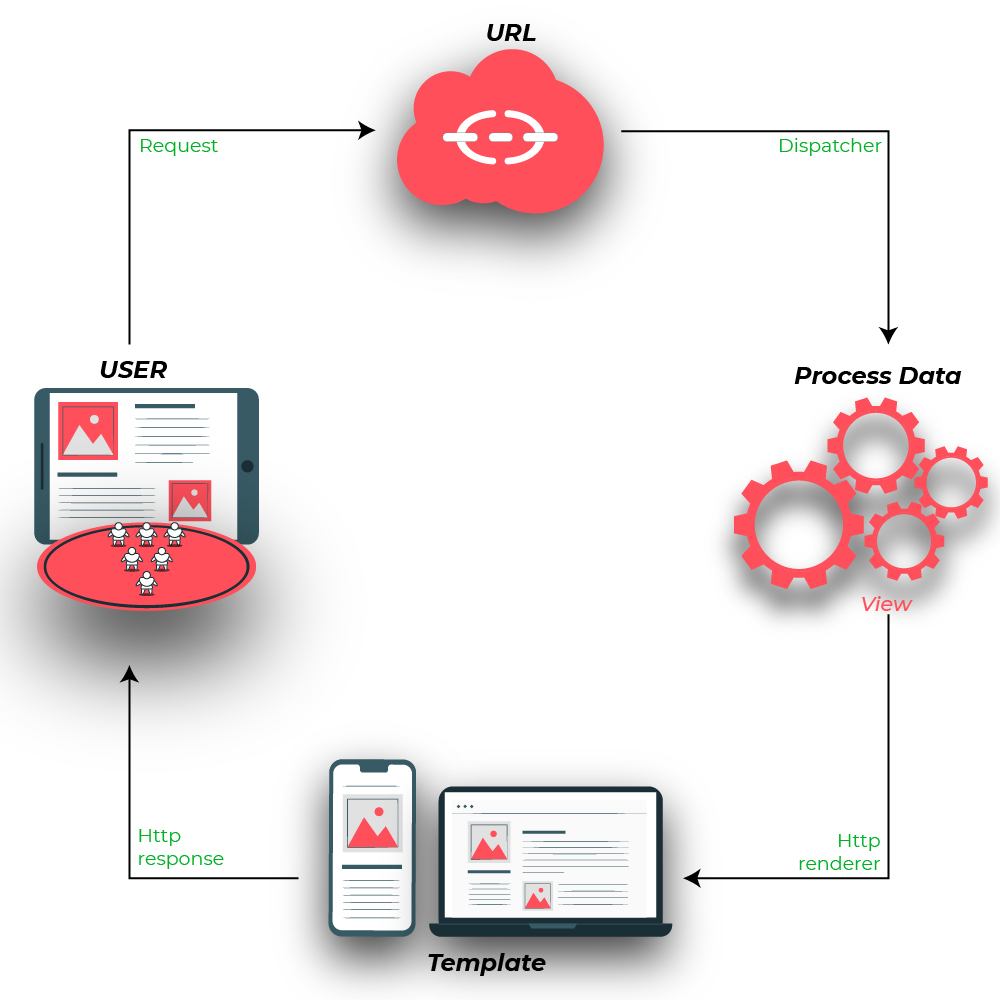
Illustration of **How to create and use a Django view using an Example. Consider a project named geeksforgeeks having an app named geeks.
Refer to the following articles to check how to create a project and an app in Django.
After you have a project ready, we can create a view in geeks/views.py,
Python3 `
import Http Response from django
from django.http import HttpResponse
get datetime
import datetime
create a function
def geeks_view(request): # fetch date and time now = datetime.datetime.now() # convert to string html = "Time is {}".format(now) # return response return HttpResponse(html)
`
Let’s step through this code one line at a time:
- First, we import the class **HttpResponse from the django.http module, along with Python’s datetime library.
- Next, we define a function called geeks_view. This is the view function. Each view function takes an HttpRequest object as its first parameter, which is typically named request.
- The view returns an HttpResponse object that contains the generated response. Each view function is responsible for returning an **HttpResponse object.
For more info on HttpRequest and HttpResponse visit – Django Request and Response cycle – HttpRequest and HttpResponse Objects
Let’s get this view to working, in geeks/urls.py,
Python3 `
from django.urls import path
importing views from views..py
from .views import geeks_view
urlpatterns = [ path('', geeks_view), ]
`
Now, visit http://127.0.0.1:8000/.

To check how to make a basic project using MVT (Model, View, Template) structure of Django, visit Creating a Project Django.
Django Class Based Views vs Function Based Views
Django views are divided into two major categories:
- Function Based Django Views
- Class Based Django Views
Function Based Views in Django
Function based views are written using a function in python which receives as an argument HttpRequest object and returns an HttpResponse Object. Function based views are generally divided into 4 basic strategies, i.e., CRUD (Create, Retrieve, Update, Delete). CRUD is the base of any framework one is using for development.
How to use Function based view in Django?
Let’s Create a function-based view list view to display instances of a model. Let’s create a model of which we will be creating instances through our view. In geeks/models.py,
Python3 `
import the standard Django Model
from built-in library
from django.db import models
declare a new model with a name "GeeksModel"
class GeeksModel(models.Model):
# fields of the model
title = models.CharField(max_length = 200)
description = models.TextField()
# renames the instances of the model
# with their title name
def __str__(self):
return self.title`
After creating this model, we need to run two commands in order to create Database for the same.
Python manage.py makemigrations Python manage.py migrate
Now let’s create some instances of this model using shell, run form bash,
Python manage.py shell
Enter following commands
from geeks.models import GeeksModel GeeksModel.objects.create( title="title1", description="description1").save() GeeksModel.objects.create( title="title2", description="description2").save() GeeksModel.objects.create( title="title2", description="description2").save()
Now if you want to see your model and its data in the admin panel, then you need to register your model.
Let’s register this model. In geeks/admin.py,
Python3 `
from django.contrib import admin from .models import GeeksModel
Register your models here.
admin.site.register(GeeksModel)
`
Now we have everything ready for the back end. Verify that instances have been created from http://localhost:8000/admin/geeks/geeksmodel/
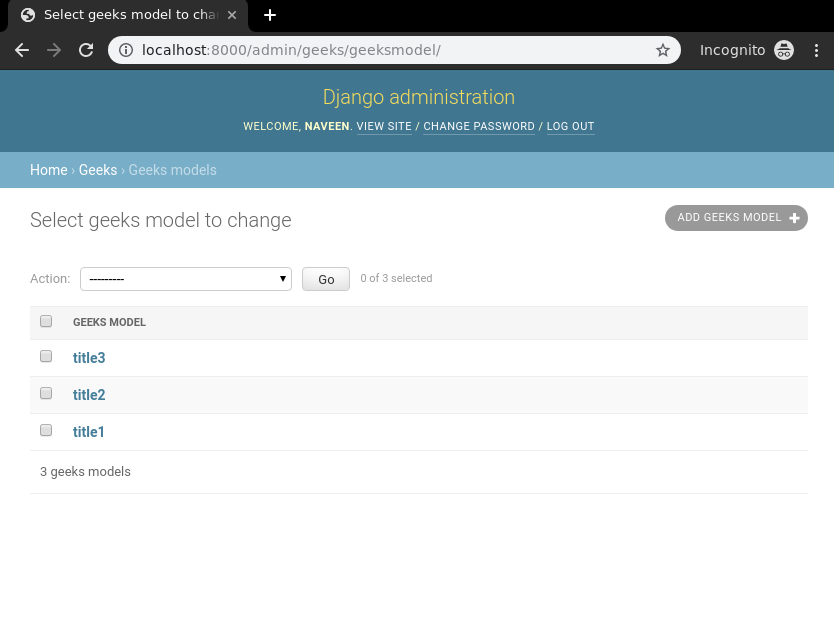
Let’s create a view and template for the same. In geeks/views.py,
Python3 `
from django.shortcuts import render
relative import of forms
from .models import GeeksModel
def list_view(request): # dictionary for initial data with # field names as keys context ={}
# add the dictionary during initialization
context["dataset"] = GeeksModel.objects.all()
return render(request, "list_view.html", context)`
Create a template in templates/list_view.html,
html `
{% for data in dataset %}.
{{ data.title }}<br/>
{{ data.description }}<br/>
<hr/>
{% endfor %}`
Let’s check what is there on http://localhost:8000/
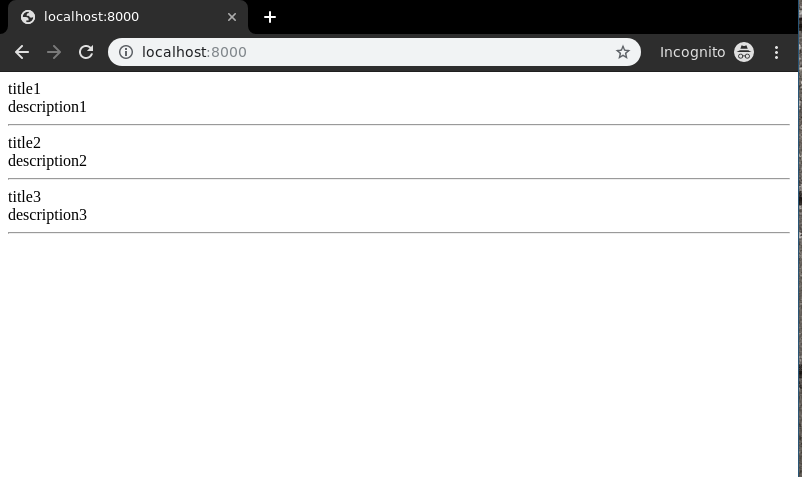
Similarly, function based views can be implemented with logics for create, update, retrieve and delete views.
**Django CRUD (Create, Retrieve, Update, Delete) Function Based Views :-
- Detail View – Function based Views Django
- Create View – Function based Views Django
- Update View – Function based Views Django
- Delete View – Function based Views Django
- List View – Function based Views Django
Class Based Views in Django
Class-based views provide an alternative way to implement views as Python objects instead of functions. They do not replace function-based views, but have certain differences and advantages when compared to function-based views:
- Organization of code related to specific HTTP methods (GET, POST, etc.) can be addressed by separate methods instead of conditional branching.
- Object oriented techniques such as mixins (multiple inheritance) can be used to factor code into reusable components.
Class-based views are simpler and efficient to manage than function-based views. A function-based view with tons of lines of code can be converted into class-based views with few lines only. This is where Object-Oriented Programming comes into impact.
How to use Class based view in Django?
In geeks/views.py,
Python3 `
from django.views.generic.list import ListView from .models import GeeksModel
class GeeksList(ListView):
# specify the model for list view
model = GeeksModel`
Now create a URL path to map the view. In geeks/urls.py,
Python3 `
from django.urls import path
importing views from views..py
from .views import GeeksList urlpatterns = [ path('', GeeksList.as_view()), ]
`
Create a template in templates/geeks/geeksmodel_list.html,
html `
-
{% for object in object_list %}
- {{ object.title }}
- {{ object.description }}
<hr/>
<!-- If objet_list is empty -->
{% empty %}
<li>No objects yet.</li>
{% endfor %}`
Let’s check what is there on http://localhost:8000/

**Django CRUD (Create, Retrieve, Update, Delete) Class Based Generic Views :-